Irish Potato Famine facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Great Faminean Gorta Mór |
|
|---|---|

Scene at Skibbereen during the Great Famine, by Cork artist James Mahony (1810–1879), commissioned by The Illustrated London News, 1847.
|
|
| Country | United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland |
| Location | Ireland |
| Period | 1845–1852 |
| Total deaths | 1 million |
| Observations | Policy failure, potato blight, Corn Laws |
| Relief | see below |
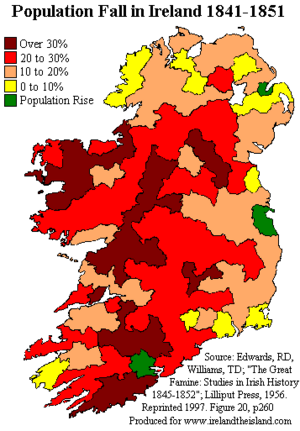
| Impact on demographics | Population fell by 20–25% due to mortality and emigration |
| Consequences | Permanent change in the country's demographic, political and cultural landscape |
| Website | See List of memorials to the Great Famine |
| Preceded by | Irish Famine (1740–41) (Bliain an Áir) |
| Succeeded by | Irish Famine, 1879 (An Gorta Beag) |
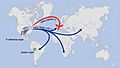
The Great Famine, also known as the Great Hunger (Irish: an Gorta Mór), the Famine and the Irish Potato Famine, was a period of mass starvation in Ireland lasting from 1845 to 1852. The population of Ireland on the eve of the famine was about 8.5 million, by 1901 it was just 4.4 million. During the Great Hunger, roughly 1 million people died and more than 1 million more fled the country, causing the country's population to fall by 20–25% (in some towns, populations fell as much as 67%) between 1841 and 1871. Between 1845 and 1855, at least 2.1 million people left Ireland, primarily on packet ships but also on steamboats and barques—one of the greatest exoduses from a single island in history.
For both the native Irish and those in the resulting diaspora, the famine entered folk memory.
Contents
Causes
The cause of the famine was the infection of potato crops by blight (Phytophthora infestans) throughout Europe during the 1840s. Experts are still unsure of how and when blight arrived in Europe; it almost certainly was not present prior to 1842, and probably arrived in 1844. The origin of the pathogen has been traced to the Toluca Valley in Mexico, whence it spread within North America and then to Europe. By mid-August 1845, it had reached much of northern and central Europe; Belgium, The Netherlands, northern France, and southern England had all already been affected.
In 1846, three-quarters of the Irish harvest was lost to blight. Seed potatoes were scarce in 1847. Few had been sown, so, despite average yields, hunger continued. 1848 yields were only two-thirds of normal. Since over three million Irish people were totally dependent on potatoes for food, hunger and famine were widespread.
The historian Cecil Woodham-Smith wrote in The Great Hunger: Ireland 1845–1849 that no issue has provoked so much anger and embittered relations between England and Ireland "as the indisputable fact that huge quantities of food were exported from Ireland to England throughout the period when the people of Ireland were dying of starvation".
Death toll
It is not known exactly how many people died during the period of the famine, although it is believed that more died from disease than from starvation. State registration of births, marriages, or deaths had not yet begun, and records kept by the Catholic Church are incomplete. A census taken in 1841 recorded a population of 8,175,124. A census immediately after the famine in 1851 counted 6,552,385, a drop of over 1.5 million in 10 years. The census commissioners estimated that, at the normal rate of population increase, the population in 1851 should have grown to just over 9 million if the famine had not occurred.
The greatest mortality was not from nutritional deficiency diseases, but from famine-induced ailments. The malnourished are very vulnerable to infections; therefore, these were more severe when they occurred. Measles, diphtheria, diarrhoea, tuberculosis, most respiratory infections, whooping cough, many intestinal parasites, and cholera were all strongly conditioned by nutritional status. Potentially lethal diseases, such as smallpox and influenza, were so virulent that their spread was independent of nutrition. The best example of this phenomenon was fever, which exacted the greatest death toll. In the popular mind, as well as medical opinion, fever and famine were closely related. Social dislocation—the congregation of the hungry at soup kitchens, food depots, and overcrowded workhouses—created conditions that were ideal for spreading infectious diseases such as typhus, typhoid, and relapsing fever.
Memorials
Ireland's National Famine Memorial is situated in Murrisk Millennium Peace Park, a five-acre park overlooking the Atlantic Ocean in the village of Murrisk, County Mayo at the foot of Croagh Patrick mountain.
The National Famine Commemoration Day is observed annually in Ireland, usually on a Sunday in May.
It is also memorialized in many locations throughout Ireland, especially in those regions of Ireland which suffered the greatest losses, and it is also memorialized overseas, particularly in cities with large populations which are descended from Irish immigrants, such as New York City. Among the memorials in the US is the Irish Hunger Memorial near a section of the Manhattan waterfront.
Kindred Spirits, a large stainless steel sculpture of nine eagle feathers by artist Alex Pentek was erected in 2017 in the Irish town of Midleton, County Cork, to thank the Choctaw people for its financial assistance during the famine.
An annual Great Famine walk from Doolough to Louisburgh, County Mayo was inaugurated in 1988 and has been led by such notable personalities as Archbishop Desmond Tutu of South Africa and representatives of the Choctaw nation of Oklahoma. The walk, organised by Afri, takes place on the first or second Saturday of May and links the memory of the famine with contemporary human rights issues.
Images for kids
-
A potato infected with late blight, showing typical rot symptoms
-
A starving Irish family from Carraroe, County Galway, during the Great Famine (National Library of Ireland)
-
Scene at the gate of the workhouse, c. 1846
-
Lord Palmerston, then British Foreign Secretary, evicted some 2,000 of his tenants.
-
The Emigrants' Farewell, engraving by Henry Doyle (1827–1893), from Mary Frances Cusack's Illustrated History of Ireland, 1868
See also
 In Spanish: Gran hambruna irlandesa para niños
In Spanish: Gran hambruna irlandesa para niños