Llŷn Peninsula facts for kids


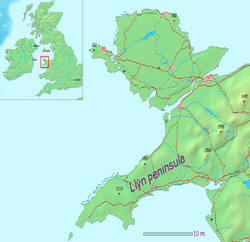
The Llŷn Peninsula (Welsh: Penrhyn Llŷn or Pen Llŷn) extends 30 miles (50 km) into the Irish Sea from North West Wales, south west of the Isle of Anglesey. It is part of the historic county of Caernarfonshire, and historic region and local authority area of Gwynedd. Much of the eastern part of the peninsula, around Criccieth, may be regarded as part of Eifionydd rather than Llŷn, although the boundary is somewhat vague. The area of Llŷn is about 400 km2 (150 sq miles), and its population is at least 20,000.
Historically, the peninsula was travelled by pilgrims en route to Bardsey Island (Welsh: Ynys Enlli), and its relative isolation has helped to conserve the Welsh language and culture, for which the locality is now famous. This perceived remoteness from urban life has lent the area an unspoilt image which has made Llŷn a popular destination for both tourists and holiday home owners. Holiday homes remain contentious among locals, many of whom are priced out of the housing market by incomers. From the 1970s to the 1990s, a group known as Meibion Glyndŵr claimed responsibility for several hundred arson attacks on holiday homes using incendiary devices, some of which took place in Llŷn.
The Llyn Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty covers c. 62 square miles.
Contents
Etymology
The name Llŷn is also sometimes spelled Lleyn, although this spelling is now less common and is generally considered to be an anglicisation. The name is thought to be of Irish origin, and to have the same root – Laigin (Laighin) in Irish – as the word Leinster and which also occurs in Porth Dinllaen on the north coast.
History
Following the death of Owain Whitetooth (Ddantgwyn), king of Gwynedd, Owain's son Saint Einion seems to have ruled Llŷn as a kingdom separate from his brother Cuneglas' kingdom in Rhos. He is credited with having sponsored Saint Cadfan's monastery on Bardsey Island, which became a major centre of pilgrimage during medieval times. There are numerous wells throughout the peninsula, many dating back to the pre-Christian era. Many have holy connotations and they were important stops for pilgrims heading to the island.
The most rural parts are characterised by small houses, cottages and individual farms, resembling parts of south west Ireland. There are small compact villages, built of traditional materials. The only large-scale industrial activities were quarrying and mining, which have now largely ceased. The granite quarries of northern Llŷn have left a legacy of inclines and export docks, and were the reason for the growth of villages such as Llithfaen and Trefor. Copper, zinc and lead were mined around Llanengan, while 196,770 long tons (199,930 t) of manganese were produced at Y Rhiw between 1894 and 1945. The Penrhyn Dû mines have also been extensively mined since the seventeenth century around Abersoch. Shipbuilding was important at Nefyn, Aberdaron, Abersoch and Llanaelhaearn, although the industry collapsed after the introduction of steel ships from 1880. Nefyn was also an important herring port, and most coastal communities fished for crab and lobster.
Farming was originally simple and organic, but underwent major changes after the Second World War as machines came into widespread use. Land was drained and fields expanded and reseeded. From the 1950s onwards, extensive use was made of artificial fertilizers, herbicides and pesticides, leading to drastic changes in the appearance of the landscape.
Tourism developed after the railway to Pwllheli was built in 1867. The town expanded rapidly, with several large houses and hotels constructed, and a tramway was built linking the town to Llanbedrog. After the Second World War, Butlins established a holiday camp at Penychain, which attracted visitors from the industrial cities of North West England and the West Midlands. As car ownership increased, the tourist industry spread to the countryside and to coastal villages such as Aberdaron, Abersoch, Llanbedrog and Nefyn, where many families supplemented their income by letting out rooms and houses.
Pwllheli was the administrative centre of Llŷn for over 700 years. It was a royal maerdref of the Kingdom of Gwynedd, and became a free borough following the English conquest. In the 18th and 19th centuries over 400 ships were built there.
Geography
Llŷn is an extensive plateau dominated by numerous volcanic hills and mountains. The largest of these is Yr Eifl, although Garn Boduan, Garn Fadrun and Mynydd Rhiw are also distinctive. Large stretches of the northern coast consist of steep cliffs and rugged rocks with offshore islands and stacks, while there are more extensive sandy beaches on the southern coast, such as Porth Neigwl and Castellmarch Beach. North of Abersoch a series of sand dunes have developed. The landscape is divided into a patchwork of fields, with the traditional field boundaries, stone walls, hedgerows and cloddiau, a prominent feature.
Geology
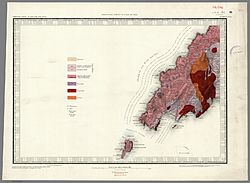
The geology of Llŷn is complex: the majority is formed from volcanic rocks of the Ordovician period. Rocks of Cambrian origin occur south of Abersoch. Numerous granite intrusions and outcrops of rhyolite form prominent hills such as Yr Eifl, whilst gabbro is found at the west end of Porth Neigwl. The western part of the peninsula (northwest of a line drawn from Nefyn to Aberdaron) is formed from Precambrian rocks, the majority of which are considered to form a part of the Monian Complex and thus to be closely related to the rocks of Anglesey. Numerous faults cut the area and a major shear zone - the Llyn Shear Zone - runs northeast to southwest through the Monian rocks. In 1984 there was an earthquake beneath the peninsula, which measured 5.4 on the Richter Scale and was felt in many parts of Ireland and western Britain.
The area was overrun by Irish Sea ice during the ice ages and this has left a legacy of boulder clay and of meltwater channels.
Protected sites
Llŷn is notable for its large number of protected sites, including a national nature reserve at Cors Geirch, a National Heritage Coastline and a European Marine Special Area of Conservation, and 20 Sites of Special Scientific Interest. The peninsula is home to a rare species of mason bee, found nowhere else. Much of the coastline and hills are part of the Llŷn Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. The Llŷn Coastal Path, a long distance footpath, enables walkers to fully explore both coasts of the peninsula.
Lleyn sheep
The peninsula is the original home of the Lleyn breed of sheep. This is a hardy and prolific breed that has become much more prominent over the last 20 years due to its excellent prolificacy and mothering ability. The sheep are white-faced; on average, ewes weigh about 70 kilograms (150 lb) and rams 90 kilograms (200 lb).
Welsh language
Until at least the 1960s a number of Welsh monoglots still lived in the Llŷn Peninsula. However, before 2001 there had been a decline in Welsh speakers in Gwynedd, which includes the Llŷn Peninsula. According to the 2001 census the number of Welsh speakers in Wales increased for the first time in over 100 years, with 20.5 per cent of a population of over 2.9 million claiming fluency in Welsh. The 2001 Census also showed that 73.1% of the population of Llŷn could speak Welsh. Additionally, 28 per cent of the population of Wales claimed to understand Welsh. However, the number of Welsh speakers declined in Gwynedd from 72.1 per cent in 1991 to 68.7 per cent in 2001. By 2003 however, a survey of schools showed that just over 94 per cent of children between the ages of 3 and 15 were able to speak Welsh, making Llŷn one of the foremost heartlands of the language, although, as in the rest of north west Wales, many people are concerned that the influx of English speakers is damaging the standing of Welsh and threatening its future as a living community language in the area. The Welsh Language and Heritage Centre of Nant Gwrtheyrn is situated on the north coast.
Tân yn Llŷn 1936
Concern for the Welsh language was ignited in 1936 when the United Kingdom government settled on establishing a bombing school at Penyberth on the peninsula. The events surrounding the protest became known as Tân yn Llŷn (Fire in Llŷn). The government had settled on Llŷn as the site for its new bombing school after similar locations in Northumberland and Dorset were met with protests. However, British Prime Minister Stanley Baldwin refused to hear the case against the bombing school in Wales, despite a deputation representing half a million Welsh protesters. Protest against the bombing school was summed up by Saunders Lewis when he wrote that the British government was intent upon turning one of the "essential homes of Welsh culture, idiom, and literature" into a place for promoting a barbaric method of warfare. On 8 September 1936 the bombing school building was set on fire by Saunders Lewis, Lewis Valentine and D.J. Williams, who immediately gave themselves up to the police and claimed responsibility. The trial at Caernarfon failed to agree on a verdict and the case was sent to the Old Bailey in London. The "Three" were sentenced to nine months imprisonment in Wormwood Scrubs, and on their release they were greeted as heroes by 15,000 people at a pavilion in Caernarfon.
Relationship with the property market
The decline in the use of the Welsh language in Llŷn has been attributed to a rise in property prices. Local Welsh speakers are increasingly unable to afford housing in the area as the rise in house prices has outpaced average earnings in Wales. On the other hand, there has been an influx of non-Welsh speakers purchasing properties for retirement or holiday homes. The issue of locals being priced out of the local housing market is common to many rural communities throughout Britain, but in Wales the added dimension of language further complicates the issue, as many new residents do not learn the Welsh language.
Governance
The whole of Llŷn is governed by Cyngor Gwynedd, a unitary authority established in 1996. The area had traditionally formed part of Caernarfonshire, for which an elected county council had been formed in 1889. Caernarfonshire was abolished in 1974 and incorporated into the new county of Gwynedd, which became a unitary authority under the 1996 reorganisation.
Llŷn Rural District, based in Pwllheli, was created under the Local Government Act 1894 from the area of Pwllheli Rural Sanitary District. At the time it covered 91,449 acres (370.08 km2) and consisted of 30 civil parishes, although the number was subsequently reduced. At the 1901 census it had a population of 16,816. Under a County Review Order in 1934, 18 parishes were abolished with their areas distributed among other parishes; a new parish of Buan was formed by the merger of Ceidio and Llanfihangel Bachellaeth; and the parish of Dolbenmaen was transferred from Glaslyn Rural District. Five years later, in 1939, Edern was abolished and incorporated into Nefyn. The rural district was abolished in 1974, with its area being included in the Dwyfor District of Gwynedd, which was itself abolished in 1996, when Gwynedd became a unitary authority. At the time of abolition, the rural district covered 114,232 acres (462.28 km2) and had a population at the 1971 census of 15,190.
Pwllheli Municipal Borough was the successor to a free borough which was granted a charter by Edward, the Black Prince in 1355. The corporation was abolished by the Municipal Corporations Act 1835, and replaced by an elected council, which existed until Pwllheli was included in Dwyfor in 1974, as a result of the Local Government Act 1972. At the 1841 census Pwllheli had a population of 2,367. By the time of abolition the borough covered 1,211 acres (4.90 km2) and had a population at the 1961 census of 3,647.
Criccieth Urban District was created under the Local Government Act 1894, and covered the area of the former borough, which had been abolished in 1886 by the Municipal Corporations Act 1883. The borough charter had been granted by Edward I in 1284. The urban district covered 472 acres (1.91 km2) and at the 1901 census had a population of 1,406. By the time of abolition and incorporation into Dwyfor in 1974, it covered 1,721 acres (6.96 km2), and had a population at the 1961 census of 1,672.
List of ancient parishes
| Image | Name | Period | Population 1961 |
Community | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Aberdaron | 1894 1974 |
1,161 | Aberdaron | |
 |
Abererch | 1894 1934 |
Llannor | ||
 |
Bardsey Island | 1894 1974 |
17 | Aberdaron | |
 |
Bodferin | 1894 1934 |
Aberdaron | ||
 |
Botwnnog | 1894 1974 |
1,176 | Botwnnog | |
 |
Bryncroes | 1894 1934 |
Aberdaron Botwnnog |
||
 |
Buan | 1934 1974 |
619 | Buan | |
 |
Carnguwch | 1894 1934 |
Pistyll | ||
 |
Ceidio | 1894 1934 |
Buan | ||
 |
Criccieth Urban District | 1894 1974 |
1,672 | Criccieth | |
 |
Dolbenmaen | 1934 1974 |
1,447 | Dolbenmaen | |
 |
Edern | 1894 1939 |
Nefyn | ||
 |
Llanaelhaearn | 1894 1974 |
1,242 | Llanaelhaearn | |
 |
Llanarmon | 1894 1934 |
Llanystumdwy | ||
 |
Llanbedrog | 1894 1974 |
883 | Llanbedrog | |
 |
Llandegwning | 1894 1934 |
Botwnnog | ||
 |
Llandudwen | 1894 1934 |
Buan Tudweiliog |
||
 |
Llanengan | 1894 1974 |
2,116 | Llanengan | |
 |
Llanfaelrhys | 1894 1934 |
Aberdaron | ||
 |
Llanfihangel Bachellaeth | 1894 1934 |
Buan | ||
 |
Llangian | 1894 1934 |
Botwnnog Llanengan |
||
 |
Llangwnnadl | 1894 1934 |
Aberdaron Tudweiliog |
||
 |
Llangybi | 1894 1934 |
Llannor Llanystumdwy |
||
 |
Llaniestyn | 1894 1934 |
Botwnnog Tudweiliog |
||
 |
Llannor | 1894 1974 |
2,039 | Llannor | |
 |
Llanystumdwy | 1894 1974 |
2,056 | Llanystumdwy | |
 |
Mellteyrn | 1894 1934 |
Botwnnog Tudweiliog |
||
 |
Nefyn | 1894 1974 |
2,164 | Nefyn | |
 |
Penllech | 1894 1934 |
Tudweiliog | ||
 |
Penllyn | 1894 1934 |
Criccieth Llanystumdwy |
||
 |
Penrhos | 1894 1934 |
Llannor | ||
 |
Pistyll | 1894 1974 |
599 | Pistyll | |
 |
Pwllheli Municipal Borough |
1835 1974 |
3,647 | Pwllheli | |
 |
Tudweiliog | 1894 1974 |
1,003 | Tudweiliog |
See also
 In Spanish: Península de Lleyn para niños
In Spanish: Península de Lleyn para niños