Lunenburg County, Virginia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Lunenburg County
|
||
|---|---|---|

Lunenburg County Courthouse
|
||
|
||
| Motto(s):
The Old Free State
|
||
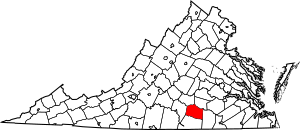
Location within the U.S. state of Virginia
|
||
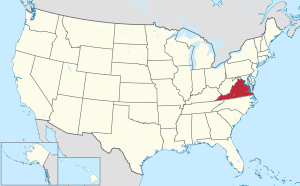 Virginia's location within the U.S. |
||
| Country | ||
| State | ||
| Founded | 1746 | |
| Named for | Brunswick-Lüneburg | |
| Seat | Lunenburg | |
| Largest town | Victoria | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 432 sq mi (1,120 km2) | |
| • Land | 432 sq mi (1,120 km2) | |
| • Water | 0.7 sq mi (2 km2) 0.2% | |
| Population
(2020)
|
||
| • Total | 11,936 | |
| • Density | 27.63/sq mi (10.668/km2) | |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | |
| Congressional district | 5th | |
Lunenburg County is a county located in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 11,936. Its county seat is Lunenburg.
Contents
History
Lunenburg County was established on May 1, 1746, from Brunswick County. The county is named for the former Duchy of Brunswick-Lünenburg in Germany, because one of the titles also carried by Britain's Hanoverian kings was Duke of Brunswick-Lünenburg. Bedford, Charlotte, Halifax, and Mecklenburg Counties were later formed from Lunenburg County. It is nicknamed "The Old Free State" because during the buildup of the Civil War, it let Virginia know the county would break off if the state did not join The Confederacy.
Among the earliest settlers of the county was William Taylor, born in King William County, Virginia. He was the son of Rev. Daniel Taylor, a Virginia native and Anglican priest educated at Trinity College, Cambridge University in England, and his wife Alice (Littlepage) Taylor. William Taylor married Martha Waller, a daughter of Benjamin Waller of Williamsburg, Virginia.
In 1760 Taylor purchased three adjoining tracts of land in Lunenburg County totaling 827 acres (3.35 km2). Taylor soon became one of the county's leading citizens, representing Lunenburg in the Virginia House of Burgesses from 1765 until 1768. In that capacity, Taylor voted in 1765 to support statesman Patrick Henry's Virginia Resolves in 1765. Taylor served as County Clerk for 51 years (1763–1814).
Taylor was succeeded as County Clerk by his son William Henry Taylor, who held the office for another 32 years—from 1814 until 1846. Another son, General Waller Taylor, represented Lunenburg in the Virginia legislature, then moved to Vincennes, Indiana. There he became a judge and subsequently Adjutant General of the United States Army under General William Henry Harrison in the War of 1812. General Waller Taylor later served as one of the first United States senators from the newly created state of Indiana from 1816 to 1825. He died on a visit home to see his relatives in Lunenburg County in 1826.
During much of the American Civil War, the family of Missionary Bishop Henry C. Lay lived in Lunenberg County, where Mrs. Lay (the former Eliza Withers Atkinson) grew up. Both of Bishop Lay's brothers served as Confederate colonels, and Mrs. Lay's uncle, Thomas Atkinson was bishop of North Carolina.
Cases surrounding an 1895 Lunenburg County murder are the subject of historian Suzanne Lebsock's book, A Murder in Virginia: Southern Justice on Trial.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 432 square miles (1,120 km2), of which 432 square miles (1,120 km2) is land and 1 square mile (2.6 km2) (0.16%) is water.
Adjacent counties
- Brunswick County (east)
- Charlotte County (west)
- Mecklenburg County (south)
- Nottoway County (northeast)
- Prince Edward County (north)
Major highways
 US 360 (Eastbound Only – Three-Sixty Hwy)
US 360 (Eastbound Only – Three-Sixty Hwy)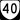 SR 40 (Lunenburg County Rd; joins SR 49 and becomes Courthouse Rd; Court St and Main St in Victoria; K-V Rd; Main St and S Broad St in Kenbridge, Blackstone Rd)
SR 40 (Lunenburg County Rd; joins SR 49 and becomes Courthouse Rd; Court St and Main St in Victoria; K-V Rd; Main St and S Broad St in Kenbridge, Blackstone Rd) SR 49 (Falls Rd; joins SR 40 in Victoria and becomes Main St; Courthouse Rd
SR 49 (Falls Rd; joins SR 40 in Victoria and becomes Main St; Courthouse Rd SR 137 (E 5th Ave; S Hill Rd; Dundas Rd)
SR 137 (E 5th Ave; S Hill Rd; Dundas Rd) SR 138 (E 5th Ave; S Hill Rd)
SR 138 (E 5th Ave; S Hill Rd)
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 8,959 | — | |
| 1800 | 10,381 | 15.9% | |
| 1810 | 12,265 | 18.1% | |
| 1820 | 10,662 | −13.1% | |
| 1830 | 11,957 | 12.1% | |
| 1840 | 11,055 | −7.5% | |
| 1850 | 11,692 | 5.8% | |
| 1860 | 11,983 | 2.5% | |
| 1870 | 10,403 | −13.2% | |
| 1880 | 11,535 | 10.9% | |
| 1890 | 11,372 | −1.4% | |
| 1900 | 11,705 | 2.9% | |
| 1910 | 12,780 | 9.2% | |
| 1920 | 15,260 | 19.4% | |
| 1930 | 14,058 | −7.9% | |
| 1940 | 13,844 | −1.5% | |
| 1950 | 14,116 | 2.0% | |
| 1960 | 12,523 | −11.3% | |
| 1970 | 11,687 | −6.7% | |
| 1980 | 12,124 | 3.7% | |
| 1990 | 11,419 | −5.8% | |
| 2000 | 13,146 | 15.1% | |
| 2010 | 12,914 | −1.8% | |
| 2020 | 11,936 | −7.6% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790–1960 1900–1990 1990–2000 2010 2020 |
|||
2020 census
| Race / Ethnicity (NH = Non-Hispanic) | Pop 2010 | Pop 2020 | % 2010 | % 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White alone (NH) | 7,730 | 7,016 | 59.86% | 58.78% |
| Black or African American alone (NH) | 4,451 | 3,773 | 34.47% | 31.61% |
| Native American or Alaska Native alone (NH) | 37 | 32 | 0.29% | 0.27% |
| Asian alone (NH) | 25 | 25 | 0.19% | 0.21% |
| Pacific Islander alone (NH) | 3 | 5 | 0.02% | 0.04% |
| Some Other Race alone (NH) | 9 | 31 | 0.07% | 0.26% |
| Mixed Race or Multi-Racial (NH) | 189 | 465 | 1.46% | 3.90% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 470 | 589 | 3.64% | 4.93% |
| Total | 12,914 | 11,936 | 100.00% | 100.00% |
Education
Lunenburg County Public Schools operates the following schools:
- Kenbridge Elementary School- Kenbridge, VA
- Victoria Elementary School- Victoria, VA
- Lunenburg Middle School- Victoria, VA
- Central High School- Victoria, VA
There are no private or independent schools in Lunenburg County, and no colleges or universities are located there. Kenston Forest School in Nottoway County, approximately 20 minutes away, offers the closest K-12 private education available to Lunenburg County residents.
Communities
Towns
Census-designated place
Other unincorporated communities
- Dundas
- Fort Mitchell
- Meherrin
- Rehoboth
Notable people
- Lewis Archer Boswell, experimented with flying aircraft. Local legends claim he achieved heavier-than-air flight before the Wright Brothers, though there is no historical evidence.
- Justice Paul Carrington (1733–1818), second member appointed of the Virginia Supreme Court.
- Roy Clark, born in Meherrin, he became a highly acclaimed country musician and a United Nations Goodwill Ambassador.
- Henry W. Collier, born in the county, was elected fourteenth Governor of Alabama, from 1849 to 1853.
- Alfred L. Cralle, born in the county, became an inventor and businessman in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. He is best remembered for inventing the lever-operated ice cream scoop in 1897.
- Anthony Davis, an NFL football player, currently for the New Orleans Saints (beginning 2009). From Lunenburg County, he attended Central High School in Victoria, Virginia.
- Richard Ellis, born and raised in Lunenburg County, settled in Alabama where he was a member of Alabama's Constitutional Convention in 1818 and an associate justice of the Alabama Supreme Court (1819–1826).
- James Greene Hardy, a county native, was elected Lt. Governor of the Commonwealth of Kentucky, serving from 1855 to 1856.
- John A. Murrell (1806?–1844), born in the county, bandit, known for the Mystic Clan or Mystic Confederacy and Murrell Insurrection Conspiracy
- Verner Moore White (1863–1923), born in the county, was a noted landscape and portrait artist.
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Lunenburg para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Lunenburg para niños


