Pressure in liquids facts for kids
Fluid pressure is a measurement of the force per unit area. Fluid pressure can be caused by gravity, acceleration, or forces in a closed container. Since a fluid has no definite shape, its pressure applies in all directions. Fluid pressure can also be amplified through hydraulic mechanisms and changes with the velocity of the fluid.
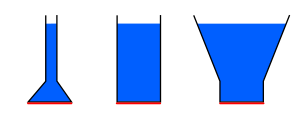
In a fluid column, as the depth increases, the pressure increases as well. Pressure (P) increases because as you go deeper, fluid at a lower depth has to support fluid above it as well. Therefore to define fluid pressure, we can say that it is the pressure at a point within a fluid arising due to the weight of the fluid.
Pressure in liquids is equally divided in all directions, therefore if a force is applied to one point of the liquid, it will be transmitted to all other points within the liquid.
The pressure in fluids can be calculated using the following relation:
P = hρg (Pressure = Height/Depth of the liquid X Density of the liquid X Gravitational pull (9.81m/s)).
The SI Unit (International System of Unit) of pressure is the Pascal, or Newton per meter squared (N/m^2).
Points along the same depth will have the same pressure, while points at different depths will have different pressure.
An object that is partly, or completely submerged in a fluid experiences a greater pressure on its bottom surface than on its top surface. This causes a resultant force upwards. This force is called upthrust, and is also known as buoyancy.

