Gram staining facts for kids
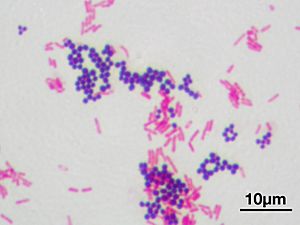
Gram staining (or Gram's method) is a way of classifying bacteria into two large groups: gram-positive and gram-negative. The name comes from its inventor, Hans Christian Gram.
Gram's method stains bacteria according to the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls. First, a violet dye is put on the bacteria. This dye stains peptidoglycan, a thick layer that is only found in gram-positive bacteria. After the first stain, another stain (usually safranin or fuchsin) gives all gram-negative bacteria a red or pink colour.
The Gram stain is almost always the first step in the identification of a bacterial organism. However, not all bacteria can be classified by this technique. Bacteria for which the method does not work are called 'gram-variable' or 'gram-indeterminate'.
Gram developed the technique working with another scientist, Carl Friedländer in a hospital in Berlin. However, Gram first used the test to make bacteria in the lungs easier to see. He published his finished method in 1884.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Tinción de Gram para niños
In Spanish: Tinción de Gram para niños


