Pygmy people facts for kids

Aka Pygmies on the Congo Basin in 2014
|
|
| Regions with significant populations | |
|---|---|
| Central Africa, Oceania, Southeast Asia |
Pygmy is a word that describes several ethnic groups whose average height is unusually short. According to anthropologists, pygmies can be any group where adult men are less than 150 centimetres (4.9 ft) tall on average.
The word "pygmy" is sometimes thought to be pejorative (an insult).
Contents
Name
The name "pygmy" comes from the Greek word πυγμαίος (pygmaios). This word was derived from (came from) the word πυγμή which is the length between a person's elbow and knuckles. The Latin word Pygmaeus (pl. pygmaei) came from this older Greek word.
The word was first used in Greek mythology by the poet Homer. He wrote about a tribe called Pygmies who lived in India and Ethiopia.
Origins
The height of such people is hereditary, which means it is passed on from parents to children. Scientists believe that pygmies make less vitamin D in their skin due to the low ultraviolet light found in rainforests, where many of them live. Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, which is important for bones to grow. Lack of calcium results in smaller bones and skeletons.
Other theories that try to explain the unusual height of these people include:
- there is less food in the rainforest
- there is less calcium in the soil, so the food has less calcium
- it is easier for smaller people to move in thick jungle
- it is an adaptation to heat and humidity
Some research shows that the genes for the growth hormone receptor and growth hormone are found much less in pygmies than in related tribes. These genes are important for humans to grow tall.
Africa
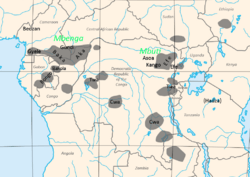
Pygmies can be found in Rwanda, Burundi, Uganda, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Central African Republic, Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Angola, Botswana, Namibia, and Zambia. Most of these groups are partly hunter-gatherers. They get food from the environment and trade it with nearby farmers. From the farmers they get crops and tools. There are about 250,000-600,000 Pygmies living in the Congo rainforest.
Groups
There are a number of Pygmy groups living in Africa. The three best-known groups are the Mbenga, Mbuti, and Twa groups. Each big group includes several tribes that have their own language.
The Mbenga people, sometimes called the Ba-Mbenga, live in the western Congo basin. The Mbenga include the Aka people, who speak the Aka language. The Aka live in the Central African Republic and the Republic of Congo. The M-Benzélé people, or "western Aka", and the Ba-Sese people, "eastern Aka", are also related.
Other Mbenga pygmies are the Baka people of Cameroon, Gabon, and Republic of Congo. They speak three very similar languages: Baka language, Ganzi language, and Gundi language. Another group of Mbenga pygmies are the Gyele people. The Gyele live in Cameroon and speak Gyele language.
The Mbuti people, sometimes called the Bambuti, live in the Ituri rainforest in eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. They include the Efé people, Asua people, and the Kango people. The Efé speak the Efé language. The Asua speak the Asoa language. The Kango speak the Kango language.
The Twa people, or Ba-Twa, live in Rwanda, Burundi, Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Uganda. The Twa speak Kirundi and Kinyarwanda.
Images for kids
-
Ati woman of the Philippines