Fragile X syndrome facts for kids
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is a genetic syndrome that causes a range of intellectual disabilities as well as unusual physical and behavioural characteristics. It is one of the most common causes of autism and mental retardation among boys. Basically, these individuals lack an important gene product.
Technical account
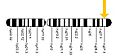
Fragile X syndrome occurs as a result of a mutation of the FMR1 gene on the X chromosome. This causes an increase an increase in the number of CGG repeats in the 5' untranslated region of FMR1.
In unaffected individuals, the FMR1 gene contains 5–44 repeats of the CGG codon, most commonly 29 or 30 repeats. Between 45 and 54 repeats is considered a "grey zone". Between 55 and 200 repeats in length is described as a premutation allele. Individuals with fragile X syndrome have a full mutation of the FMR1 allele, with over 200 repeats of the CGG codon.
In these individuals with a repeat expansion greater than 200, there is methylation of the CGG repeat expansion and FMR1 promoter. This silences the FMR1 gene, and its end-product is not made.
Images for kids
-
Location of the FMR1 gene on the X chromosome
See also
 In Spanish: Síndrome X frágil para niños
In Spanish: Síndrome X frágil para niños