Mount Akutan facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Mount Akutan |
|
|---|---|

Aerial view of Akutan volcano that forms the west part of Akutan Island
|
|
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 4,275 ft (1,303 m) |
| Geography | |
| Parent range | Aleutian Range |
| Topo map | USGS Unimak A-6 NW |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | Pleistocene |
| Mountain type | Stratovolcano |
| Volcanic arc/belt | Aleutian Arc |
| Last eruption | December 1992 |
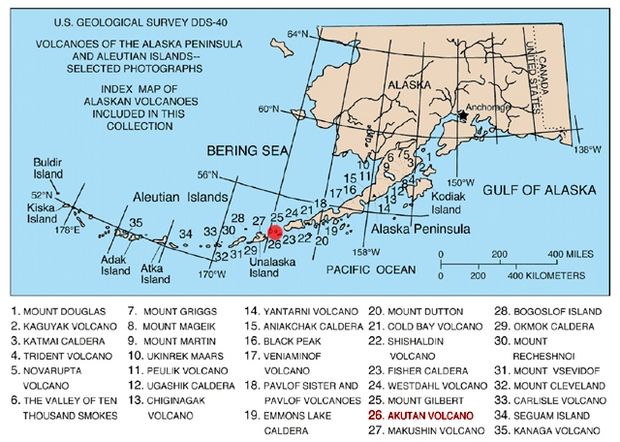
Mount Akutan, officially Akutan Peak, is a stratovolcano in the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. Akutan Peak, at 4,275 feet (1,303 m), is the highest point on the caldera of the Akutan stratovolcano. Akutan contains a 2 km-wide caldera formed during a major explosive eruption about 1600 years ago. Recent eruptive activity has originated from a large cinder cone on the NE part of the caldera. It has been the source of frequent explosive eruptions with occasional lava effusion that blankets the caldera floor. A lava flow in 1978 traveled through a narrow breach in the north caldera rim to within 2 km of the coast. A small lake occupies part of the caldera floor. Two volcanic centers are located on the NW flank: Lava Peak is of Pleistocene age; and, a cinder cone lower on the flank which produced a lava flow in 1852 that extended the shoreline of the island and forms Lava Point. An older, mostly buried caldera seems to have formed in Pleistocene or Holocene time, while the current caldera formed in a VEI-5 eruption c. 340 AD. AVO has recorded 33 confirmed eruptions at Akutan, making it the volcano with the most eruptions in Alaska.
The volcano erupted most recently in 1992, but there is still fumarolic activity at the base of Lava Point and there are hot springs North-East of the caldera. In March 1996, an earthquake swarm was followed by deformation of the volcanic edifice, including a lowering of the eastern side and a rise of the western side of the volcano.
See also
 In Spanish: Monte Akutan para niños
In Spanish: Monte Akutan para niños