Least weasel facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Least weaselTemporal range: Late Pleistocene–Recent
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Least weasel at the British Wildlife Centre, Surrey, England | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Mustela
|
| Species: |
nivalis
|
 |
|
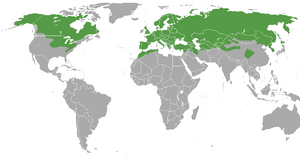
| Global range of M. nivalis | |
The least weasel (Mustela nivalis), is the smallest member of the genus Mustela. It is the smallest member of the family Mustelidae and order Carnivora. It is also called the little weasel, common weasel. It is native to Eurasia, North America and North Africa. It has been introduced to New Zealand, Malta, Crete, Bermuda, Madeira Island, the Azores, the Canary Islands, São Tomé, the Falkland Islands, Argentina and Chile. It is a least concern species.
Description
The least weasel has a thin, long and very flexible body. It has a small, long, head. The legs and tail are short. The feet have sharp, dark-coloured claws, and the bottom of the feet has lots of hairs. The least weasel moves by jumping.
Males have an average length of 130 to 260 mm (5 to 10 in) long. Females have an average length of 114 to 204 mm (4.5 to 8.0 in) long. Males weigh 36 to 250 g (1.3 to 8.8 oz). Females weigh 29 to 117 g (1.0 to 4.1 oz).
Breeding
The least weasel mates from April to July. The gestation period is 34 to 37 days. In the Northern Hemisphere, the least weasel usually give birth to 6 kits. The least weasel reach sexual maturity in 3 to 4 months.
The female takes care of its kits without help from the male. The kits are 1.5 to 4.5 g (0.05 to 0.16 oz) in weight. Newborn kits are born pink, naked, blind and deaf. They will have a white coat of downy fur at the age of 4 days. The milk teeth comes out at the age of 2 to 3 weeks. The young ones start to eat solid food at that time.
The eyes and ears open at the age of at 3 to 4 weeks. By 8 weeks they learn how to kill the animals that they eat. The young ones leave the family after 9 to 12 weeks. Least weasels can live for 7 or 8 years.
Feeding
The least weasel mostly feeds on rodents that look like mouse, including mice, hamsters, gerbils and others. It usually does not attack adult hamsters and rats. Frogs, fish, small birds and bird eggs are almost never eaten. It can attack adult pikas and gerbils. but usually cannot overcome brown rats and sousliks. Least weasels sometimes kill prey larger than themselves, such as capercaillie, hazel grouse and hares. In England, the least weasel likes to eat the field vole.
Despite its small size, the least weasel is a great hunter. It is able to kill a rabbit five to 10 times its own weight. Even though they are commonly eaten, the rabbits are usually young ones. Rabbits become an important source of food during the spring, when there are few small rodents and lots of rabbit kits.
Predators
The predators of the least weasel include red foxes, sables, steppe and forest polecat, stoats, eagle owls and buzzards. The owls are very efficient at catching least weasels. Some of the owls that hunt least weasels include barn owls, barred owls, and great horned owls. Other birds of prey that eat least weasel include broad-winged buzzards and rough-legged buzzards. Some types of snake may eat the least weasel. They include the black rat snake and the copperhead.
Distribution
The least weasel lives in Europe and North Africa, Asia and parts of northern North America. It mostly lives in places where there are no stoats. It has become extinct from New York. It has been introduced in New Zealand, Malta, Crete, the Azore Islands and also São Tomé off West Africa. It is found throughout Europe (but not Ireland). It is also found on many islands, including the Azores, Great Britain, and all major Mediterranean islands. It also lives in Honshu and Hokkaido Islands in Japan and on Kunashir, Iturup, and Sakhalin Islands in Russia.
It can be found in fields, open woodland, bushy or rocky places, parks and gardens. It can be found at altitudes of up to about 3,000 metres (9,800 ft).
Images for kids
-
Least weasel at the British Wildlife Centre
-
Skulls of a long-tailed weasel (top), a stoat (bottom left) and least weasel (bottom right), as illustrated in Merriam's Synopsis of the Weasels of North America
-
Skeleton, as illustrated in Lydekker's The New Natural History
-
Taxidermy exhibit showing a least weasel attacking a European hare, in the Natural History Museum of Genoa
-
Least weasels driven from a mountain hare carcass by a stoat, as illustrated in Barrett-Hamilton's A History of British Mammals
-
17th century print of a least weasel confronting a basilisk
See also
 In Spanish: Comadreja para niños
In Spanish: Comadreja para niños