Image: Vaccines-08-00587-g002-A
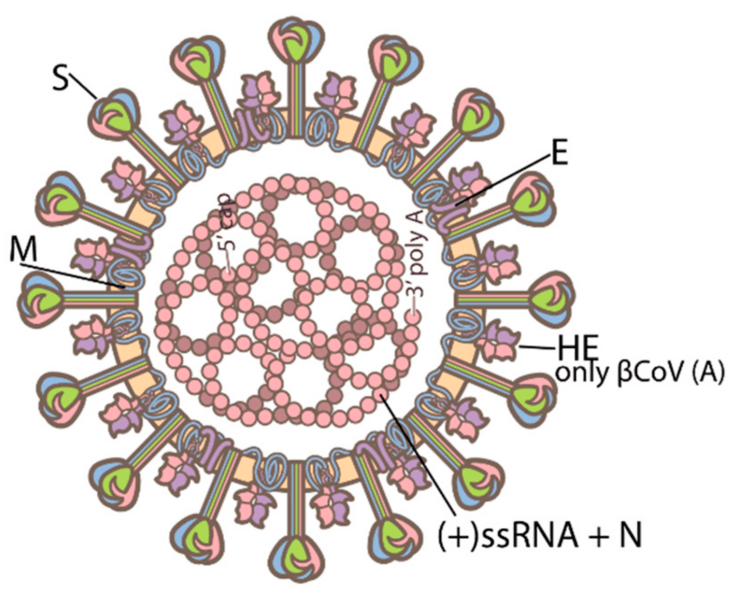
Description: Schematic structures of a coronavirus (CoV) and its spike protein. (a) The CoV is a pleomorphic spherical enveloped particle. It contains a linear positive-sense, single-stranded RNA (+ssRNA) with a 5′ cap and a 3′ poly(A) tail that are enclosed by nucleocapsid (N) proteins. The lipid bilayer envelope carries 3–4 structural proteins. (i) Membrane (M) proteins are the most abundant small triple-spanning transmembrane proteins that define the virion morphology and are major coordinators of virion assembly . (ii) Envelope (E) proteins are minor channel-spanning transmembrane proteins that work together with the M proteins for virion assembly, budding and release. (iii) Spike (S) proteins are homotrimeric type I transmembrane glycoproteins protruding from the virion envelope (20 nm in length) that resemble a crown (Latin: corona) under an electron microscope. S proteins are major antigenic surface proteins and are critical for virion entry into a specific host cell by binding to a specific receptor(s) on the host cell surface and mediating membrane fusion. (iv) The members of βCoV lineage A have additional short hemagglutinin esterase (HE) spikes (5 nm in length), which are homodimeric type I transmembrane glycoproteins. CoV HE has the potential to evolve its O-Ac-Sia receptor-binding specificity and activity, along with its companion S proteins, in balance with its receptor-destroying sialate O-acetylesterase activity for efficient virus infection and spread.
Title: Vaccines-08-00587-g002-A
Credit: Sriwilaijaroen, N.; Suzuki, Y. Host Receptors of Influenza Viruses and Coronaviruses—Molecular Mechanisms of Recognition. Vaccines 2020, 8, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8040587
Author: Nongluk Sriwilaijaroen and Yasuo Suzuki
Usage Terms: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0
License: CC BY 4.0
License Link: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0
Attribution Required?: Yes
Image usage
The following page links to this image:

