Database facts for kids
A database is a system for storing and taking care of data (any kind of information).
A database engine can sort, change or serve the information on the database. The information itself can be stored in many different ways; before digital computers, card files, printed books and other methods were used. Now most data is kept on computer files.
A database system is a computer program for managing electronic databases. A very simple example of a database system would be an electronic address book.
The data in a database is organized in some way. Before there were computers, employee data was often kept in filing cabinets. There was usually one card for each employee. On the card, information such as the date of birth or the name of the employee could be found. A database also has such "cards". To the user, the card will look the same as it did in old times, only this time it will be on the screen. To the computer, the information on the card can be stored in different ways. Each of these ways is known as a database model. The most commonly used database model is called the relational database model. It uses relations and sets to store the data. Normal users talking about the database model will not talk about relations; instead, they will talk about database tables.
Contents
Uses for database systems
Uses for database systems include:
- They store data and provide facilities (tools) to search for specific records in a given set of data.
- They store special information used to manage the data. This information is called metadata and it is not shown to all the people looking at the data.
- They can solve cases where many users want to access (and possibly change) the same entries of data.
- They manage access rights (who is allowed to see the data, who can change it)
- When there are many users asking questions to the database, the questions must be answered faster. In this way, the last person to ask a question can get an answer in a reasonable time.
- Certain attributes are more important than others and can be used to find other data. This is called indexing. An index contains all the important data and can be used to find other data.
- They ensure that the data always has context. There are a lot of different rules that can be added to tell the database system if the data makes sense. One of the rules might say November has 30 days. This means if someone wants to enter November 31 as a date, this change will be rejected.
Changing data
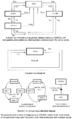
In databases, some data changes occasionally. There may be problems when data is changed; for example, an error might have occurred. The error might make the data useless. The database system looks at the data to ensure that it meets certain requirements. It does this by using a transaction. There are two points in time in the database, the time before the data was changed, and the time after the data was changed. If something goes wrong when changing the data, the database system simply puts the database back into the state before the change happened. This is called a rollback. After all the changes are done successfully, they are committed. This means that the data makes sense again; committed changes can no longer be undone.
In order to be able to do this, databases follow the ACID principle:
- All. Either all tasks of a given set (called a transaction) are done, or none of them is. This is known as Atomicity.
- Complete. The data in the database always makes sense. There is no half-done (invalid) data. This is known as Consistency.
- Independent. If many people work on the same data, they will not see (or impact) each other. Each of them has their own view of the database, which is independent of the others. This is known as Isolation.
- Done. Transactions must be committed, when they are done. Once the committed, they can not be undone. This is known as Durability.
Database model
There are different ways how to represent the data.
- Simple files (called flat files): This is the most simple form of Database system. All the data is stored in a file in plain text. Every piece of information can be separated by a new line or a comma etc.
- Hierarchical model: The data is organized like a tree structure. The interesting data is at the leaves of the tree. The relationships among the data entries is such that some entries are directly dependent to other entries.
- Network model: Use records and sets to store the data. Similar to Hierarchical model, but this has much more complex structure.
- Relational model: This uses set theory and predicate logic. It is widely used. Data looks like it is organized in tables. These tables can then be joined together so that simple queries can be chosen from them.
- Object oriented model: The data is represented in the form of objects as used in Object Oriented Programming. They can interact directly with the OOP language being used, as both of them have the same representation of the data internally.
- Object relational model: This is a hybrid of the Object oriented model and the relational model.
- NoSQL model: This is a new kind of database model and is increasing being used in the industry in big data and real-time web applications. The data in this model is stored as key-value pairs without any strict hierarchy as in other models. NoSQL systems are also referred to as "Not only SQL" because they do not allow Structured Query Language-like query languages to be used.
Ways to organize the data
As in real life, the same data can be looked at from different perspectives, and it can be organized in different ways. There are different things to consider, when organizing the data:
- Each item of data should be stored as few times as possible. Imagine that an unmarried woman is listed in the county records, State Motor Vehicle Department, Federal Social Security Department and International Passport Department. If she marries, and decides to change her name, all the these departments have to be notified. If all the departments were linked, and her name stored in only one place, then updating is easy.
- If the data is stored in several different databases, it may contradict itself.
- This problem makes finding data slower. If there is a lot of data, this problem of storing one piece of data in many places, will take up a lot of space. In our example there were four databases for one person. That will be eight changes made, if a second person has exactly the same problem.
- If you have this problem, a method called Database Normalisation was developed to solve it. Currently there are six Normal forms. These are ways to make a database faster, and make the data take less space.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Base de datos para niños
In Spanish: Base de datos para niños