Education in the United States facts for kids

Education in the United States is provided by the public sector. The federal, state and local governments control and give funds to help local schools. Public education is available everywhere in the United States. School's curriculum, funds, teaching, employment and other policies are created by the elected school boards.
School districts are sometimes different from other local jurisdictions. They have their own officials and budgets. Education standards and state tests are created by the state governments. Since child education is required by law, ages to start school are different from each state. Children usually start school between the ages of five to eight. They usually end their education when they are between the ages of fourteen and eighteen. Education requirements can be done by educating children in public schools, private schools (who is known by the government to be trusted) or a home school program. In most public schools, education is divided into three levels. The first level is elementary school. Grades in elementary school are different in each state. The second level is middle school. Grades in middle school are different in each state as well. The last level is high school. In some states, middle school is called "junior high school". Grades in high school are also different in each state. After a child has completed their senior year (12th grade), they will earn a high school diploma.
If a child would like to continue on with their education or want to start a career, they can apply for college. Students who cannot afford to attend a four year college or university can study at a two-year community college. Some two-year community colleges are called "Junior colleges". Colleges are not required and are not forced by local laws. After college, the now adult can earn a number of certificates for a career.
Other pages
Images for kids
-
A building of New York Institute of Technology on its Manhattan campus
-
Brookings Hall of Washington University in St. Louis, established in 1853.
-
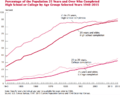
Cost of US college education relative to the consumer price index (inflation)
-
President George W. Bush signing the No Child Left Behind Act
See also
 In Spanish: Sistema educativo de Estados Unidos para niños
In Spanish: Sistema educativo de Estados Unidos para niños