Pituitary adenoma facts for kids
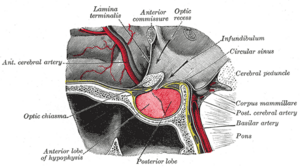
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Pituitary tumors are generally divided into three kinds dependant upon their biological functioning: benign adenoma, invasive adenoma or carcinomas, with carcinomas accounting for 0.1% to 0.2%, appoximately 35% being invasive adenomas and most being benign adenomas. Pituitary adenomas represent from 10% to 25% of all brain tumors and is thought to happen in about 17% to 25% of most people.
Non-invasive and non-secreting pituitary adenomas are considered to be benign [harmless]; but a recent large study (Fernández-Balsells, et al. 2011) has shown there are few studies to prove if this is true or not.
Adenomas that are bigger than 10 millimetres (0.39 in) are called macroadenomas, and those smaller than 10 mm are called microadenomas. Most pituitary adenomas are microadenomas. Most pituitary microadenomas often remain undiagnosed and those that are diagnosed are often found as an incidental finding [which means found by chance], and are called incidentalomas.
Invasive adenomas may invade the dura mater, cranial bone, or sphenoid bone. It used to be thought that clinically active pituitary adenomas were rare but recent studies have suggested that they may affect about one in 1000 of the general population.
Images for kids
-
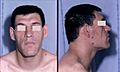
Morphological facial changes caused by acromegaly; frontal bossing, enlarged nose, prognathism and maxillary widening with separation of teeth and unseen, enlargement of the tongue (macroglossia).
See also
 In Spanish: Tumor de hipófisis para niños
In Spanish: Tumor de hipófisis para niños