Kenneth Stewart Cole facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Kenneth Stewart Cole
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Born | July 10, 1900 |
| Died | April 18, 1984 (aged 83) |
| Alma mater | Oberlin College Cornell University |
| Known for | Cole–Cole equation Voltage clamp |
| Spouse(s) | Elizabeth Evans Roberts |
| Children | 2 |
| Awards | ForMemRS (1972) National Medal of Science (1967) Guggenheim Fellowship (1941) |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Biophysics |
Kenneth Stewart Cole (July 10, 1900 – April 18, 1984) was an American biophysicist described by his peers as "a pioneer in the application of physical science to biology". Cole was awarded the National Medal of Science in 1967.
Biography
He was born on July 10, 1900, in Ithaca, New York, to Charles Nelson Cole, an instructor in Latin at Cornell University and Mabel Stewart. Kenneth had a younger brother, Robert H. Cole, with whom he remained very close throughout his life despite a large difference in age; they were joint authors of four papers published between 1936 and 1942.
In 1902 the family moved to Oberlin, Ohio, when his father took a post at Oberlin College. His father would later become the Dean. Kenneth's mother was, and Cole graduated from Oberlin College in 1922 and received a Ph.D. in physics with Floyd K. Richtmyer from Cornell University in 1926. He spent summers working at the General Electric laboratory in Schenectady, New York.
In 1932, Cole married Elizabeth Evans Roberts, an attorney. Later, her work was mostly concerned with civil rights and in 1957 she joined the staff of the United States Commission on Civil Rights
Kenneth joined the staff of Columbia University in 1937 and remained there until 1946. He had also been associated with the Presbyterian Hospital, and the Guggenheim Foundation for Advanced Study at Princeton University and the University of Chicago.
From 1949 to 1954 he was the technical director of the Naval Medicine Research Institute in Bethesda, Maryland. In 1954 he became chief of the laboratory of biophysics of the National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Blindness.
He achieved advances that led to the "sodium theory" of nerve transmission that later won Nobel Prizes for Alan L. Hodgkin and Andrew F. Huxley in 1963. Cole was elected a Fellow of the American Physical Society in 1931, a member of the National Academy of Sciences in 1956, and a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1964. He was awarded the National Medal of Science in 1967, the award citation, read: "As a result, we know far more about how the nervous system functions." In 1972 he was made a member of the Royal Society of London. The Biophysical Society awards the Kenneth S. Cole medal to a scientist studying cell membranes.
In 1980 he became an adjunct professor of the Department of Neurosciences at the Scripps Institute of Oceanography in San Diego. He had a son, Roger Braley Cole, and a daughter, Sarah Roberts Cole.
He died on April 18, 1984, in La Jolla, California.
Electrical Model of Tissue
Tissue can be modeled as an electrical circuit with resistive and capacitive properties:
Its dispersion and absorption are represented by the empirical formula:

In this equation 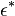 is the complex dielectric constant,
is the complex dielectric constant,  and
and 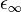 are the "static" and "infinite frequency" dielectric constants,
are the "static" and "infinite frequency" dielectric constants,  times the frequency, and
times the frequency, and 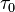 is a generalized relaxation time. The parameter
is a generalized relaxation time. The parameter 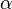 can assume values between 0 and 1, the former value giving the result of Debye for polar dielectrics. This expression requires that the locus of the dielectric constant in the complex plane be a circular arc with end points on the axis of reals and center below the axis.
can assume values between 0 and 1, the former value giving the result of Debye for polar dielectrics. This expression requires that the locus of the dielectric constant in the complex plane be a circular arc with end points on the axis of reals and center below the axis.
It is worth emphasizing that the Cole–Cole model is an empirical model of the measured data. It has been successfully applied to a wide variety of tissues over the past 60 years, but it does not give any information about the underlying causes of the phenomena being measured.
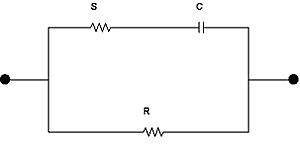
Several references in the literature use a form of the Cole equation written in terms of impedance instead of a complex permittivity. The impedance 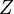 is given by:
is given by:
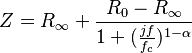
Where  and
and 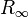 are the resistances at zero frequency (i.e. DC) and infinity, respectively.
are the resistances at zero frequency (i.e. DC) and infinity, respectively. 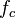 is often referred to as the characteristic frequency. The characteristic frequency is not the same when the analysis is carried out in terms of the complex permittivity. A simple interpretation of the above equation is in terms of a circuit where a resistance
is often referred to as the characteristic frequency. The characteristic frequency is not the same when the analysis is carried out in terms of the complex permittivity. A simple interpretation of the above equation is in terms of a circuit where a resistance 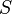 is in series with a capacitor
is in series with a capacitor 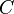 and this combination is placed in parallel with a resistance
and this combination is placed in parallel with a resistance 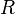 . In this case
. In this case  and
and  . It can be shown that
. It can be shown that 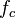 is given by
is given by 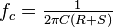 .
.
Electrical measurements of tissues
In a series of papers in 1930s -- 1940s, he experimentally studied the electric properties of living tissues, such as Nitella, frog eggs, and most famously, the squid giant axon.
Figure 4 of is sometimes used as artistic representations of biophysics. It also appeared, rotated 90 degrees, in Swedish apartments as modern art.
See also
- Action potential
- Cable theory
- Dendrite