Lockheed U-2 facts for kids
The U-2 (nicknamed the Dragon Lady) is an espionage fixed-wing aircraft made by Lockheed (now Lockheed Martin). It first flew in 1955 and was introduced in 1957. It flies a lot like a glider. It was made during the Cold War, because the United States needed a way to look at the Soviet military from high up. Taiwan also used it to spy on China.
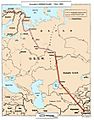
The United States wanted to keep the purpose of the U-2 secret, but on May 1, 1960, Francis Gary Powers was shot down in his U-2 by a Soviet SAM SA-2 missile. In 1962, Powers was released and traded for captured Soviet spy Rudolf Abel. After this, the SR-71 Blackbird started spying on the Soviet Union, which was faster and harder to see on radar.
The U-2 is still in service even though the design is over 50 years old.
U-2 details (U-2 model)
The U-2S is 62.99 feet (19.20 meters) long, 104.99 feet (32 meters wide), and is 15.75 feet (4.80 meters) tall. It weighs 14,991 pounds (6,800 kilograms) empty, but when full, it weighs 41,006 pounds (18,600 kilograms). It is powered by one General Electric F118-101 engine with 17,000 pounds (7711.2 kilograms) of thrust. It can go 475 miles per hour (764 kilometers per hour), fly 7,000 miles (11,265 kilometers) without refueling, and can fly upwards of 70,000 feet (21,336 meters), possibly as high as 84,974 feet (25,900 meters).
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Model "B" U-2 camera on display at the National Air and Space Museum
-
U-2 at the Imperial War Museum, Duxford
-
A pilot in a U-2 cockpit. Note the pressure suit worn by the pilot, similar to that used in the Lockheed SR-71.
-
U-2S with the Senior Span/Spur communications suite at Al Dhafra Air Base, United Arab Emirates, ca. 2017
-
Cockpit of a U-2S Block 20, at Osan Air Base, South Korea, circa June 2006
-
A Lockheed U-2F being refueled by a KC-135Q
See also
 In Spanish: Lockheed U-2 para niños
In Spanish: Lockheed U-2 para niños