Italian Campaign (World War I) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Italian Front |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of World War I | |||||||
 From left to right: Ortles, autumn 1917; Fort Verena, June 1915; Mount Paterno, 1915; Carso, 1917; Toblach, 1915. |
|||||||
|
|||||||
The Italian Front ("Mountain war") was a series of battles at the border between Austria-Hungary and Italy, fought between 1915 and 1918 in World War I. Following the secret promises made by the Allies in the Treaty of London, Italy entered the war in order to annex the Austrian Littoral and northern Dalmatia, and the territories of present-day Trentino and South Tyrol.
Although Italy had hoped to gain the territories with a surprise offensive, the front soon bogged down into trench warfare, similar to the Western Front fought in France, but at high altitudes and with very cold winters. Fighting along the front displaced much of the civilian population, of which several thousand died from malnutrition and illness in Italian and Austrian refugee camps. The Allied victory at Vittorio Veneto and the disintegration of Austria-Hungary ended the military operations.
Tunnel warfare in the mountains

From 1915, the high peaks of the Dolomites range were an area of fierce mountain warfare. In order to protect their soldiers from enemy fire and the hostile alpine environment, both Austro-Hungarian and Italian military engineers constructed fighting tunnels which offered a degree of cover and allowed better logistics support. Working at high altitudes in the hard carbonate rock of the Dolomites, often in exposed areas near mountain peaks and even in glacial ice, required extreme skill of both Austro-Hungarian and Italian miners.
Beginning on the 13th, later referred to as White Friday, December 1916 would see 10,000 soldiers on both sides killed by avalanches in the Dolomites.
In addition to building underground shelters and covered supply routes for their soldiers like the Italian Strada delle 52 Gallerie, both sides also attempted to break the stalemate of trench warfare by tunneling under no man's land and placing explosive charges beneath the enemy's positions. Between 1 January 1916 and 13 March 1918, Austro-Hungarian and Italian units fired a total of 34 mines in this theatre of the war.
The war ends
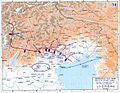
By October 1918, Italy finally had enough soldiers to mount an offensive. The attack targeted Vittorio Veneto, across the Piave. The Italian Army broke through a gap near Sacile and poured in reinforcements that crushed the Austrian defensive line. On 3 November, 300,000 Austrian soldiers surrendered.
On 3 November, the military leaders of the already disintegrated Austria-Hungary sent a flag of truce to the Italian commander to ask again for an armistice and terms of peace. The terms were arranged by telegraph with the Allied authorities in Paris, communicated to the Austrian commander, and were accepted. The Armistice with Austria was signed in the Villa Giusti, near Padua, on 3 November, and took effect at three o'clock in the afternoon of 4 November. Austria and Hungary signed separate armistices following the overthrow of the Habsburg Monarchy and the collapse of the Austro-Hungarian Empire.
Cumulative casualties of the numerous battles of the Isonzo were enormous. Half of the entire Italian war casualty total – some 300,000 of 600,000 – were suffered along the Soča (Isonzo). Austro-Hungarian losses, while by no means as numerous were nevertheless high at around 400,000 (of an overall total of around 1.2 million casualties).
Images for kids
-
A pro-war demonstration in Bologna, 1914.
-
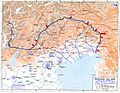
The Italian front in 1918 and the Battle of Vittorio Veneto.
-
Italian troops landing in Trieste, 3 November 1918
See also
 In Spanish: Frente italiano (Primera Guerra Mundial) para niños
In Spanish: Frente italiano (Primera Guerra Mundial) para niños