Image: Fimmu-09-01581-g004
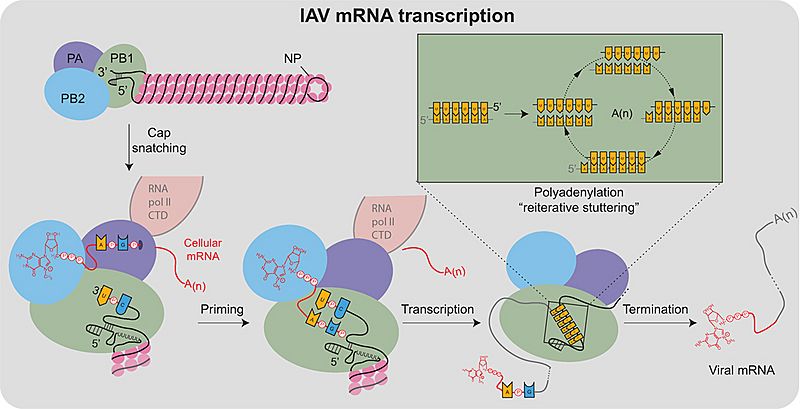
Description: Transcription of IAV mRNAs by the viral polymerase. Viral mRNA transcription occurs when the viral ribonucleoproteins reach the host cell nucleus and is assisted by the association of the viral polymerase (PA subunit) with the cellular RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain (RNA pol II CTD). Transcription initiates by a “cap-snatching” mechanism where the PB2 subunit binds to the 5′ cap of a host mRNA (red). Cap binding positions the region of the mRNA 10–13 nucleotides downstream for cleavage by the endonuclease domain in the PA subunit. Following cleavage, a conformational shift repositions the acquired mRNA capped primer to the PB1 subunit where the 3′ end base-pairs with a complimentary sequence at the vRNA 3′ end. Following the priming event, the viral polymerase extends the mRNA transcript. The transcription is terminated by a “reiterative stuttering” process (depicted in the box), which occurs when the polymerase encounters the 5–7 consecutive uracil bases at the vRNA 5′ end. The “reiterative stuttering” function likely involves multiple cycles of dissociation and reannealing, and effectively polyadenylates [A(n)] the viral mRNA by continuously repositioning the elongating 3′ end on the uracil-rich region of the vRNA template.
Title: Fimmu-09-01581-g004
Credit: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01581/full
Author: Dan Dou, Rebecca Revol, Henrik Östbye, Hao Wang, and Robert Daniels
Usage Terms: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0
License: CC BY 4.0
License Link: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0
Attribution Required?: Yes
Image usage
The following page links to this image:

