Half Moon Island facts for kids

Half Moon Island from Kuzman Knoll, Livingston Island, with Greenwich Island in the background
|
|
 |
|
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Antarctica |
| Coordinates | 62°35′24″S 59°54′36″W / 62.59000°S 59.91000°W |
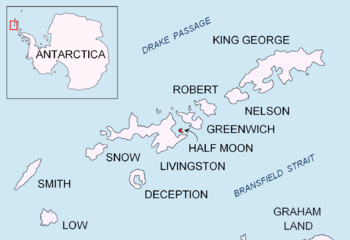
| Archipelago | South Shetland Islands |
| Area | 171 ha (420 acres) |
| Administration | |
| Administered under the Antarctic Treaty System | |
| Demographics | |
| Population | Uninhabited |
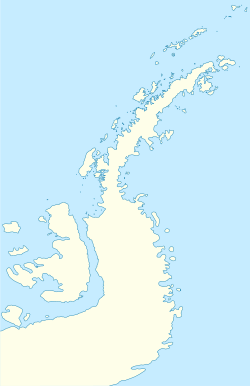
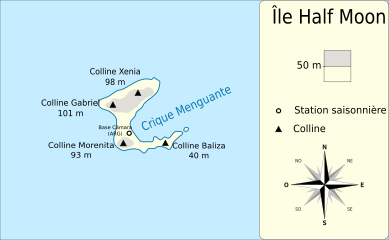
Half Moon Island is a minor Antarctic island, lying 1.35 km (0.84 mi) north of Burgas Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands of the Antarctic Peninsula region. Its surface area is 171 hectares (420 acres). The Argentine Cámara Base is located on the island. It is only accessible by sea and by helicopter; there is no airport of any kind. The naval base is operational occasionally during the summer, but is closed during the winter.
Geography
The island is a series of gravel bars (tombolos) connecting volcanic bedrock islands. The volcanism is not recent and may be millions of years old. The crescent shaped island may be the result of an eroded caldera similar to the much more recent Deception Island volcano complex. The parallel gravel bars are a result of post-glacial (isostatic) uplift of the area after the much larger Pleistocene ice cap melted and the pressure was released.
Wildlife
Plants found on the island include several lichen and moss species as well as Antarctic Hairgrass.
The island has been identified as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because it supports a breeding colony of about 100 pairs of south polar skuas. Other birds nesting on the island include chinstrap penguins (2000 pairs), Antarctic terns (125 pairs), kelp gulls (40 pairs), Wilson's and black-bellied storm petrels, Cape petrels, brown skuas, snowy sheathbills and imperial shags.
Weddell and Antarctic fur seals regularly haul out on the beaches. Southern elephant seals have been recorded. Whales are often seen patrolling the shores.
Access
The island is used as a stop during Antarctic cruises, with the peak of visitation during November–March. There is a 2,000 m (2,200 yd) walking track on the southern part of the Island which allows tourists to get a close view of the wildlife (mainly chinstrap penguins and skuas), and of the surrounding mountainous scenery of nearby Livingston and Greenwich Islands. The path begins on the south side of Menguante Cove, runs westwards along the beach to Cámara Base, then turns north along the head of Menguante Cove, and eventually ascends northeastwards to the top of Xenia Hill.
Google Street View
In September 2010, Google added Street View imagery of Half Moon Island to its Google Earth and Google Maps services. The expansion of Google Street View onto the island means all seven continents had imagery through the service. As the island has no roads, the images appear to have been taken with a camera on a tripod. The shadow of the photographer can clearly be seen if one were to move the view so as to look at the ground. Also, the iconic Pegman from Google was replaced with a Penguin, due to the island's use as a breeding colony by them. The penguin has since been changed back to Pegman.
Maps
- L.L. Ivanov et al., Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands (from English Strait to Morton Strait, with illustrations and ice-cover distribution), 1:100000 scale topographic map, Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, Sofia, 2005
- L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands. Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. ISBN: 978-954-92032-6-4
- L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Smith Island. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2017. ISBN: 978-619-90008-3-0
Gallery
-
The wreck of an old whaling boat, located at the south end of Island.
-
Topographic map of Livingston Island
See also
 In Spanish: Isla Media Luna para niños
In Spanish: Isla Media Luna para niños