Planoise facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Planoise
|
|
|---|---|
|
Part of Besançon
|
|

Top: Planoise from Rosemont Hill.
Centre: the tower of Planoise; Époisses sector; the Diversity statue. Bottom: View from the hill of Planoise. |
|
| Country | France |
| Region | Bourgogne-Franche-Comté |
| Department | Doubs |
| Arrondissement | Besançon |
| Canton | Besançon-1 |
| Commune | Besançon |
| Area
1
|
2.5 km2 (1.0 sq mi) |
| Population
(January 2006)
|
21,000 |
| • Density | 8,400/km2 (21,800/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Website | http://planoise-forever.skyrock.com/ |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
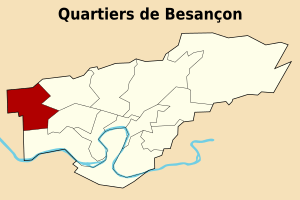
Planoise is an urban area in the western part of Besançon, France, built in the 1960s between the hill of Planoise and the district of Hauts-de-Chazal. It is the most populous district of Besançon, with 21,000 inhabitants (17% of the total inhabitants). Its inhabitants are called Planoisiens and Planoisiennes.
The area is constantly changing and developing. Despite difficult economic and social conditions, Planoise has become a commercial crossroads and a multicultural sector; the area is home to people from over 50 different cultural origins. It is a highly urbanized area (8,700 inhabitants per square kilometer) with few monuments or sites of interest, but the area contains notable buildings like the Departmental archives of Doubs and the Statue of Diversity.
Contents
History
The first traces of life in Planoise date back to 3000 BCE, during the Middle Paleolithic era. Objects were found in the Epoisses area during archaeological excavations, including a flint point dating to the Middle Paleolithic, three bracelets dating to the end of the Iron Age (500 BCE), and an oil lamp dating to Hellenistic Greece (between the first and fourth century BCE.) The objects are conserved in the Musée des Beaux-Arts et d'archéologie de Besançon (Museum of Fine Arts and Archeology.)
During the 13th century the territory of Planoise officially became part of the Imperial city of Besançon, according to Jean de Chalon (earl of Bourgogne). In the 15th century the clergy of Besançon bought the territory and the hill of Planoise. The name "Planoise" first appears officially in records in 1435. The name comes from the Latin word "planesium", which means "plain." At that time, the sector consisted of a large wood and had few inhabitants, mostly farmers.
Between the Middle Ages and the modern era, the area continued to be almost uninhabited. It was an agricultural area, farming mainly potatoes. The prince of Liechtenstein wanted to take the city of Besançon in 1815. He sent an army, which was stopped at Planoise. They abandoned their plans to take the city.
At the beginning of the 20th century, many farms were built in the area. As the population grew, agriculture became a major sector of the economy. The First and Second World Wars did not have a big impact on Planoise, although an American soldier was killed there. At the end of the 1950s, Planoise become a new urban area of Besançon.
Construction began in 1962 on 13,000 new dwellings in Planoise, and continued until 1985. The first inhabitants settled in the new buildings in 1968.
At the beginning of the 1970s, the first shops were under construction, and the church of Planoise was built in 1972. Soon after, Diderot school was built and the Cassin sector expanded. This period is known as the "golden age" of Planoise. In 1977 the population was 12,000 inhabitants.
Geography
Planoise is located in the west of Besançon, in the Canton of Besançon-1. Planoise is bounded on the west by Franois and Grandfontaine; Pirey to the north; Saint-Ferjeux and the center of Besançon to the east; and Velotte and Avanne-Aveney to the south. The area is located in a plain measuring 300 hectares, between the hill of Planoise (490m) and the hill of Rosemont (466m). Doubs river is one kilometre away. Two large woods surround the neighborhood: the wood "Monsieur" (en: "Sir Wood") and the wood of Pirey.
The principal road is Dole street, which is also the principal road of Besançon. The west boulevard joins the area at Velotte. In the center of Planoisen the principal roads are Île-de-France avenue, Bourgonge road, and Franche-Comté street.
Environment
Wildlife in Planoise consists of rats, hedgehogs, and some snakes. Common birds are pigeons and ravens. Many cats and dogs are at large. Livestock, including horses and goats, are kept in the Malcombe area.
Planoise, while urban, has a rich environmental heritage and a lot of wooded space, and urban trees, particularly beeches, firs, Aesculus, and birches, are present on all streets. The urban park of Planoise is a wooded park with playgrounds, and is located in Cassin sector. The municipality plans to build a new playground.
The wood of Planoise (located at the hill of Planoise) has a large diversity of animals and flora. Foxes, boars, squirrels, and birds are present. Vegetation includes beeches, firs, aesculus, oaks, ferns, and Platanus. A network of trails allows an easy access to the Fort of Planoise in the wood. The only new infrastructure is the Water tower of Planoise.
Images for kids
-
Church of Francis of Assisi
See also
 In Spanish: Planoise para niños
In Spanish: Planoise para niños