Herd immunity facts for kids
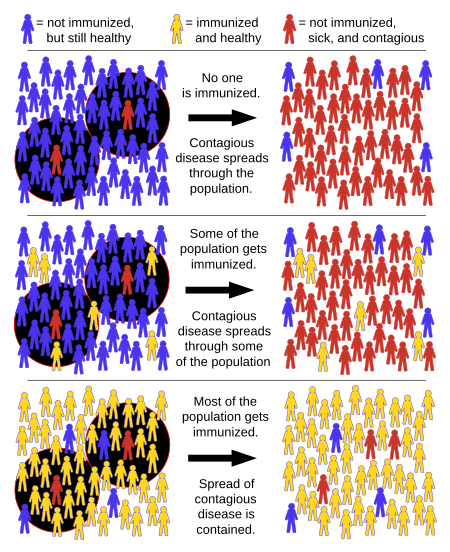
Herd immunity (also called herd effect, community immunity, population immunity, or social immunity) is a form of protection from infectious disease. This happens when a large percentage of a population has become immune to an infection, whether through previous infections or vaccination.
When many individuals have immunity, they do not spread the disease any more. This either stops or slows the spread of disease.
Images for kids
-
A cow with rinderpest in the "milk fever" position, 1982. The last confirmed case of rinderpest occurred in Kenya in 2001, and the disease was officially declared eradicated in 2011.
-
Measles vaccine coverage and reported measles cases in Eastern Mediterranean countries. As coverage increased, the number of cases decreased.
-
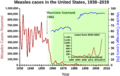
Measles cases in the United States before and after mass vaccination against measles began.
See also
 In Spanish: Inmunidad de grupo para niños
In Spanish: Inmunidad de grupo para niños