Fulkerson Prize facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Fulkerson Prize |
|
|---|---|
| Presented by |
|
| Country | United States |
| Reward | $1,500 |
| First awarded | 1979 |
The Fulkerson Prize for outstanding papers in the area of discrete mathematics is sponsored jointly by the Mathematical Optimization Society (MOS) and the American Mathematical Society (AMS). Up to three awards of $1,500 each are presented at each (triennial) International Symposium of the MOS. Originally, the prizes were paid out of a memorial fund administered by the AMS that was established by friends of the late Delbert Ray Fulkerson to encourage mathematical excellence in the fields of research exemplified by his work. The prizes are now funded by an endowment administered by MPS.
Winners
- 1979:
- Richard M. Karp for classifying many important NP-complete problems.
- Kenneth Appel and Wolfgang Haken for the four color theorem.
- Paul Seymour for generalizing the max-flow min-cut theorem to matroids.
- 1982:
- D.B. Judin, Arkadi Nemirovski, Leonid Khachiyan, Martin Grötschel, László Lovász and Alexander Schrijver for the ellipsoid method in linear programming and combinatorial optimization.
- G. P. Egorychev and D. I. Falikman for proving van der Waerden's conjecture that the matrix with all entries equal has the smallest permanent of any doubly stochastic matrix.
- 1985:
- Jozsef Beck for tight bounds on the discrepancy of arithmetic progressions.
- H. W. Lenstra Jr. for using the geometry of numbers to solve integer programs with few variables in time polynomial in the number of constraints.
- Eugene M. Luks for a polynomial time graph isomorphism algorithm for graphs of bounded maximum degree.
- 1988:
- Éva Tardos for finding minimum cost circulations in strongly polynomial time.
- Narendra Karmarkar for Karmarkar's algorithm for linear programming.
- 1991:
- Martin E. Dyer, Alan M. Frieze and Ravindran Kannan for random-walk-based approximation algorithms for the volume of convex bodies.
- Alfred Lehman for 0,1-matrix analogues of the theory of perfect graphs.
- Nikolai E. Mnev for Mnev's universality theorem, that every semialgebraic set is equivalent to the space of realizations of an oriented matroid.
- 1994:
- Louis Billera for finding bases of piecewise-polynomial function spaces over triangulations of space.
- Gil Kalai for making progress on the Hirsch conjecture by proving subexponential bounds on the diameter of d-dimensional polytopes with n facets.
- Neil Robertson, Paul Seymour and Robin Thomas for the six-color case of Hadwiger's conjecture.
- 1997:
- Jeong Han Kim for finding the asymptotic growth rate of the Ramsey numbers R(3,t).
- 2000:
- Michel X. Goemans and David P. Williamson for approximation algorithms based on semidefinite programming.
- Michele Conforti, Gérard Cornuéjols, and M. R. Rao for recognizing balanced 0-1 matrices in polynomial time.
- 2003:
- J. F. Geelen, A. M. H. Gerards and A. Kapoor for the GF(4) case of Rota's conjecture on matroid minors.
- Bertrand Guenin for a forbidden minor characterization of the weakly bipartite graphs (graphs whose bipartite subgraph polytope is 0-1).
- Satoru Iwata, Lisa Fleischer, Satoru Fujishige, and Alexander Schrijver for showing submodular minimization to be strongly polynomial.
- 2006:
- Manindra Agrawal, Neeraj Kayal and Nitin Saxena, for the AKS primality test.
- Mark Jerrum, Alistair Sinclair and Eric Vigoda, for approximating the permanent.
- Neil Robertson and Paul Seymour, for the Robertson–Seymour theorem showing that graph minors form a well-quasi-ordering.
- 2009:
- Maria Chudnovsky, Neil Robertson, Paul Seymour, and Robin Thomas, for the strong perfect graph theorem.
- Daniel A. Spielman and Shang-Hua Teng, for smoothed analysis of linear programming algorithms.
- Thomas C. Hales and Samuel P. Ferguson, for proving the Kepler conjecture on the densest possible sphere packings.
- 2012:
- Sanjeev Arora, Satish Rao, and Umesh Vazirani for improving the approximation ratio for graph separators and related problems from
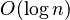 to
to 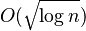 .
. - Anders Johansson, Jeff Kahn, and Van H. Vu for determining the threshold of edge density above which a random graph can be covered by disjoint copies of a given smaller graph.
- László Lovász and Balázs Szegedy for characterizing subgraph multiplicity in sequences of dense graphs.
- Sanjeev Arora, Satish Rao, and Umesh Vazirani for improving the approximation ratio for graph separators and related problems from
- 2015:
- Francisco Santos Leal for a counter-example of the Hirsch conjecture.
- 2018:
- Robert Morris, Yoshiharu Kohayakawa, Simon Griffiths, Peter Allen, and Julia Böttcher for The chromatic thresholds of graphs
- Thomas Rothvoss for his work on the extension complexity of the matching polytope.
- 2021:
- Béla Csaba, Daniela Kühn, Allan Lo, Deryk Osthus, and Andrew Treglown for Proof of the 1-factorization and Hamilton decomposition conjectures
- Jin-Yi Cai and Xi Chen for Complexity of Counting CSP with Complex Weights
- Ken-Ichi Kawarabayashi and Mikkel Thorup for Deterministic Edge Connectivity in Near-Linear Time
Source: Mathematical Optimization Society official website.
See also
 In Spanish: Premio Fulkerson para niños
In Spanish: Premio Fulkerson para niños
- List of mathematics awards

All content from Kiddle encyclopedia articles (including the article images and facts) can be freely used under Attribution-ShareAlike license, unless stated otherwise. Cite this article:
Fulkerson Prize Facts for Kids. Kiddle Encyclopedia.
