Migraine facts for kids
A migraine is a medical condition which usually causes a pounding, throbbing headache on one side of the head. The pain may be very bad and hurt so much that a person may have a hard time doing anything. While most people who have migraines get a headache, not everyone does. There are different kinds of migraines and some do not cause a headache but do have other symptoms.
Most migraines cause a headache and nausea and might make the person dizzy or very sensitive to bright lights or loud noises. Some people have "auras" before a migraine starts, which means their ability to see becomes different. They may see funny patterns, have blurry vision, or may not be able to see at all. Other senses can change before or during a migraine, and the person may sense funny smells or tastes. Migraines can last a long time. Most migraines only last about 4 hours. Some can last up to 72 hours.
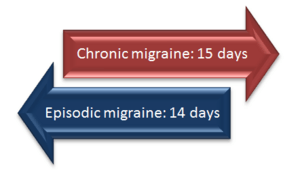
Migraines have been classified, based on how often they happen in a month: If a person has a headache for less than fifteen days, the migraine is called episodic migraine (EM). If it happens more than fifteen days, it is called chronic migraine (CM). Chronic means it happens over a long amount of time. Some people who start off getting episodic migraines may start to get chronic migraines later. Chronic migraine then may revert or go back to episodic migraine.
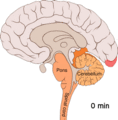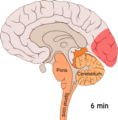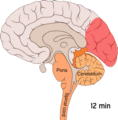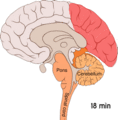
The exact causes of migraines are not known for sure. People used to believe that the main cause of migraines were unusual things in the blood vessels in the brain. However, now people believe that migraines start with a problem in the central nervous system. When this problem is triggered by various factors it sets off a cascade of neurological and biochemical reactions. Among these are reactions that disturb the trigeminal nerve. This nerve is the largest nerve in the head (cranial nerve) and the blood vessels (vascular system) which supply blood to the brain.
There are different risk factors which make a person more likely to have migraines. Being a female is a risk factor, and so is having family members who had migraines. For a person who has migraines, there are different trigger factors which may set off a migraine attack. In a large group of females who have migraines, one of the main trigger factors is when the amount of the hormone estrogen in their body either drops too low or fluctuates (goes up and down).
The World Health Organization says that migraine headache is the most costly brain problem for treatment and disability in the European Union and the United States.
Contents
Types
Migraine with aura
- Acephalgic migraine also called a silent migraine is a kind of migraine with aura but without the head pain. This type of migraine usually starts sometime during middle-age, which is after a person is 40 years old, and becomes more common as a person gets older. Unlike other migraines, males have acephalgic migraines more often then females do.
- Basilar-type migraine is a type of migraine with aura that causes headache usually in the occipital region of the brain with neurological symptoms that is believed to come from the brainstem, occipital cortex, and cerebellum and/or affects both hemispheres of the brain at the same time. Most people who have basilar-type migraine also experience migraines with aura without the basilar symptoms. This type of migraine usually more common in people under age 20 and young females.
- Familial hemiplegic migraine (FHM) is a type of migraine with aura that also may cause paralysis on one side of the body. When the migraine stops, the person can move normally again.
- Retinal migraine has repeated times of vision loss in one eye, that may happen before or during a headache. People who have retinal migraines usually have a history of having one of the other more common types of migraine.
Migraine without aura
- Menstrual migraine or catamenial migraine is a type of migraine that happens perimenstrually, which means around the time of menstruation during a woman's monthly menstrual cycle. Menstrual migraine is usually a migraine without aura, but sometimes a menstrual migraine with aura happens. About 7%-14% of women have migraines exclusively at the time of menstruation. These are considered true menstrual migraines. Most female migraneurs experience migraine attacks at all times during the menstrual cycle, with an increased number perimenstrually. These are referred to as menstrually related or menstrually triggered migraine. Both true menstrual migraines and menstrually related migraines are categorized under menstrual migraine.
- The role of estrogen
-
- Estrogen is a hormone that is mostly made in a woman's ovaries. There are three types of estrogen: estrone, estradiol and estriol.In women who have migraines it is usually connected with their menstruation cycle. About 60% of women have these menstrual or menstrually-related migraines and the main trigger is believed to be reduced circulating estrogen levels, i.e. the amount of estrogen in the body, specifically estradiol. In some cases, fluctuation (going up and down) in the amount of circulating estrogen levels may trigger a migraine, i.e. not only too little but sometimes too much estrogen may trigger a migraine.
Childhood periodic syndromes
Childhood periodic syndromes are a group of migraine syndromes that children may have. When a child has one of these child periodic syndromes there is a greater chance that they will get one of the other, more common types of migraines when they are adults.
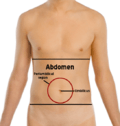
Abdominal migraine is a kind of migraine which causes a very bad pain in the area of the abdomen, usually around the 'belly-button' which is called the periumbilical area. Abdominal migraine usually affects children starting at about age 7, but it may affect younger children and older children, and it may also sometimes affect adults.
Benign paroxysmal vertigo of childhood (BPVC for short): (this means harmless dizziness, that happens again and again and happens suddenly) is a medical condition which occurs in children usually starting between two and five years of age; it often disappears by the age of eight. BPVC causes vertigo.
Cyclic vomiting syndrome or cyclical vomiting syndrome( CVS), is a medical condition whose main symptoms are nausea and repeated vomiting. CVS happens more often in children but it can occur at any age.
Chronic vs. episodic migraine
Episodic migraine (EM) is when a person has migraine symptoms for 14 days or less in one month, while chronic migraine (CM) is when a person has migraine symptoms for 15 or more days in one month. When compared to persons with episodic migraine those with CM where less likely to have full-time jobs and had a larger risk of headache-related disability.Persons with CM are almost twice as likely to have anxiety, chronic pain, and/or depression; they also have a 40% greater chance of having heart disease and angina and are 70% more likely to have a history of stroke.
About 7.68% of total migraine cases are chronic migraines and about 1% of people in the United States have CM, with a higher rate among females, middle-aged people, and in those households that had the lowest annual income. (The American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention Study)
Aura
Aura (from the Greek word for breeze) is the word used to describe a series of neurological symptoms that may begin before an epileptic seizure or a migraine headache. About 15% of people who have a migraine will have the kind with an aura. The symptoms may include visual problems such as scotomas (losing vision for a short time, seeing zig-zag lines or floating spots etc.), vertigo, a ringing noise in the ears (tinnitus) and problems speaking.
Scotoma (came from the Greek word for darkness: skotos): a blind spot or area of reduced vision surrounded by a normal visual field. i.e.: A person can see normally except where the scotoma is.Scotomas may affect one or both eyes and be either and be either absolute where nothing can be seen within the scotoma or, relative with some ability to see within the area of the scotoma.
Scotomas may also have different patterns and shapes like the fortification scotoma; it is called fortification because it looks like the outline of an old fort. Scotomas can start of small and then get bigger, move around to different parts of a person's visual field, and they can also look like flickering lights.
History
Symptoms that mimic those of migraines have been recorded in various cultures throughout written history. The first known mention was found on cuneiform tablets from Babylonia dating to 2000-1880 B.C.E.A treatment for migraine can be found in the Ebers Papyrus, an Ancient Egyptian medical text named after George Ebers, the German Eygptologist who discovered them. In the ancient text dated to 1552 B.C.E. migraine is refereed to as "suffering in half the head".
| Another remedy for suffering in half the head. The skull of a catfish fried in oil. Anoint the head herewith.-Ebers Papyrus,1552 B.C.E. |
The Ancient Greek physician Aretaeus of Cappadocia's description of a type of headache he dubbed heterocrania is considered a description of migraine.
Images for kids
-
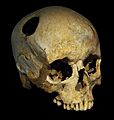
A trepanated skull, from the Neolithic. The perimeter of the hole in the skull is rounded off by ingrowth of new bony tissue, indicating that the person survived the operation.
See also
 In Spanish: Migraña para niños
In Spanish: Migraña para niños