Jackal facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Jackal |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Golden jackal (Canis aureus) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Caniformia |
| Family: | Canidae |
| Subfamily: | Caninae |
| Tribe: | Canini |
| Subtribe: | Canina |
| Species referred to as jackals | |
 |
|
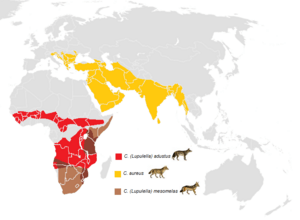
Jackals are medium-sized omnivorous mammals of the subtribe Canina, which also includes wolves and the domestic dog, among other species. While the word "jackal" has historically been used for many small canines, in modern use it most commonly refers to three species: the closely related black-backed jackal (Lupulella mesomelas) and side-striped jackal (Lupulella adusta) of sub-Saharan-Africa, and the golden jackal (Canis aureus) of south-central Europe and Asia.
Jackals are opportunistic omnivores, predators of small to medium-sized animals and proficient scavengers. Their long legs and curved canine teeth are adapted for hunting small mammals, birds, and reptiles, and their large feet and fused leg bones give them a physique well-suited for long-distance running, capable of maintaining speeds of 16 km/h (10 mph) for extended periods of time. Jackals are crepuscular, most active at dawn and dusk.
Their most common social unit is a monogamous pair, which defends its territory from other pairs by vigorously chasing intruding rivals and marking landmarks around the territory with their urine and feces. The territory may be large enough to hold some young adults, which stay with their parents until they establish their own territories. Jackals may occasionally assemble in small packs, for example, to scavenge a carcass, but they normally hunt either alone or in pairs.
Etymology
The English word "jackal" dates back to 1600 and derives from the French chacal, derived from the Persian شغال shoghāl, which is in turn derived from the Sanskrit शृगाल śṛgāla meaning "the howler".
Taxonomy and relationships
| The extant wolf-like canids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phylogenetic relationships between the extant wolf-like clade of canids based on mitochondrial DNA. |
Similarities between jackals and coyotes led Lorenz Oken, in the third volume of his Lehrbuch der Naturgeschichte (1815), to place these species into a new separate genus, Thos, named after the classical Greek word θώς "jackal", but his theory had little immediate impact on taxonomy at the time. Angel Cabrera, in his 1932 monograph on the mammals of Morocco, questioned whether or not the presence of a cingulum on the upper molars of the jackals and its corresponding absence in the rest of Canis could justify a subdivision of that genus. In practice, Cabrera chose the undivided-genus alternative and referred to the jackals as Canis instead of Thos.
Oken's Thos theory was revived in 1914 by Edmund Heller, who embraced the separate genus theory. Heller's names and the designations he gave to various jackal species and subspecies live on in current taxonomy, although the genus has been changed from Thos to Canis.
The wolf-like canids are a group of large carnivores that are genetically closely related because they all have 78 chromosomes. The group includes genus Canis, Cuon, and Lycaon. The members are the dog (C. lupus familiaris), gray wolf (C. lupus), coyote (C. latrans), golden jackal (C. aureus), Ethiopian wolf (C. simensis), black-backed jackal (C. mesomelas), side-striped jackal (C. adustus), dhole (Cuon alpinus), and African wild dog (Lycaon pictus). The latest recognized member is the African golden wolf (C. anthus), which was once thought to be an African branch of the golden jackal. As they possess 78 chromosomes, all members of the genus Canis are karyologically indistinguishable from each other, and from the dhole and the African hunting dog. The two African jackals are shown to be the most basal members of this clade, indicating the clade's origin from Africa. Canis arnensis arrived in Mediterranean Europe 1.9 million years ago and is probably the ancestor of modern jackals.
The paraphyletic nature of Canis with respect to Lycaon and Cuon has led to suggestions that the two African jackals should be assigned to different genera, Schaeffia for the side-striped jackal and Lupulella for the black-backed jackal or Lupulella for both.
The intermediate size and shape of the Ethiopian wolf has at times led it to be regarded as a jackal, thus it has also been called the "red jackal" or the "Simien jackal".
Species
| Species | Binomial authority | Description | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black-backed jackal Lupulella mesomelas |
Schreber, 1775 | The most lightly built jackal, once considered to be the oldest living member of the genus Canis, it is now placed in the genus Lupulella. It is the most aggressive of the jackals, being known to attack animal prey many times its own weight, and it has more quarrelsome intrapack relationships. | Southern Africa and eastern coast of Kenya, Somalia, and Ethiopia |
| Side-striped jackal Lupulella adustus  |
Sundevall, 1847 | It primarily resides in wooded areas, unlike other jackal species. It is the least aggressive of the jackals, rarely preying on large mammals. | Central and southern Africa |
| Golden jackal Canis aureus  |
Linnaeus, 1758 | The largest and most widespread of the jackals, it is more closely related to wolves than to African jackal species. | Southeastern Europe, Middle East, western Asia, and South Asia |
Folklore and literature
Like foxes and coyotes, jackals are often depicted as clever sorcerers in the myths and legends of their regions. They are mentioned roughly 14 times in the Bible. It is frequently used as a literary device to illustrate desolation, loneliness, and abandonment, with reference to its habit of living in the ruins of former cities and other areas abandoned by humans. It is called "wild dog" in several translations of the Bible. In the King James Bible, Isaiah 13:21 refers to 'doleful creatures', which some commentators suggest are either jackals or hyenas.
In the Indian Panchatantra stories, the jackal is mentioned as wily and wise. In Bengali tantrik tradition, they represent the goddess Kali. It is said she appears as jackals when meat is offered to her.
The Serer religion and creation myth posits jackals were among the first animals created by Roog, the supreme deity of the Serer people.
See also
 In Spanish: Chacal para niños
In Spanish: Chacal para niños




