Pan-African flag facts for kids
 |
|
| Name | Pan-African Flag Various other names |
|---|---|
| Adopted | 13 August 1920 |
| Design | A horizontal triband of red, black, and green. |
| Designed by | Marcus Garvey |
The Pan-African flag (also known as the Afro-American flag, Black Liberation flag, UNIA flag, and various other names) is a tri-color flag consisting of three equal horizontal bands of (from top down) red, black, and green. The Universal Negro Improvement Association and African Communities League (UNIA-ACL) formally adopted it on August 13, 1920, in Article 39 of the Declaration of the Rights of the Negro Peoples of the World, during its month-long convention at Madison Square Garden in New York City. Variations of the flag can and have been used in various countries and territories in the Americas to represent Garveyist ideologies.
Contents
History
The flag was created in 1920 by members of UNIA in response to the "coon song", a late nineteenth century craze for songs that belittle and mock African Americans and imitated of stereotyped AAVE speech, that became a hit around 1900 "Every Race Has a Flag but the Coon". This song has been cited as one of the three songs that "firmly established the term coon in the American vocabulary". In a 1927 report of a 1921 speech appearing in the Negro World weekly newspaper, Marcus Garvey was quoted as saying:
Show me the race or the nation without a flag, and I will show you a race of people without any pride. Aye! In song and mimicry they have said, "Every race has a flag but the coon." How true! Aye! But that was said of us four years ago. They can't say it now. ...
The Universal Negro Catechism, published by the UNIA in 1921, refers to the colors of the flag meaning:
Red is the color of the blood which men must shed for their redemption and liberty; black is the color of the noble and distinguished race to which we belong; green is the color of the luxuriant vegetation of our Motherland.
Journalist Charles Mowbray White has asserted that Garvey proposed the colors red, black and green for the following reasons: "Garvey said red because of sympathy for the 'Reds of the world', and the Green their sympathy for the Irish in their fight for freedom, and the Black [for] the Negro."
According to the UNIA more recently, the three colors on the Black Nationalist flag represent:
- red: the blood that unites all people of Black African ancestry, and shed for liberation;
- black: black people whose existence as a nation, though not a nation-state, is affirmed by the existence of the flag; and
- green: the abundant natural wealth of Africa.
The flag later became a Black Nationalist symbol for the worldwide liberation of Black people. As an emblem of Black pride, the flag became popular during the Black Liberation movement of the 1960s. In 1971, the school board of Newark, New Jersey, passed a resolution permitting the flag to be raised in public school classrooms. Four of the board's nine members were not present at the time, and the resolution was introduced by the board's teen member, a mayoral appointee. Fierce controversy ensued, including a court order that the board show cause why they should not be forced to rescind the resolution, and at least two state legislative proposals to ban ethnic flags and national flags (other than the U.S. flag) in public classrooms.
In the United States, the flag is currently widely available through flag shops or ethnic specialty stores. It is commonly seen at parades commemorating Martin Luther King, Jr. Day, civil rights rallies, and other special events.
Juneteenth holiday
Many in the African American community have adopted the Pan-African flag to represent Juneteenth. The Juneteenth holiday does have its own flag however, created in 1997.
2010s usage
In the United States, following the refusal of a grand jury to indict a police officer in the August 9, 2014 shooting of Michael Brown in Ferguson, Missouri, a Howard University student replaced the U.S. flag on that school's Washington, D.C. campus flagpole with a "black solidarity" flag (this tricolor) flying at half-mast.
Derivative flags
Flags of nation states
-
Flag of Saint Kitts and Nevis
-
Flag of Kenya
-
Flag of South Sudan
-
Flag of Malawi
-
Proposed flag for Angola (1996)
A number of flags of nation states in African and the Caribbean have been inspired by the UNIA flag. The Biafran flag is another variant of the UNIA flag with a sunburst in the center. Designed by the Biafran government and first raised in 1967, the colors are directly based on Garvey's design.
The flag of Malawi issued in 1964 is very similar, reflects the Black Nationalist flag's order of stripes. It is not directly based on Garvey's flag, although the colors have the same symbolism: Red for blood symbolizing the struggle of the people, green for vegetation, and black for the race of the people.
The Kenyan flag (Swahili: Bendera ya Kenya) is a tricolor of black, red, and green with two white fimbriations imposed, with a Masai shield and two crossed spears. It was officially adopted on 12 December 1963 after Kenya's independence, inspired by the pan-African tricolour.
The flag of Saint Kitts and Nevis has similar colors, arranged diagonally and separated by yellow lines. It similar to the Malawian flag in that the colors are not directly taken from the Pan-African flag but the symbolism is the same.
Derivative flags in the United States
-
Flag of the Republic of New Afrika
In response to the controversy over the flying of the Confederate flag, an African American-run company called NuSouth created a flag based on the Confederate naval jack, with the white stars and saltire outline replaced by green and the blue saltire made black.
The Kwanzaa Bendera
In the 1960s The Us Organization redesigned the UNIA flag also changing order and significance of the colours to: black, red and green. Defining "black" for the people, "red" for struggle, and "green" for the future built "out of struggle".
United States Postal Service issued a stamp in 1997 to commemorate the African-American festival of Kwanzaa with a painting by artist Synthia Saint James of a dark-skinned family wearing garments traditional in parts of Africa and fashionable for special occasions among African-Americans. The family members are holding food, gifts, and a flag. The flag in the stamp may have been meant to represent the Pan-African flag but instead used the similar flag (a black, red, and green horizontal tricolour) of the Black nationalist organisation Us Organization, which shares it's founder, professor and activist Maulana Karenga, with Kwanzaa.
The bendera (flag in the Kiswahili language) was documented as an supplemental symbol of Kwanzaa, in Karenga's 1998 book The African American Holiday of Kwanzaa, and included in ceremonial use during the festival.
Artworks
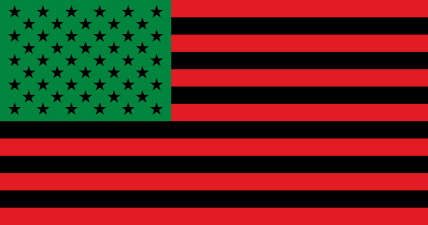
In 1990, artist David Hammons created a work called African-American Flag, which is held by the Museum of Modern Art in New York City. Based on the standard U.S. flag, its stripes are black and red, the canton field is green, and the stars on the canton field are black.
-
African American Flag in New York city
Alternative names
The flag goes by several other names with varying degrees of popularity:
- the Afro-American flag
- the Bendera Ya Taifa (Kiswahili for "flag of the Nation"), in reference to its usage during Kwanzaa
- the Black Liberation flag
- the International African flag
- the Marcus Garvey flag
- the UNIA flag, after its originators
- the Universal African flag
- the Red Black Green (RBG) flag
- the Black Nationalist flag
Proposed holiday
In 1999, an article appeared in the July 25 edition of The Black World Today suggesting that, as an act of global solidarity, every August 17 should be celebrated worldwide as Universal African Flag Day by flying the red, black, and green banner. August 17 is the birthday of Marcus Garvey.
See also
 In Spanish: Bandera panafricana para niños
In Spanish: Bandera panafricana para niños