Divergent boundary facts for kids
In plate tectonics, a divergent boundary or divergent plate boundary is a linear feature that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other.
Divergent boundaries within continents initially produce rifts, which eventually become rift valleys.
Most active divergent plate boundaries occur between oceanic plates and exist as mid-oceanic ridges.
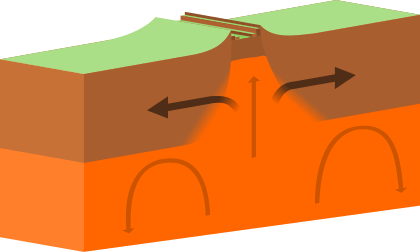
Divergent boundaries also form volcanic islands, which occur when the plates move apart to produce gaps that molten lava rises to fill.
Over millions of years, tectonic plates may move many hundreds of kilometers away from both sides of a divergent plate boundary. Because of this, rocks closest to a boundary are younger than rocks further away on the same plate.
Description

At divergent boundaries, two plates move away from each other and the space that this creates is filled with molten magma that forms below.
The origin of new divergent boundaries at triple junctions is sometimes thought to be associated with the phenomenon known as hotspots. Here, hot mantle convecting up from the earth's core bring lots of hot material near the surface, and the kinetic energy is thought to be sufficient to break apart the lithosphere (crust and mantel around the earth).
The hot spot which may have started the Mid-Atlantic Ridge system is under Iceland which is widening at a rate of a few centimeters per year.
Examples
Other plate boundary types
See also
 In Spanish: Borde divergente para niños
In Spanish: Borde divergente para niños