Lake Wairarapa facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Lake Wairarapa |
|
|---|---|

Western shore looking South
|
|
| Location | South Wairarapa District, Wellington Region, North Island |
| Coordinates | 41°13′S 175°15′E / 41.217°S 175.250°E |
| Primary inflows | Ruamahanga |
| Primary outflows | Ruamahanga |
| Basin countries | New Zealand |
| Surface area | 78 km2 (30 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in) |
| Settlements | Featherston |
| Official name: Wairarapa Moana Wetland | |
| Designated: | 20 August 2020 |
| Reference #: | 2432 |
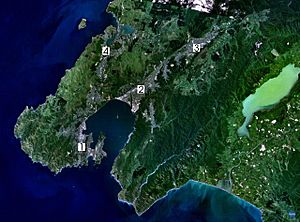
Lake Wairarapa is a lake at the southern end of the North Island of New Zealand, 50 kilometres (31 mi) east of Wellington. The lake covers an area of 78 km2 (30 sq mi), and at its deepest is 2.5 m (8.2 ft). The lake is the third largest in the North Island, fractionally smaller than Lake Rotorua. The nearest town to the lake is Featherston, which is located five kilometres from its northern shore. The lake forms part of the Wairarapa Moana Wetlands Park.
The lake's catchment area is large, and includes the eastern slopes of the Remutaka and Tararua Ranges. The lake takes water from several rivers and was originally the main outflow for the Ruamahanga. This in turn drained slowly into Palliser Bay and Cook Strait ten kilometres south near the settlement of Lake Ferry, via what is now Lake Onoke. The river, however, was diverted in the 1960s to assist flow, thereby reducing flooding for farmers. The lake today therefore covers an area significantly smaller than its historical size of around 210 km2 (81 sq mi).
The area around the lake is low-lying and swampy, and recent efforts have been made to preserve its important wetland features and restore wildlife habitat that has been degraded through human use. Agriculture and river development, flood control, and waterway diversions have resulted in the drainage of large areas of the wetlands, reducing their ecological values.
Lake Wairarapa is classed as supertrophic on the trophic level index, meaning that it is highly polluted with nitrates which leach from intensified agriculture surrounding the lake. This is in line with the wider trend of agriculture polluting New Zealand rivers and lakes.
The lake has long been used by Māori as a source of readily available food, and many species of waterfowl and fish uncommon elsewhere in New Zealand can be found in or around the lake.