Crawford County, Michigan facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Crawford County
|
|
|---|---|

Crawford County Building in Grayling
|
|
Location within the U.S. state of Michigan
|
|
 Michigan's location within the U.S. |
|
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1840 |
| Named for | William Crawford |
| Seat | Grayling |
| Largest city | Grayling |
| Area | |
| • Total | 563 sq mi (1,460 km2) |
| • Land | 556 sq mi (1,440 km2) |
| • Water | 7.0 sq mi (18 km2) 1.2%% |
| Population
(2020)
|
|
| • Total | 12,988 |
| • Density | 25/sq mi (10/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 1st |
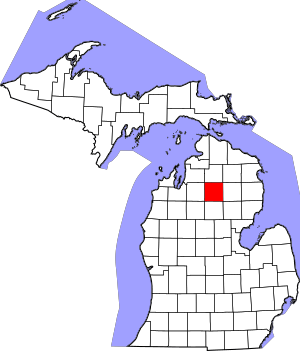
Crawford County is a county in the U.S. state of Michigan. Its population was 12,988 as of the 2020 census. The county seat of Crawford County is Grayling, the county's only incorporated community.
Crawford County is located in the Northern Lower Peninsula of Michigan. It contains land within three of Michigan's largest watersheds, belonging to the Au Sable, Manistee, and Muskegon rivers and 75% of the county is publicly owned by the Department of Military Affairs, the United States Forest Service or the State of Michigan.
History
The county is named for Col. William Crawford, a Revolutionary War officer captured by Native Americans near Sandusky, Ohio and burned at the stake in 1792. Created by the Michigan Legislature as Shawono County in 1840, before being renamed in 1843 as Crawford County. "Shawono" was derived from an Ojibwe word, zhaawanong, meaning "from the south". The area was administered by other Michigan counties before 1879 when the county government was organized.
Due to the location in rural northern Michigan, Crawford County's greatest economic growth occurred in the 1800s when lumbering clear-cut most of the extensive forests of Norway pine, birch, maple, beech and hemlock. With the trees gone, tourism became the center of the economy. In the 1870s Crawford County became a popular destination for recreational fishing. The Michigan grayling, found in the Au Sable River, first gained the attention of anglers. The Crawford County Avalanche began publishing a weekly paper in 1879. Their first edition featured a fishing story on the front-page. By the end of the century, the grayling species vanished due to a combination of overfishing, river degradation due to logging, and the impact of human-introduced brown trout. The Au Sable River of today boasts large populations of brown and rainbow trout and remains a premiere trout fishing area in both Michigan and the nation.
1900s
A 1912 text, A History of Northern Michigan and its people by Perry F. Powers & Harry Gordner Cutler describes Crawford County: The topography is rolling hills but not so steep as to impede farm equipment. The Au Sable River, along with its tributaries, traverse the entire county, providing water and locations for ranching livestock. It also presents an opportunity for superb trout fishing. On the western county line is a natural reservoir that forms the Manistee River. Transportation is primarily provided by the Michigan Central railroad. The Detroit & Charlevoix railroad has track to Frederic, Michigan to the northwest. Half of the land is the county is a gravel loam soil which can produce standard crops. Thousands of acres of clear-cut old growth pine in Crawford County is available to settle. Potatoes, clover and root crops will thrive in this soil. Growing clover seed has become recognized as a “money crop”. Fruit trees are becoming a popular choice with apples being prolific and flavorful. “Plains” soil supports native grasses which stockmen are using for profitable sheep and cattle ranches throughout the county. There are few swamps and lowlands, all along narrow strips beside waterways, which can be productive with proper drainage. Over a hundred years ago, people journeyed "up north" for rest, recreation and their health. Hunting has always been popular, and for wild game, large tracts of second-growth timber on land originally clear-cut provide better food and protection than the original forests did. Deer populations are stable despite the hundreds that are taken every year by settlers and sportsmen.
Winter Sports Park
The Grayling Winter Sports Park (GWSP) was opened in 1929. It started as a toboggan run that grew into Michigan's first ski resort. Following the popular 1932 Winter Olympics, Grayling constructed a 66-foot ski jump in 1934. A few years later, a Winter Carnival was started that included a parade, ice sculpture competition, and a Snow Queen pageant. The park's popularity increased to the point where a "Snow Train" was established to bring skiers to Grayling from across the state. Transportation from Lodges in Grayling to the park was provided by flat-bed trucks. Groomed trails were provided for Cross-country skiing and snowshoeing.
The Cass City Chronicle noted in March 1941, "Due to generous support of the federal park service, state conservation department, and Civilian Conservation Corps, Grayling offers today the finest public toboggan set-up in the entire United States, and this isn't paid ballyhoo. Six steel slides are the only ones of their kind anywhere not excluding Lake Placid or Sun Valley (Idaho). Two ski tows have been in operation; next season there will be three."
The Crawford County operated the GWSP into the late 1960s when Fred Bear, owner of Bear Archery, and other local businessmen assumed operational control. It was renamed, Bear Mountain and they attempted to create a commercial ski area to compete with resorts further north. A legal challenge in 1973 resulted in a judgement giving control back to the county, which has operated it since then as Hanson Hills Recreation Area by the Grayling Recreation Authority.
The annual canoe / kayak race record winning time is held by Scott Norman in his significantly modified kayak, which not only gave him the speed record, but also the distance record, as his brakes failed to deploy and he was retrieved by snowmobile outside of the park near M-93. "
Military
In 1913, lumber baron Rasmus Hanson donated 147,000 acres (590 km2) of harvested timberland to the state of Michigan for military training. Most of the land is situated in Crawford County, with parcels in Kalkaska and Otsego counties. Troops first began training there in 1914. It is the primary training facility for the Michigan National Guard and is the largest National Guard training facility in the United States.
Hartwick Pines
Edward Hartwick graduated from Grayling High School in 1888 and received an appointment to West Point in 1889. Four years later he graduated with high honors and was assigned to the 4th Cavalry. He soon transferred to the 9th Cavalry, known as the Buffalo Soldiers on the western frontier. With the advent of the Spanish–American War, his unit was sent to Cuba where he participated in the Battle of San Juan Hill. At wars end, he returned to Grayling and married Karen Bessie Michelson, then resigned his commission nine months later. He engaged in the banking and lumber business, prospered, and later moved to Detroit. When the United States entered World War I, he volunteered for service at age 46 and was commissioned an Army Major. After just a few months in France, he contracted meningitis and died. In 1927, Karen Michelson Hartwick purchased 8,000 acres (3,200 ha) including the last 85 acres (34 ha) of virgin old growth pine forest in Michigan's lower peninsula and donated it to the state of Michigan to honor her husband. Hartwick Pines State Park is the largest state park in the lower peninsula.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 563 square miles (1,460 km2), of which 556 square miles (1,440 km2) is land and 7.0 square miles (18 km2) (1.2%) is water. Although it is located on Michigan's Lower Peninsula, Crawford County is considered to be part of Northern Michigan. The county contains land within three of Michigan's largest watersheds, belonging to the Au Sable, Manistee, and Muskegon rivers.
Crawford County has relatively few lakes, mostly in the northern part of the county. Lake Margrethe is the county's largest and has a surface area of 1,920 acres (7.8 km2). Other water bodies >100 acres include Big Bradford Lake, Big Bear Lake, KP Lake, Shellenbarger Lake, Shupac Lake and Wakeley Lake. Some of these are so-called kettle lakes,' formed by the melting of blocks of glacial ice, left as the glacier retreated, which created a depression in the soil. The Manistee River flows on the western edge of the county; branches of the Au Sable River flow throughout the remainder of the county.
The county is part of the Au Sable State Forest, specifically the Grayling FMU (Alcona, Crawford, Oscoda, and northern Iosco counties). Parts of the county are also within the Huron National Forest. Glaciers shaped the area, creating a unique regional ecosystem. A large portion of the area is the so-called Grayling outwash plain, which consists of broad outwash plain including sandy ice-disintegration ridges; jack pine barrens, some white pine-red pine forest, and northern hardwood forest. Large lakes were created by glacial action.
Rivers
- Au Sable River, begins in Otsego County, Michigan and flows through Crawford, Oscoda, Alcona, then Iosco before flowing into Lake Huron.
- Manistee River begins in Antrim County, Michigan and flows through Otsego, Crawford, Kalkaska, Wexford, then Manistee before flowing into Lake Michigan.
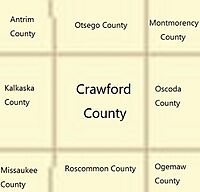
Adjacent counties
- Otsego County - north
- Montmorency County - northeast
- Oscoda County - east
- Ogemaw County - southeast
- Roscommon County - south
- Missaukee County - southwest
- Kalkaska County - west
- Antrim County - northwest
Protected areas
- Huron National Forest (part)
- Au Sable State Forest
- Huron–Manistee National Forests
- Kirtlands Warbler Wildlife Management Area
State Parks
Communities

City
Charter township
- Grayling Charter Township
Civil townships
- Beaver Creek Township
- Frederic Township
- Lovells Township
- Maple Forest Township
- South Branch Township
Unincorporated communities
Ghost towns
- Bucks
- Deward
- Pere Cheney
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1880 | 1,159 | — | |
| 1890 | 2,962 | 155.6% | |
| 1900 | 2,943 | −0.6% | |
| 1910 | 3,934 | 33.7% | |
| 1920 | 4,049 | 2.9% | |
| 1930 | 3,097 | −23.5% | |
| 1940 | 3,765 | 21.6% | |
| 1950 | 4,151 | 10.3% | |
| 1960 | 4,971 | 19.8% | |
| 1970 | 6,482 | 30.4% | |
| 1980 | 9,465 | 46.0% | |
| 1990 | 12,260 | 29.5% | |
| 2000 | 14,273 | 16.4% | |
| 2010 | 14,074 | −1.4% | |
| 2020 | 12,988 | −7.7% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 13,538 | −3.8% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790-1960 1900-1990 1990-2000 2010-2018 |
|||
As of the census of 2000, there were 14,273 people, 5,625 households, and 4,038 families residing in the county. The population density was 26 people per square mile (10 people/km2). There were 10,042 housing units at an average density of 18 per square mile (6.9/km2). At the 2020 census, its population was 12,988.
In 2000, the racial makeup of the county was 96.38% White, 1.50% Black or African American, 0.60% Native American, 0.25% Asian, 0.02% Pacific Islander, 0.20% from other races, and 1.05% from two or more races. 0.99% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 24.8% were of German, 12.5% English, 10.1% American, 8.9% Irish, 7.4% Polish and 5.9% French ancestry. 97.7% spoke English and 1.5% Spanish as their first language.
There were 5,625 households, out of which 30.00% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 57.60% were married couples living together, 9.70% had a female householder with no husband present, and 28.20% were non-families. 24.00% of all households were made up of individuals, and 10.50% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.45 and the average family size was 2.87.
In the county, 24.50% of the population was under the age of 18, 6.30% was from 18 to 24, 26.60% from 25 to 44, 26.00% from 45 to 64, and 16.60% was 65 years of age or older. The median age was 41 years. For every 100 females there were 104.00 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 100.40 males.
In 2000, the median income for a household in the county was $33,364, and the median income for a family was $37,056. Males had a median income of $31,504 versus $21,250 for females. The per capita income for the county was $16,903. About 10.00% of families and 12.70% of the population were below the poverty line, including 17.60% of those under age 18 and 7.60% of those age 65 or over.
Religion
Crawford County is part of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Gaylord. It is also located in the Episcopal Diocese of Eastern Michigan, based in Saginaw, Michigan.
Economy
The largest employer in the county is Camp Grayling followed by the Grayling Hospital. The small size of the population won't support any big box stores; Tractor Supply Company moved into the building that Kmart vacated in the late 2010s. There have been a few small employers added to the industrial park at West Four Mile Road south of Grayling. Several microbreweries and a new art gallery opened prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, and summer tourist spending is rising again.
Banking
Crawford County has branches of two large commercial banks, Fifth Third Bank and Huntington Bank; two area banks, Horizon Bank (from Indiana) and State Savings Bank (from Gaylord); and two Michigan credit unions, Northland Area Federal Credit Union and North Central Area Credit Union.
Logistics
Several trucking companies have operations in Crawford County.
Media
The Crawford County Avalanche states that it has been "Grayling's Hometown Newspaper Since 1879".
Military
Camp Grayling is the primary training facility for the Michigan National Guard and is the largest National Guard training facility in the United States.
Education
Primary and secondary
Due to their small population, the county can only sustain one high school, middle school and elementary school. The Crawford AuSable School Board is elected to establish policy to provide the best programs to meet the needs of the students while being fiscally responsible and hiring a superintendent to execute those policies. The current superintendent is Tim Sanchez.
| Board Member | Term Ends |
|---|---|
| Matt Cragg | 2028 |
| Wendy Kucharek | 2024 |
| Pam LaGattuta | 2024 |
| Josh Peters | 2024 |
| Nicole Persing-Wethington | 2028 |
| Lori Johnsonn | 2024 |
| Ryan Finstrom | 2026 |
- Crawford AuSable School District serves 1,619 students in Crawford County.
- Grayling Adventist Elementary School serves 9 students.
Post-secondary
Crawford County is home to Kirtland Community College, a public community college in Grayling.
Public library
The Deveraux Memorial Library in Grayling is the public library in Crawford County.
Infrastructure
Transportation
Due to its size, the county has no scheduled bus service and limited taxi service. The Crawford County Transportation Authority offers dial-a-ride service at low rates.
Air service
Crawford County is not served by commercial airlines. Grayling Army Airfield, (ICAO: KGOV, FAA LID: GOV) is a public/military use airport located one nautical mile (1.85 km) northwest of the central business district of Grayling. Built in 1977, the United States Army owns it, and a fixed-base operator provides support services to general aviation users.
Bus service
- Indian Trails provides daily intercity bus service in Grayling between St. Ignace and East Lansing, Michigan.
Major highways
 I-75 from Detroit in the south enters on the west side of Crawford County, passes to the east of Grayling, and connects with the Mackinac Bridge to the north.
I-75 from Detroit in the south enters on the west side of Crawford County, passes to the east of Grayling, and connects with the Mackinac Bridge to the north. BL I-75 is a business loop route running through Grayling. It follows the former route of US 27, in part.
BL I-75 is a business loop route running through Grayling. It follows the former route of US 27, in part. US 127 in Lansing goes north through Clare into Roscommon County where it enters Crawford County and terminates at I-75 in Beaver Creek township south of Grayling.
US 127 in Lansing goes north through Clare into Roscommon County where it enters Crawford County and terminates at I-75 in Beaver Creek township south of Grayling. M-18 begins on M-72 in South Branch Township near the Oscoda County line and runs south before curving to the west in a loop to Roscommon.
M-18 begins on M-72 in South Branch Township near the Oscoda County line and runs south before curving to the west in a loop to Roscommon. M-72 is one of only three roads that stretch east–west from Lake Huron to Lake Michigan. It enters South Branch Township from Oscoda County in the southeast, passes through Grayling and continues northeast through Frederic Township to Traverse City.
M-72 is one of only three roads that stretch east–west from Lake Huron to Lake Michigan. It enters South Branch Township from Oscoda County in the southeast, passes through Grayling and continues northeast through Frederic Township to Traverse City. M-93 is an 11-mile (18 km) route connecting the main gate of Michigan Army National Guard's Camp Grayling, 4 miles (6.4 km) southwest of Grayling, with Hartwick Pines State Park, 7 miles (11 km) northeast of Grayling.
M-93 is an 11-mile (18 km) route connecting the main gate of Michigan Army National Guard's Camp Grayling, 4 miles (6.4 km) southwest of Grayling, with Hartwick Pines State Park, 7 miles (11 km) northeast of Grayling. F-32 begins at BL I-75/M-93 on the northern edge of Grayling and continues east toward Mio.
F-32 begins at BL I-75/M-93 on the northern edge of Grayling and continues east toward Mio. F-97 is a north–south route that begins at Gladwin and goes north through Prudenville, St. Helen, follows M-18 in Crawford County, then continues into southern Otsego County.
F-97 is a north–south route that begins at Gladwin and goes north through Prudenville, St. Helen, follows M-18 in Crawford County, then continues into southern Otsego County.- County Highway 612 is an east–west roadway that starts southwest of Manistee Lake in Manistee county and continues east through Frederic in northern Crawford County, has an interchange at I-75, passes through Lewiston and ends at M-33 in Montmorency county.
Bicycle route
- There are bicycle lanes identified on some roadways.
- Grayling Bicycle Turnpike begins at Hartwick Pines State Park and parallels
 M-93 for 6.5 miles, ending at Michigan Avenue in Grayling.
M-93 for 6.5 miles, ending at Michigan Avenue in Grayling.
Utilities
The City of Grayling provides municipal water and sewer to residents, and Beaver Creek/GraylingTownship Utility Authority provides municipal water and sewer to residents on the Four Mile Road corridor. All other county residents utilize well water and private septic systems approved by the Crawford County Health Department.
Electrical service throughout the county is provided by either Consumers Energy or Great Lakes Energy Co-op. Natural gas is provided by DTE Energy. Propane Service is provided by half a dozen providers.
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Crawford (Míchigan) para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Crawford (Míchigan) para niños