Congregation Kesher Israel (Philadelphia) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Congregation Kesher Israel |
|
|---|---|
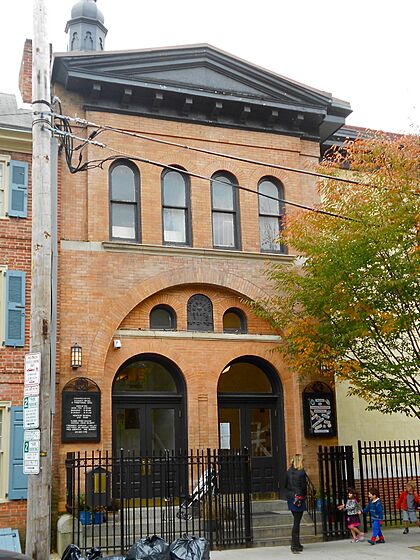

The synagogue, in 2014
|
|
| Religion | |
| Affiliation | Conservative Judaism |
| Rite | Nusach Ashkenaz |
| Ecclesiastical or organizational status | |
| Year consecrated |
|
| Status | Active |
| Location | |
| Location | 412-418 Lombard Street, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania |
| Country | United States |
| Architecture | |
| Architect(s) | J. Franklin Stuckert (1895) |
| Architectural type | Church |
| Date established | 1883 (as a Jewish congregation) |
| Completed |
|
| Direction of façade | North |
Congregation Kesher Israel is a Conservative Jewish congregation and synagogue located in the Society Hill section of Center City Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in the United States. The synagogue is home to an active congregation with Shabbat and holy day services, a Hebrew school, adult education, and community programming.
History
Church
Joseph Priestley is credited with inspiring the creation in 1796 of the first Unitarian Society of Philadelphia. This group founded the first Independent Church of Christ and constructed its building at 412 Lombard Street in 1796. Priestly himself would come occasionally to preach at the church he inspired.
The original building extended 80 feet (24 m) along Lombard Street and was 50 feet (15 m) deep. There were originally five arched openings along Lombard Street. A passageway led from Lombard Street to a graveyard at the rear.
The Unitarian Society rented its sanctuary out to other Christian societies. Joseph Smith during a visit to Philadelphia preached at the Universalist Church in December 1839.
The church had vacated the building at 412 Lombard Street by 1887.
Synagogue
Bnai Jacob synagogue was founded in 1883 and purchased the vacant church and converted it to a synagogue in 1889. As a condition of the sale, the Unitarian Society removed the graves from the church yard; they were reinterred at Fernwood Cemetery in Lansdowne, Pennsylvania.
Rodephe Tzedek, another neighborhood shul founded in 1887, merged with Bnai Jacob in 1894. They formed a new congregation called Kesher Israel. The synagogue's charter was filed on June 21, 1894 and approved by Judge M. Arnold, July 14, 1894, in Common Pleas No. 4, Philadelphia County. Henry Morias updated his history of the Jews of Philadelphia to include the creation of Kesher Israel that year:
"Bene Ya'acob" Congregation and Chebrah Rodephe Tsedek, Anshe Szager ... united during August, 1894-5654, and substituted, for their respective names, "Kesher 'Israel" (The Bond of Israel). A Congregational charter has been obtained, and the worship will continue at the Synagogue of the former Congregation, on the south side of Lombard Street, west of Fourth Street. The building will be enlarged and altered...
On January 24, 1897, the congregation dedicated its new synagogue building. Capacity was listed as 1,400.
In the fall of 1897, one of the first large Zionist meetings in the United States was held at Kesher Israel after Theodor Herzl convened the First Zionist Congress in Basle Switzerland. Kesher Israel became a central meeting hall for early Zionists in Philadelphia.
On December 4, 1919, the basement heater ignited a fire that damaged the building's sanctuary, hallways, and rooms. While the total loss was $1,500, no one was hurt and congregants who lived nearby helped retrieve holy objects from the building.
Rabbi Ivan Caine led Kesher Israel on a part-time basis in the mid-1970s, splitting his time with Society Hill Synagogue also in the neighborhood. The synagogue during this period held morning as well as afternoon services but struggled to secure a minyan of ten men. One wealthier member paid others between $8 and $15 a week to attend and preserve the services.
The building fell into disrepair in the 1970s and 1980s. The building's roof leaked unchecked for 20 years. The water created a hole in the ceiling was repaired for $80,000. Much of the funds came from historic preservation grants.
In 1995, Kesher Israel had neither rabbi nor janitor, and its membership dues remained $10/year. The congregation had replaced the roof but its ceiling, stained glass, bricks, and masonry all required repair.
In 1998, congregant Michael Yaron donated $2 million to the synagogue to renovate the sanctuary and building. The congregation began the renovations in January 1998, and in September 1998 celebrated the completion of the project.
Harry Boonin chronicled the history of the synagogue and published the book The Life and Times of Congregation Kesher Israel in 2007. Mitchell Romirowsky has served as the synagogue's interim rabbi since 2018.
See also