Hipparcos facts for kids
Hipparcos is a satellite that was used to make the Hipparcos catalog of 118,000 stars with unprecedented precision. The European Space Agency (ESA) launched it in 1989 and it operated until 1983. It was named for the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus and is also an acronym for HIgh Precision PARallax COllecting Satellite.
Images for kids
-
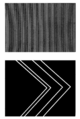
Optical micrograph of part of the main modulating grid (top) and the star mapper grid (bottom). The period of the main grid is 8.2 micrometres.
-
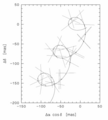
Principles of the astrometric measurements. Filled circles and solid lines show three objects from one field of view (about 1° in size), and open circles and dashed lines show three objects from a distinct sky region superimposed by virtue of the large basic angle. Left: object positions at one reference epoch. Middle: their space motions over about four years, with arbitrary proper motion vectors and scale factors; triangles show their positions at a fixed epoch near the end of the interval. Right: the total positional changes including the additional apparent motions due to annual parallax, the four loops corresponding to four Earth orbits around the sun. The parallax-induced motions are in phase for all stars in the same region of sky, so that relative measurements within one field can provide only relative parallaxes. Although the relative separations between the stars change continuously over the measurement period, they are described by just five numerical parameters per star (two components of position, two of proper motion, and the parallax).
-
The path on the sky of one of the Hipparcos Catalogue objects, over a period of three years. Each straight line indicates the observed position of the star at a particular epoch: because the measurement is one-dimensional, the precise location along this position line is undetermined by the observation. The curve is the modelled stellar path fitted to all the measurements. The inferred position at each epoch is indicated by a dot, and the residual by a short line joining the dot to the corresponding position line. The amplitude of the oscillatory motion gives the star's parallax, with the linear component representing the star's proper motion.
-
Artist's concept of our Milky Way galaxy, showing two prominent spiral arms attached to the ends of a thick central bar. Hipparcos mapped many stars in the solar neighbourhood with great accuracy, though this represents only a small fraction of stars in the galaxy.
See also
 In Spanish: Hipparcos para niños
In Spanish: Hipparcos para niños