Inverter facts for kids
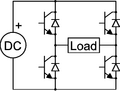
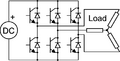
An inverter is an electric apparatus that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). It is not the same thing as an alternator, which converts mechanical energy (e.g. movement) into alternating current.
Direct current is created by devices such as batteries and solar panels. When connected, an inverter allows these devices to provide electric power for small household devices. The inverter does this through a complex process of electrical adjustment. From this process, AC electric power is produced. This form of electricity can be used to power an electric light, a microwave oven, or some other electric machine.
An inverter usually also increases the voltage. In order to increase the voltage, the current must be decreased, so an inverter will use a lot of current on the DC side when only a small amount is being used on the AC side.
Inverters are made in many different sizes. They can be as small as 150 watts, or as large as 1 megawatt (1 million watts).
Types
- Sine wave inverters produce good-quality AC power. They are expensive.
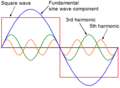
- A modified sine wave inverter produces a lower quality of AC power, with strong power system harmonics but is cheaper. Various modulation strategies are used in cascaded multilevel inverters to reduce the harmonic contents.
Images for kids
-
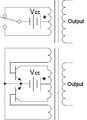
Top: Simple inverter circuit shown with an electromechanical switch and automatic equivalent auto-switching device implemented with two transistors and split winding auto-transformer in place of the mechanical switch.
See also
 In Spanish: Inversor (electrónica) para niños
In Spanish: Inversor (electrónica) para niños