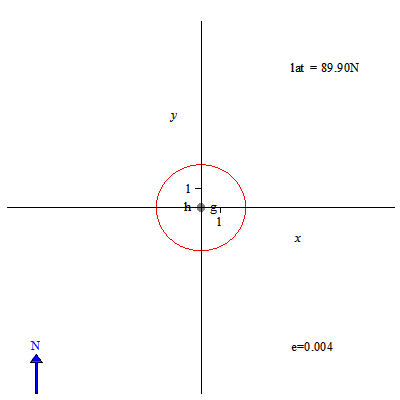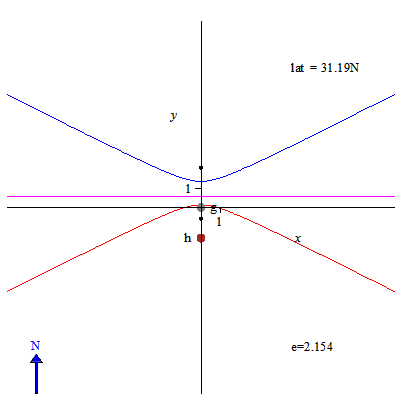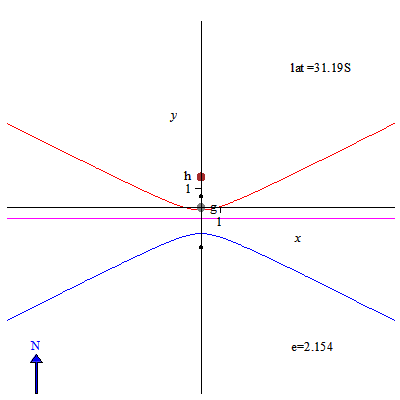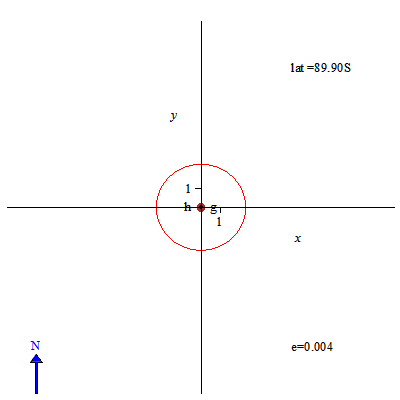
Image: Sundial solstice declination lines for different latitudes - slow
Description: Gnomon height is 1, its base point is denoted by g. The tip of the gnomon during a day casts a shadow along a declination line. Here the declination line at winter solstice is in blue, and the declination at summer solstice is in red, while the declination line at equinox is in magenta. North is up. Eccentricity of the declination line is denoted by e. Latitude of the point on the Earth where the gnomon is located is denoted by lat. The origin of corresponding horizontal sundial is denoted by h.Two small black dots are foci of declination lines. To obtain the equation for declination lines I used the approach attributed to Apollonius of Perga: the double cone formed by lines from the tip of the gnomon to positions of the Sun at each day of the year, is cut by the plane of the ground. For hyperbolas I verified the equation using a formula from this book. Using this approach, for eccentricity we get a very simple formula: e=cos(latitude)/sin(Sun's declination).So, on the equator eccentricity of solstice lines is the highest, approx. 2.52.
Title: Sundial solstice declination lines for different latitudes - slow
Credit: Own work
Author: Cmapm
Usage Terms: Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0
License: CC BY-SA 3.0
License Link: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0
Attribution Required?: Yes
Image usage
The following page links to this image: