Epiglottis facts for kids
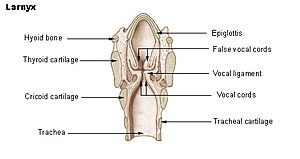
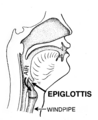
The epiglottis is a thin flap in the oesophagus. It is the top part of the Larynx. It closes to stop food from going down the trachea, and opens to allow breathing.
Function
The epiglottis is normally pointed upward during breathing with its underside functioning as part of the pharynx. During swallowing, elevation of the hyoid bone draws the larynx upward; as a result, the epiglottis folds down to a more horizontal position, with its superior side functioning as part of the pharynx. In this manner, the epiglottis prevents food from going into the trachea and instead directs it to the esophagus, which is at the back. Should food or liquid enter the windpipe due to the epiglottis failing to close properly, the gag reflex is induced to protect the respiratory system.
Gag reflex
The glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) sends fibers to the upper epiglottis that contribute to the afferent limb of the gag reflex. (The gag reflex is variable in people from a limited to a hypersensitive response.) The superior laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve (CN X) sends fibers to the lower epiglottis that contribute to the efferent limb of the cough reflex. This initiates an attempt to try to dislodge the food or liquid from the windpipe.
Speech sounds
In some languages, the epiglottis is used to produce epiglottal consonant speech sounds, though this sound-type is rather rare.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Epiglotis para niños
In Spanish: Epiglotis para niños