Hip replacement is a surgery where the hip joint is replaced by a prosthetic implant. This joint replacement is usually done to relieve arthritis pain or fix very bad joint damage.
Images for kids
-
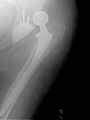
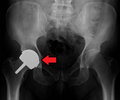
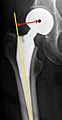
Dislocated artificial hip
-
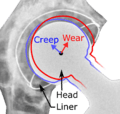
Liner wear, particularly when over 2 mm, increases the risk of dislocation. Liner creep, on the other hand, is normal remoulding.
-
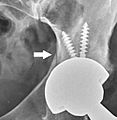
Intraoperative acetabular fracture.
-
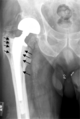
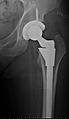
Hip prosthesis displaying aseptic loosening (arrows)
-
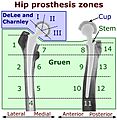
Hip prosthesis zones according to DeLee and Charnley, and Gruen. These are used to describe the location of for example areas of loosening.
-
-
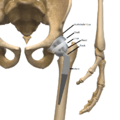
Different Parts of Hip Prosthesis
-
-
Metal on metal prosthetic hip
-
Cement-free implant sixteen days after surgery. Femoral component is cobalt chromium combined with titanium which induces bone growth into the implant. Ceramic head. Acetabular cup coated with bone growth-inducing material and held temporarily in place with a single screw.
-
Femoral (neck) offset is defined as the perpendicular distance between the intramedullary or longitudinal axis of the femur and the center of rotation of the native or prosthetic femoral head. An offset of less than 33 mm is associated with hip dislocation.
-
Gosset-style hip prosthesis from 1960
-
Hip prostheses on display in the London Science Museum
-
Hip prosthesis for hemiarthroplasty. This example is bipolar, meaning that the head has two separate articulations.
See also
 In Spanish: Reemplazo total de cadera para niños
In Spanish: Reemplazo total de cadera para niños
 In Spanish: Reemplazo total de cadera para niños
In Spanish: Reemplazo total de cadera para niños