Hand facts for kids
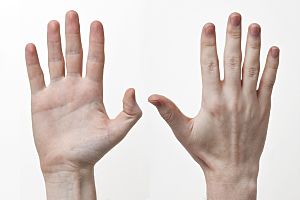
A hand is the part of the body at the end of an arm. Most humans have two hands. Each hand usually has four fingers and a thumb. On the inside of the hand is the palm. When the fingers are all bent tightly, the hand forms a fist. The joints that are the hardest part of the fist are called knuckles. Many other animals, especially other primates, have hands that can hold things. Human hands can do things other hands cannot.
Structure
Many mammals and other animals have grasping appendages similar in form to a hand such as paws, claws, and talons, but these are not scientifically considered to be grasping hands. The only true grasping hands appear in the mammalian order of primates. Hands must also have thumbs.
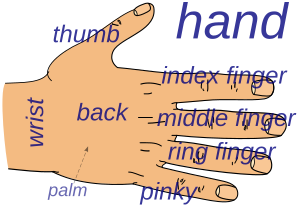
Areas of the human hand include:
- The palm
- Fingers
- Thumb.
The four fingers can be folded over the palm which allows the grasping of objects. Each finger, starting with the one closest to the thumb, has a colloquial name to distinguish it from the others:
- index finger, pointer finger, forefinger, or 2nd digit
- middle finger or long finger or 3rd digit
- ring finger or 4th digit
- little finger, pinky finger, small finger, baby finger, or 5th digit
Evolution
The prehensile hands and feet of primates evolved from the mobile hands of semi-arboreal tree shrews that lived about 60 million years ago. This development has been accompanied by important changes in the brain and the relocation of the eyes to the front of the face, together allowing the muscle control and stereoscopic vision necessary for controlled grasping. Hominidae (great apes including humans) acquired an erect bipedal posture about 3.6 million years ago, which freed the hands from the task of locomotion and paved the way for the precision and range of motion in human hands.
Functional analyses of the features unique to the hand of modern humans have shown that they are consistent with the stresses and requirements associated with the effective use of paleolithic stone tools. It is possible that the refinement of the bipedal posture in the earliest hominids evolved to facilitate the use of the trunk as leverage in accelerating the hand.
Interesting facts
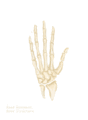
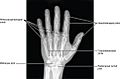
- The skeleton of the human hand consists of 27 bones.
- The human hand has unique anatomical features. It has a longer thumb than that of primates, and fingers that can be controlled individually to a higher degree.
- An adult human male's hand weighs about a pound.
- A reliable way of identifying human hands is from the presence of opposable thumbs.
- Fingers contain some of the densest areas of nerve endings in the body, and are the richest source of tactile feedback. Thus, the sense of touch is intimately associated with hands.
- Like other paired organs (eyes, feet, legs) each hand is dominantly controlled by the opposing brain hemisphere, so that handedness—the preferred hand choice for single-handed activities such as writing with a pencil, reflects individual brain functioning.
- Among humans, the hands play an important function in body language and sign language.
- The ten digits of two hands and the twelve phalanges of four fingers (touchable by the thumb) have given rise to number systems and calculation techniques.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
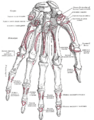
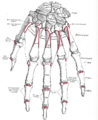
Image showing the carpal bones
-
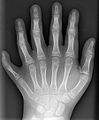
X-ray of the left hand of a ten-year-old boy with polydactyly.
-
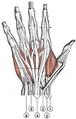
Static adult human physical characteristics of the hand.
See also
 In Spanish: Mano para niños
In Spanish: Mano para niños