Para rubber tree facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Rubber Tree |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Hevea brasiliensis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Division: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Tribe: |
Micrandreae
|
| Subtribe: |
Heveinae
|
| Species: |
H. brasiliensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.
|
|
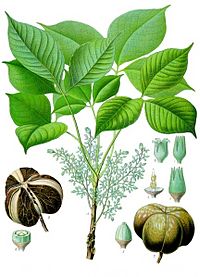
A Para rubber tree (or simply, rubber tree) is the tree which naturally produces rubber. It is native from tropical areas from South America, in the Amazon (Brazil), but was spread by English farmers to the Far East.
Para Rubber trees belong to the Euphorbiaceae family. In the wild they may reach heights of 100 to 125 ft (30-38 m) with large cylindrical trunks with or without buttresses. Crop trees reach a width of about 20 in. (50 cm), usually with a short bole, and with a sloped taper.
When trees reach 5-6 years old, they are harvested. Their trunks are cut just deep enough to tap the vessels without harming the tree's growth, and the sap is collected in small buckets. This process is known as rubber tapping. Older trees produce more latex, but they stop producing it after 26-30 years.
Rubber tree plantation
In the wild, the tree can reach a height of up to 140 feet (43 m). The white or yellow latex occurs in latex vessels in the bark, mostly outside the phloem. These vessels spiral up the tree in a right-handed helix which forms an angle of about 30 degrees with the horizontal, and can grow as high as 45 ft.
In plantations, the trees are generally smaller for two reasons: 1) trees grow more slowly when they are tapped for latex, and 2) trees are generally cut down after only 30 years, because latex production declines as trees age, and they are no longer economically productive. The tree requires a tropical or subtropical climate with a minimum of about 1,200 mm per year of rainfall, and no frost. If frost does occur, the results can be disastrous for production. One frost can cause the rubber from an entire plantation to become brittle and break once it has been refined."
Latex tapping
The natural rubber tree takes between seven and ten years to deliver the first harvest. Harvesters make incisions across the latex vessels, just deep enough to tap the vessels without harming the tree's growth, and the latex is collected in small buckets. This process is known as rubber tapping. Latex production is highly variable from tree to tree and across clone types.
Wood harvesting
As latex production declines with age, rubber trees are generally felled when they reach the age of 25 to 30 years. The earlier practice was to burn the trees, but in recent decades, the wood has been harvested for furniture making.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Árbol del caucho para niños
In Spanish: Árbol del caucho para niños







