London Borough of Newham facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
London Borough of Newham
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Motto(s):
Progress with the People
|
|||
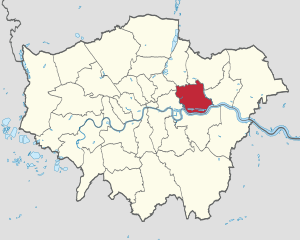
Newham shown within Greater London
|
|||
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom | ||
| Constituent country | England | ||
| Region | Inner London | ||
| Ceremonial county | Greater London | ||
| Created | 1 April 1965 | ||
| Admin HQ | East Ham | ||
| Government | |||
| • Type | London borough council | ||
| • Body | Newham London Borough Council | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 13.98 sq mi (36.22 km2) | ||
| Area rank | 298th (of 326) | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • Total | 353,134 | ||
| • Rank | 20th (of 326) | ||
| • Density | 25,252/sq mi (9,749.7/km2) | ||
| Time zone | UTC (GMT) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (BST) | ||
| Postcodes |
E, IG
|
||
| Area code(s) | 020 | ||
| ONS code | 00BB | ||
| GSS code | E09000025 | ||
| Police | Metropolitan Police | ||
The London Borough of Newham (![]() i/ˈnjuːəm/) is a London borough created in 1965 by the London Government Act 1963. It covers an area previously administered by the Essex county boroughs of West Ham and East Ham, authorities that were both abolished by the same act. The name Newham reflects its creation and combines the compass points of the old borough names. Situated in the Inner London part of East London, Newham has a population of 387,576, which is the fourth highest of the London boroughs and also makes it the 26th most populous district in England. The local authority is Newham London Borough Council.
i/ˈnjuːəm/) is a London borough created in 1965 by the London Government Act 1963. It covers an area previously administered by the Essex county boroughs of West Ham and East Ham, authorities that were both abolished by the same act. The name Newham reflects its creation and combines the compass points of the old borough names. Situated in the Inner London part of East London, Newham has a population of 387,576, which is the fourth highest of the London boroughs and also makes it the 26th most populous district in England. The local authority is Newham London Borough Council.
It is 5 miles (8 km) east of the City of London, north of the River Thames (the Woolwich Ferry and Woolwich foot tunnel providing the only crossings to the south), bounded by the River Lea to its west and the North Circular Road to its east. Newham was one of the six host boroughs for the 2012 Summer Olympics and contains most of the Olympic Park including the London Stadium, and also contains the London City Airport. Major districts include East Ham, West Ham, Stratford, Plaistow, Forest Gate, Beckton and Canning Town.
Contents
History
The borough was formed on 1 April 1965 under the London Government Act 1963, as a borough of the newly formed Greater London. It broadly covered the areas of the county borough of East Ham and the county borough of West Ham that were abolished by the same act. These in turn were successors to the ancient civil and ecclesiastical parishes of East Ham and West Ham. Green Street and Boundary Road mark the former boundary between the two.
North Woolwich also became part of the borough (previously part of the Metropolitan Borough of Woolwich, the majority of which lay south of the River Thames), as did a small area around Gallions Reach west of the River Roding which had previously been part of the Municipal Borough of Barking. East Ham, West Ham and Barking had all historically been part of the county of Essex, whilst Woolwich had been part of Kent prior to becoming part of the County of London in 1889. Newham was devised for the borough as an entirely new name.
Manor of Ham
The area of the modern borough was at one time occupied by a manor (an estate or landholding with certain legal responsibilities) called 'Ham'. The name comes from Old English 'hamm' and means 'a dry area of land between rivers or marshland', referring to the location of the settlement within boundaries formed by the rivers Lea, Thames and Roding and their marshes.
The first known written use of the term, as 'Hamme', is in an Anglo-Saxon charter of 958, in which King Edgar granted the area to Ealdorman Athelstan. The territory was undivided at that time. A subsequent charter of 1037 describes a transfer of land which has been identified with East Ham, indicating that the division of the territory occurred between 958 and 1037.
The Domesday Book shows landholdings divided further, and by the end of the 12th century these manors were being served, singly or in groups of manors, by the familiar ancient parishes of West Ham, East Ham and Little Ilford (now also known as Manor Park), with some areas by the Roding a part of Barking, and the area now known as North Woolwich attached to Woolwich. The earliest recorded use of the name West Ham, Westhamma, comes in 1186, and East Ham, Estham, is recorded in 1204.
The boundary between West and East Ham was drawn from the now lost Hamfrith Waste and Hamfrith Wood in the north (then the southernmost parts of Epping Forest which extended as far south as the Romford Road at that time), along Green Street down to the small, also lost, natural harbour known as Ham Creek. Ham Creek was filled-in in the nineteenth century, but the small residual head of the creek still formed the boundary between the two areas into the late 20th century, when what remained was also filled in.
The formation of the modern borough in 1965 saw the merger of West and East Ham, together with North Woolwich and Barking west of the River Roding. Little Ilford had become part of East Ham as part of earlier local government reorganisations.
Medieval period
The prosperity of the area increased due to the construction of Bow Bridge, the only bridge over the Lea, and the creation of Stratford Langthorne Abbey.
Governance

The local authority is Newham Council, which meets at Newham Town Hall in East Ham and has its main offices at 1000 Dockside Road, overlooking the Royal Albert Dock. Since 2002 the council has been led by a directly elected Mayor of Newham.
Greater London representation
Since 2000, for elections to the London Assembly, the borough forms part of the City and East constituency.
Demography
Population figures
| Population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1801 | 8,875 | — |
| 1811 | 11,166 | +25.8% |
| 1821 | 13,005 | +16.5% |
| 1831 | 15,553 | +19.6% |
| 1841 | 17,758 | +14.2% |
| 1851 | 24,875 | +40.1% |
| 1861 | 69,355 | +178.8% |
| 1871 | 113,835 | +64.1% |
| 1881 | 158,314 | +39.1% |
| 1891 | 259,155 | +63.7% |
| 1901 | 338,506 | +30.6% |
| 1911 | 442,158 | +30.6% |
| 1921 | 448,081 | +1.3% |
| 1931 | 454,096 | +1.3% |
| 1941 | 377,508 | −16.9% |
| 1951 | 313,837 | −16.9% |
| 1961 | 271,858 | −13.4% |
| 1971 | 235,496 | −13.4% |
| 1981 | 209,131 | −11.2% |
| 1991 | 221,146 | +5.7% |
| 2001 | 243,737 | +10.2% |
| 2011 | 307,984 | +26.4% |
| 2021 | 351,030 | +14.0% |
| Source: A Vision of Britain through time, citing Census population | ||
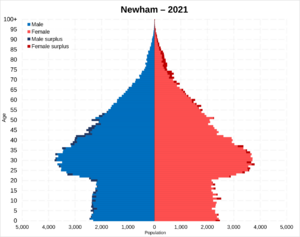
Newham has, after Barnet and Croydon, the third highest population of the London boroughs, with a population numbering 382,984 as of 2021. Despite growing since the 1980s, it is still drastically lower than its pre-war peak. In the period between 1951 and 1981, Newham's population shrunk by 28.87% owing to factors such as the war bombings and the increasingly high unemployment. The redevelopment of the Docklands as well as development related to the 2012 Olympics have contributed to reversing its declining trend.
Ethnicities
Newham has the youngest overall population and one of the lowest White British populations in the country according to the 2011 UK Census. The borough has the second-highest percentage of Muslims in the UK, after the neighbouring London Borough of Tower Hamlets, at 32%. A 2017 report from Trust for London and the New Policy Institute found that 36% of local employees in Newham are in low paid work; the highest percentage of any London borough. Newham also has a 37% poverty rate, which is the second-highest rate in London.
Newham is very ethnically diverse. When using Simpson's Diversity Index on 10 aggregated ethnic groups, the 2001 UK Census identified Newham as the most ethnically diverse district in England and Wales, with 9 wards in the top 15. However, when using the 16 ethnic categories in the Census so that White Irish and White Other ethnic minorities are also included in the analysis, Newham becomes the second-most ethnically diverse borough with six out of the top 15 wards, behind Brent with 7 out of the top 15 wards.
Newham has the lowest percentage of both total White and White British residents of all of London's boroughs. The joint-lowest wards with White British population are Green Street East and Green Street West, each having 4.8% – the third-lowest behind Southall Broadway and Southall Green in Ealing. East Ham North follows closely, at 4.9%.
As of the 2021 UK census, people of "Bangladeshi" ethnicity are the largest single group in the borough at 15.9%. "White British" are the second largest group at 14.8%, with "White Other" third largest at 14.6%, "African" fourth largest at 11.6%, "Indian" next largest at 11% and then "Pakistani" at 8.9%. Newham has had a large Asian community for many decades; more than half of Newham's Upton and Kensington wards were of ethnic minority origin in 1981. The nationality to increase the most in number since 1991 is the Bangladeshi community. Newham has the largest total population of Asian origin in London; it is notably a borough with high populations of all three largest British Asian nationalities, having the 5th highest Indian population in London and the 2nd highest each for both Pakistani and Bangladeshi.
Newham has 1,340 residents who were born in Ukraine, the highest population of Ukrainians in the UK.
| Ethnic Group | 1971 estimations | 1981 estimations | 1991 census | 2001 census | 2011 census | 2021 census | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| White: Total | – | 89.1% | 141,043 | 69% | 126,708 | 57.3% | 96,130 | 39.42% | 89,216 | 28.97% | 107,947 | 30.8% |
| White: British | – | – | – | – | – | – | 82,390 | 33.78% | 51,516 | 16.73% | 51,819 | 14.8% |
| White: Irish | – | – | – | – | – | – | 3,231 | 1.32% | 2,172 | 0.71% | 2,039 | 0.6% |
| White: Gypsy or Irish Traveller | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 462 | 0.15% | 353 | 0.1% |
| White: Roma | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 2,342 | 0.7% |
| White: Other | – | – | – | – | – | – | 10,509 | 4.31% | 35,066 | 11.39% | 51,394 | 14.6% |
| Asian or Asian British: Total | – | – | 38,203 | 18.7% | 59,257 | 26,8% | 81,651 | 33.48% | 133,895 | 43.47% | 148,187 | 42.3% |
| Asian or Asian British: Indian | – | – | 22,259 | 29,105 | 29,597 | 12.14% | 42,484 | 13.79% | 38,642 | 11.0% | ||
| Asian or Asian British: Pakistani | – | – | 9,214 | 13,162 | 20,644 | 8.46% | 30,307 | 9.84% | 31,216 | 8.9% | ||
| Asian or Asian British: Bangladeshi | – | – | 3,019 | 8,550 | 21,458 | 8.80% | 37,262 | 12.10% | 55,677 | 15.9% | ||
| Asian or Asian British: Chinese | – | – | 1,109 | 1,803 | 2,349 | 0.96% | 3,930 | 1.28% | 6,213 | 1.8% | ||
| Asian or Asian British: Other Asian | – | – | 2,602 | 6,637 | 7,603 | 3.12% | 19,912 | 6.47% | 16,439 | 4.7% | ||
| Black or Black British: Total | – | – | 23,046 | 11.3% | 32,214 | 14.6% | 52,653 | 21.59% | 60,256 | 19.56% | 61,302 | 17.4% |
| Black or Black British: African | – | – | 6,686 | 12,639 | 31,982 | 13.11% | 37,811 | 12.28% | 40,874 | 11.6% | ||
| Black or Black British: Caribbean | – | – | 13,528 | 16,015 | 17,931 | 7.35% | 15,050 | 4.89% | 13,586 | 3.9% | ||
| Black or Black British: Other Black | – | – | 2,832 | 3,560 | 2,740 | 1.12% | 7,395 | 2.40% | 6,842 | 1.9% | ||
| Mixed or British Mixed: Total | – | – | – | – | – | – | 8,248 | 3.38% | 13,945 | 4.53% | 16,419 | 4.6% |
| Mixed: White and Black Caribbean | – | – | – | – | – | – | 2,986 | 1.22% | 3,957 | 1.28% | 4,253 | 1.2% |
| Mixed: White and Black African | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1,657 | 0.68% | 3,319 | 1.08% | 3,317 | 0.9% |
| Mixed: White and Asian | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1,652 | 0.68% | 2,677 | 0.87% | 3,324 | 0.9% |
| Mixed: Other Mixed | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1,953 | 0.80% | 3,992 | 1.30% | 5,525 | 1.6% |
| Other: Total | – | – | 2,108 | 3,121 | 5,209 | 2.14% | 10,672 | 3.47% | 17,175 | 4.9% | ||
| Other: Arab | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 3,523 | 1.14% | 3,534 | 1.0% |
| Other: Any other ethnic group | – | – | – | – | – | – | 5,209 | 2.14% | 7,149 | 2.32% | 13,641 | 3.9% |
| Ethnic minority: Total | – | 10.9% | 63,397 | 31% | 94,592 | 42.7% | 147,761 | 60.58% | 218,768 | 71.03% | 246,617 | 69.2% |
| Total | – | 100% | 204,440 | 100% | 221,300 | 100% | 243,891 | 100% | 307,984 | 100% | 351,030 | 100% |
Religion
Religion in Newham as of 2021 Christianity (35.3%) Islam (34.8%) Irreligion (14.5%) Hindu (6.1%) Sikh (1.6%) Buddhist (0.6%) Jewish (0.1%) Other (7%)
The following table shows the religious identity of residents residing in Newham according to the 2001, 2011 and the 2021 censuses.
| Religion | 2001 | 2011 | 2021 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| Christian | 114,247 | 46.8 | 123,119 | 40.0 | 123,746 | 35.3 |
| Muslim | 59,293 | 24.3 | 98,456 | 32.0 | 122,146 | 34.8 |
| Jewish | 481 | 0.2 | 342 | 0.1 | 448 | 0.1 |
| Hindu | 16,901 | 6.9 | 26,962 | 8.8 | 21,405 | 6.1 |
| Sikh | 6,897 | 2.8 | 6,421 | 2.1 | 5,638 | 1.6 |
| Buddhism | 1,592 | 0.7 | 2,446 | 0.8 | 2,160 | 0.6 |
| Other religion | 664 | 0.3 | 1,090 | 0.4 | 1,765 | 0.5 |
| No religion | 21,978 | 9.0 | 29,373 | 9.5 | 50,795 | 14.5 |
| Religion not stated | 21,838 | 9.0 | 19,775 | 6.4 | 22,933 | 6.5 |
| Total | 243,891 | 100.00% | 307,894 | 100.00% | 351,100 | 100.0% |
Education
A 2017 report by Trust for London and the New Policy Institute finds that the GCSE attainment gap between advantaged and disadvantaged pupils in Newham is the 4th best out of 32 London boroughs.
Schools and colleges
The Borough is the education authority for the district providing education in a mix of Foundation, community and voluntary aided schools. The borough also owns and operates Debden House, a residential adult education college in Loughton, Essex, and is home to the Rosetta Art Centre, a dedicated visual art organisation which delivers courses at its base in Stratford and produces participatory art projects, programmes and initiatives. The Essex Primary School in Sheridan Road with over 900 pupils is one of the biggest primary schools in London.
University
The University of East London has two campuses in Newham:
- the Stratford Campus, at Stratford
- the Docklands Campus, next to the regenerated Royal Albert Dock
Birkbeck Stratford is a collaboration between Birkbeck, University of London and UEL to increase participation in adult learning. This is based on the UEL/Birkbeck shared campus, USS (University Square Stratford), in the centre of Stratford.
The University of East London had formed a partnership with the United States Olympic Committee which resulted in the United States Olympic Team using University of East London campuses as training bases during the London 2012 Olympic and Paralympic Games.
Places of interest
Community
- The Hub, a community resource centre built by the local community, in Star Lane, E16, featuring up to the minute "green" features
- Grassroots, another innovative green resource centre built by the community. Grassroots is in Memorial Recreation Ground, E15
- Rosetta Art Centre, situated in walking distance to Grassroots, also in E15
Libraries
Newham has ten libraries (Beckton, Canning Town, Custom House, East Ham, Green Street, Manor Park, North Woolwich, Plaistow, Stratford and Forest Gate).
Museums
- North Woolwich Old Station Museum. Closed in 2008.
- Three Mills, a mill complex on the east bank of the River Lea. A trading site for nearly a thousand years, the House Mill was built in 1776 and was (and remains) the country's largest tide mill. It has been restored and contains much of its original machinery including four large waterwheels, millstones and grain chutes.
Markets
There are a number of local markets in the Borough, including Queens Market, which the council was controversially seeking to redevelop. The proposal was successfully opposed by Friends of Queens Market.
Parks and open spaces
80 hectares within the borough are designated as part of the Metropolitan Green Belt.
Performance

- Stratford Circus Arts Centre , a community arts venue which presents theatre, dance, music, circus and comedy from around the world for communities in Newham and East London. The organisation works with schools and local groups in Newham to provide classes, workshops and outreach opportunities. Stratford Circus Arts Centre partners with Newham Council for Every Child a Theatre Goer which invites every year 6 child to a performance at the venue
- Theatre Royal Stratford East
- St Mark's Church, Silvertown The church was designed by Samuel Saunders Teulon. It was built between 1861 and 1862 after a cholera epidemic swept the district and local clergy appealed through the columns of The Times for funds to provide an architectural, as well as spiritual, beacon for the area. It is now the home of the Brick Lane Music Hall.
Shopping and exhibitions
- Queen's Market – an historic street market
- ICC London – ExCeL – International Conference Centre
- Gallions Reach Shopping Park
- East Shopping Centre – Europe's first purpose-built boutique Asian shopping centre
- Green Street – a shopping street mostly catering for the Asian community
- Stratford Centre
- Westfield Shopping Centre, Stratford – The largest Westfield Shopping Centre in Europe.
Sport
- Newham was one of the six host boroughs for the 2012 Summer Olympics
- West Ham United F.C. plays its home matches at the London Stadium (formerly the Olympic Stadium) in Stratford
- The Newham and Essex Beagles Athletics Club has its headquarters at the London Marathon Community Track in Queen Elizabeth Olympic Park adjacent to the London Stadium.
- Clapton F.C., a non-league football club, plays at the Terence McMillan Stadium in Plaistow
- Clapton Community F.C., a fan-owned non-league football team in Forest Gate, playing at The Old Spotted Dog Ground
- Athletic Newham F.C., a non-league football club, plays at the Terence McMillan Stadium in Plaistow
- London APSA F.C., a non-league football club, plays at the Flanders Playing Fields in Napier Road, East Ham
- London Regatta Centre, a charitable organisation promoting water sports such as rowing and dragon boats, is in Beckton
Newspapers
The local newspaper is the Newham Recorder.
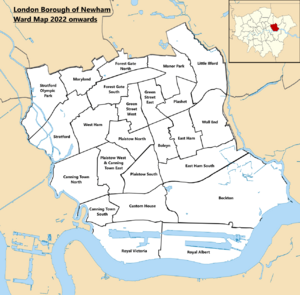
Districts
See List of districts in the London Borough of Newham for the full list, including neighbourhoods or localities which form part of the areas listed below.
- Beckton
- Canning Town
- Custom House
- East Ham
- Forest Gate
- Manor Park
- North Woolwich
- Plaistow
- Silvertown
- Stratford
- Upton Park
- West Ham
Parishes
The borough is covered by the following ecclesiastical parishes of the Church of England:
- Parish of the Divine Compassion, Plaistow and North Canning Town
- St Martin's Church, Plaistow
- St Mary's Church, Plaistow
- St Philip and St James Church, Plaistow
- St Matthias' Church, Canning Town
- St Luke's Church, Canning Town
- Church of the Ascension, Victoria Docks
- St John's Church, North Woolwich
- St Mark's Church, Beckton
- Parish of East Ham, Holy Trinity
- St George's and St Ethelbert's Church, East Ham
- St Paul's Church, East Ham
- Little Ilford
- St Barnabas, Little Ilford
- Emmanuel Forest Gate, with St Peter's, Upton Cross
- St Mark's Church, Forest Gate
- St Saviour and St James, Forest Gate
- St Margaret with St Columba, Leytonstone
- St Paul and St James, Stratford
- St John with Christchurch, Stratford
- All Saints Church, West Ham
Transport
Since the 1980s, public transport in Newham has undergone many upgrades and improvements are still continuing to this day.
The Docklands Light Railway (DLR) first opened in 1987, and was extended from Tower Hamlets through to Beckton in 1994. The network has undergone many extensions since, including to serve London City Airport, as well as Stratford International station in 2011 after its High Speed 1 link opened in late 2009. The Jubilee Line Extension was completed in 1999, including new or improved stations at Canning Town, West Ham and Stratford. The DLR network compensates for Newham's lack of tube stations, of which there are only 6, in comparison with other London boroughs. The Crossrail scheme - opening as the Elizabeth line in 2022 - also delivered improved rail connections to several stations as it heads through the borough on an east west axis. Of the 28 stations in Newham, only 4 stations lack step free access - thanks to the recent age of many of the stations in the borough.
As a result of all the recent developments, the borough contains one of only two airports located within the Greater London boundary and currently the only railway station outside of central London that is served by high speed rail.
List of stations
- Abbey Road DLR station
- Beckton DLR station
- Beckton Park DLR station
- Cyprus DLR station
- Canning Town station – Jubilee line and DLR
- Custom House station - Elizabeth line and DLR
- East Ham tube station – District and Hammersmith & City lines
- Forest Gate railway station – Elizabeth line
- Gallions Reach DLR station
- King George V DLR station
- London City Airport DLR station
- Manor Park railway station – Elizabeth line
- Maryland railway station – Elizabeth line
- Plaistow tube station – District and Hammersmith & City lines
- Pontoon Dock DLR station
- Prince Regent DLR station
- Royal Albert DLR station
- Royal Victoria DLR station
- Star Lane DLR station
- Stratford station – Abellio Greater Anglia, c2c, Elizabeth line, Jubilee and Central lines, London Overground and DLR
- Stratford High Street DLR station
- Stratford International station – Southeastern, DLR
- Pudding Mill Lane DLR station
- Upton Park tube station – District and Hammersmith & City lines
- Wanstead Park railway station – London Overground
- West Ham station – c2c, Jubilee, District and Hammersmith & City lines, and DLR
- West Silvertown DLR station
- Woodgrange Park railway station – London Overground
Travel to work
In March 2011, the main forms of transport that residents used to travel to work were: underground, metro, light rail, tram, 23.0% of all residents aged 16–74; driving a car or van, 7.6%; bus, minibus or coach, 7.6%; train, 7.2%; on foot, 4.1%; work mainly at or from home, 1.4%; bicycle, 1.0%.
River services
- Woolwich Ferry
- Royal Wharf
Cable car
- London Cable Car
International services
- Dutchflyer rail-sea service via Stratford station to the Netherlands
- London City Airport
- Stratford International station (No Eurostar trains stop)
Bus routes
Over 30 London Buses bus routes serve the London Borough of Newham, with main interchanges at Stratford, Stratford City and Beckton bus stations, with large bus interchanges also available at East Ham and Upton Park.
Town twinning
Newham is twinned with:
 Kaiserslautern, Germany
Kaiserslautern, Germany
Coat of arms
The borough adopted West Ham's coat of arms, but with a motto adapted from that of East Ham.
The arms include the following elements:
- The crosier signified the Cistercian Stratford Langthorne Abbey.
- The sword and the red and yellow chevronells are taken from the arms of William de Montfitchet, a major local landowner and founder of the abbey.
- The crossed hammers represent the Thames Ironworks and Shipbuilding Company, once a major local employer.
- The ship in full sail represents the maritime trades and the area's links to the sea.
- The arms also include a sun rising in the east.
The borough's motto, "Progress with the People" is an English translation of East Ham's Latin "Progressio cum Populo".
Freedom of the Borough
The following people and military units have received the Freedom of the Borough of Newham.
Individuals
- Sir Jack Petchey: 27 May 2010.
- Mark Noble: 15 December 2016.
Military Units
- G Company 7th Battalion The Rifles: 23 June 2012.
Notable people
See also
 In Spanish: Newham para niños
In Spanish: Newham para niños