Image: Archaeoceti geological ages 02
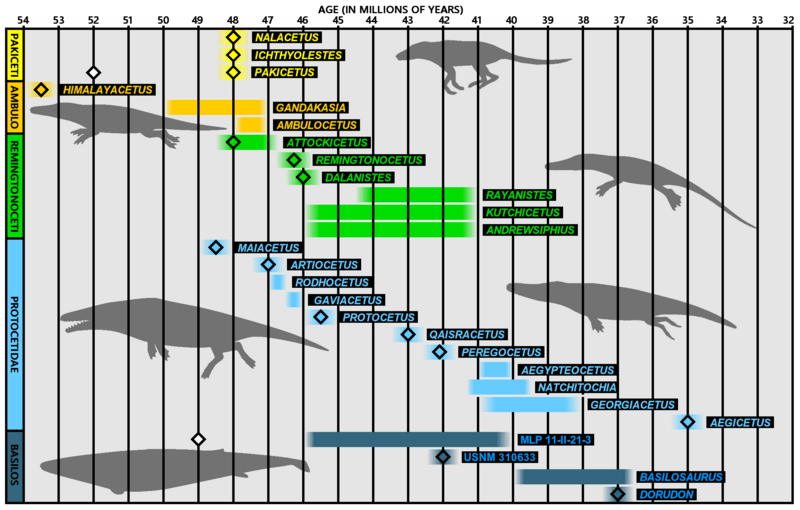
Description: Diagram showing geological ages of different Archaeocetei genera. Coloured diamonds represent absolute dates, coloured lines indicate the geological age is less certain. White diamonds (see Pakicetus and the basilosaur specinen MLP 11-II-21-3) represent previously proposed dates which subsequently have been considered inaccurate. Body silhouettes showed in diagram represent Pakicetus, Ambulocetus, Qaisracetus, Aegicetus and Dorudon. Pakicetidae are primarily found in the lower Kuldana Formation,[1] but have also been found further up, with some species of Pakicetus overlapping the geological range of the remingtonocetid Attockicetus.[2] Pakicetus was previously dated to 52 million years,[3] but have subsequently been dated to 48 million years.[4] Ichthyolestes is contemporaneous to Pakicetus.[2] Nalacetus is contemporaneous to Pakicetus.[2] Ambulocetidae is estimated to have lived about 52-49 million years ago.[5] Himalayacetus is dated to 53.5 million years.[4] Gandakasia stems from a layer below the remains of Ambulocetus.[2] Ambulocetus is dated to 48-47 million years.[6] Remingtonocetidae is dated to 49-43 million years ago.[5] Dalanistes dates to 46.5-46 million years ago.[7] Remingtonocetus dates to 46.5-46 million years ago.[7] Kutchicetus dates to 46-43 million years ago.[5] fossil remains stem from Harudi Formation in India, considered to be from the Lutetian, about 46-42 million years (or possibly 43-41 million years).[8] Andrewsiphius fossil remains stem from Harudi Formation in India, considered to be from the Lutetian, about 6-42 million years (or possibly 43-41 million years).[8] Attockicetus fossil range in Kuldana Formation overlap with late Pakicetus and precede as well as exceed that of Ambulocetus.[2] Rayanistes[9] Protocetidae consist of several genera spanning the Middle Eocene, roughly 49-37 million years ago.[10]Aegicetus expand the ending date to 35 million years ago. Maiacetus is the oldest protocetid, dated to 47.5 million years.[10] Artiocetus 47 million years.[6] Rodhocetus 47-46.5 million years.[11][6] Tacracetus 46.5-46 million years[7] (not included in the diagram). Gaviacetus 46.5-46 million years.[7] Protocetus 46-45 million years.[11] Qaisracetus have been given a date of 43 million years.[12] Peregocetus 42.6 million years.[13] Natchitochia are known from fossils dug up in Louisiana, USA. The holotype fossil (USNM 16805) was found in Milams members layers of Cook Mountain Formation[14] (dated to Early Bartonian).[15] The Milams members layers is believed to have been laid down 41.3-39.5 million years ago.[16] The specimen MMNS VP-48-49 was found in the lowest part of the Milams (Archusa Marl member).[17] This would give it a date of about 41 millon years. Aegypteocetus is dated to 41-40 million years[18] Georgiacetus has been given dates of 41-40 million years[19] or 41-38 million years.[5] Aegicetus is the protocetid with the most recent date of 35 million years.[20] Basilosauridae have been dated to 40-34 million years,[10] with the Priabonian Cynthiacetus and Saghacetus as the most recent genera.[21] An isolated jawbone (MLP 11-II-21-3) found at Seymour Island (Antarctica) in 2011 could potentially push back the temporal rage of the family.[22] MLP 11-II-21-3 is a specimen consisting of a single jawbone found in Antarctica. It was first said to be 49 million years,[23] but it has been difficult to decide an age of the rocks in which it was found.[22] In 2019, it was given an age of 46-40 million years.[24] USNM 310633 (dated to 42 million years)[25] was originally described as a protocetid and named Eocetus wardii by Mark Uhen 1999.[26]It was re-classified in 2013 to a new genus of basilosaurid, Basilotritus,[27] and subsequently to Pachycetus[28] Dorudon 37 million years.[6] Basilosaurus fossils have been assigned to the Priabonian and Bartonian stages of Eocene, 40-37 million years ago.[6][29] References ↑ [1] ↑ a b c d e [2] ↑ [3] ↑ a b [4] ↑ a b c d Thewissen J.G.M. & Bajpai S, 2001, “Whale Origins as a Poster Child for Macroevolution”, BioScience 51(12): p. 1037-1049 ↑ a b c d e [5] ↑ a b c d [6] ↑ a b [7] ↑ [8] ↑ a b c [9] ↑ a b [10] ↑ [11] ↑ [12] ↑ Uhen M.D. (1998). "New protocetid (Mammalia, Cetacea) from the late middle Eocene Cook Mountain Formation of Louisiana", Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 18(3): p. 664-668 ↑ [13] ↑ [14], diagram at p. 7 ↑ Uhen M.D. (2014). "New material of Natchitochia jonesi and a comparison of the innominata and locomotor capabilities of Protocetidae", Marine Mammal Science 30(3): p. 1029-1066 ↑ [15] ↑ [16] ↑ [17] ↑ [18] ↑ a b [19] ↑ [20] ↑ [21] ↑ Geisler J.H., Sanders A.E. & Lou Z-X. (2005). "A New Protocetid Whale (Cetacea: Archaeoceti) from the Late Middle Eocene of South Carolina", American Museum Novitates no. 3480: p. 1-65 ↑ Uhen M. (1999). "New Species of Protocetid Archaeocete Whale, Eocetus wardii (Mammalia: Cetacea) from the Middle Eocene of North Carolina". Journal of Paleontology 73(3): p. 512-528 ↑ Gol'din P & Zvonok E.A. (2013). "Basilotritus uheni, a New Cetacean (Cetacea, Basilosauridae) from the Late Middle Eocene of Eastern Europe". Journal of Paleontology 87(2): p. 254-268 ↑ van Vliet H.J., Bosselaers M, Vahldiek B-W., Paymans T & Verheijen I (2020). "Eocene cetaceans from the Helmstedt region, Germany, with some remarks on Platyosphys, Basilotritus and Pachycetus", Cainozoic Research 20(1): p. 121-148 ↑ The Paleobiology Database: "Basilosaurus" (read 29-11-2020)
Title: Archaeoceti geological ages 02
Credit: Own work
Author: Sneaking stoat 2
Usage Terms: Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0
License: CC BY-SA 4.0
License Link: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0
Attribution Required?: Yes
Image usage
The following page links to this image:

