Homo antecessor facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Homo antecessorTemporal range: Early Pleistocene
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Superfamily: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: |
H. antecessor
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Homo antecessor Bermudez de Castro et al., 1997
|
|
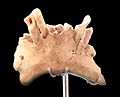
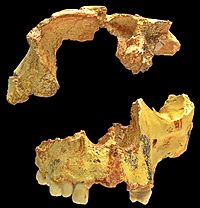
Homo antecessor is an extinct human species dating from 1.2 million to 800,000 years ago, that was discovered by Eudald Carbonell, Juan Luis Arsuaga and J. M. Bermúdez de Castro. H. antecessor is one of the earliest known human varieties in Europe. The best-preserved fossil is a maxilla that belonged to a 10-year-old individual found in Atapuerca, Spain.
Despite being so ancient, the face of H. antecessor is unexpectedly similar to that of modern humans. H. antecessor may have been broad-chested and rather heavy, much like Neanderthals, although the limbs were proportionally long. The feet indicate H. antecessor walked differently compared to modern humans.
H. antecessor was predominantly manufacturing simple pebble and flake stone tools out of quartz and chert, although they used a variety of materials. They only inhabited inland Iberia during warm periods, presumably retreating to the coast otherwise.
The fossils of sixteen animal species were recovered randomly mixed with the H. antecessor material at the Gran Dolina. Deer were the most commonly butchered animal, with 106 specimens. They were also butchering Hermann's tortoise, an easily obtainable source of meat considering how slowly tortoises move.
The cool and humid montane environment encouraged the growth of olive, mastic, beech, hazelnut, and chestnut trees, which H. antecessor may have used as food sources. H. antecessor also seem to have been consuming hackberries, which in historical times have been used for their medicinal properties more than satiating hunger because these berries provide very little flesh.
There is no evidence H. antecessor could wield fire and cook, and similarly the wearing on the molars indicates the more frequent consumption of grittier and more mechanically challenging foods than later European species, such as raw rather than cooked meat.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
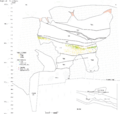
Stratigraphy of the Gran Dolina with detail on TD6
-
The Happisburgh footprints with a camera lens cap for scale
-
Bust of an H. antecessor child at the Natural History Museum, London
-
H. antecessor may have moved along the Ebro river highlighted above (the Sierra de Atapuerca lies near the source).
-
Sierra de Atapuerca today: 1) Entrance to railway ditch, 2) Sima del Elefante, 3) Galería, 4) Gran Dolina
See also
 In Spanish: Homo antecessor para niños
In Spanish: Homo antecessor para niños