Colony of Natal facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Colony of Natal
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1843–1910 | |||||||||||
|
Anthem: God Save the Queen
|
|||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||
| Status | British colony | ||||||||||
| Capital | Pietermaritzburg | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Afrikaans, English, Zulu | ||||||||||
| Religion | Anglican, Dutch Reformed, Hindu, Presbyterian, Roman Catholic | ||||||||||
| Government | Constitutional monarchy | ||||||||||
| Queen | |||||||||||
| Special Commissioner | |||||||||||
|
• 1843
|
Henry Cloete | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Scramble for Africa | ||||||||||
|
• Established
|
4 May 1843 | ||||||||||
|
• Annexed Zululand
|
1897 | ||||||||||
|
• Disestablished
|
1910 | ||||||||||
|
• Natal Province est.
|
31 May 1910 | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
| 1904 | 91,610 km2 (35,370 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||
|
• 1904
|
1108754 | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||
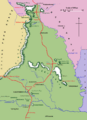
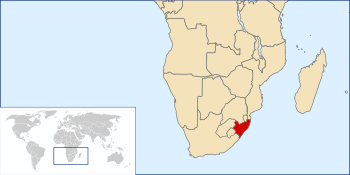
The Colony of Natal was a British colony in south-eastern Africa. It was proclaimed a British colony on 4 May 1843 after the British government had annexed the Boer Republic of Natalia, and on 31 May 1910 combined with three other colonies to form the Union of South Africa, as one of its provinces. It is now the KwaZulu-Natal province of South Africa. The Indians who were brought to this country from India called it 'Netaal Tapu' (island of Netal).
It was originally only about half the size of the present province, with the north-eastern boundaries being formed by the Tugela and Buffalo rivers beyond which lay the independent Kingdom of Zululand (KwaZulu in Zulu). The present province was also enlarged by the addition of Griqualand East to the south.

Fierce conflict with the Zulu population led to the evacuation of Durban, and eventually the Boers accepted British annexation in 1844 under military pressure. A British governor was appointed to the region and many settlers emigrated from Europe and the Cape Colony. The British established a sugar cane industry in the 1860s. Farm owners had a difficult time attracting Zulu labourers to work on their plantations, so the British brought thousands of indentured labourers from India. As a result of the importation of Indian labourers, Durban became the home to the largest concentration of Indians outside of India.
Growth of the colony
The colony's early population growth was driven by settlement from the United Kingdom between 1849 and 1851, with approximately 4500 emigrants between 1848 and 1851. From the time of the coming of the first considerable body of British settlers dates the development of trade and agriculture in the colony, followed somewhat later by the exploitation of the mineral resources of the country.
Sugar and Indian Labourers
As early as 1893, when Mahatma Gandhi arrived in Durban, Indians made up almost half of the non-African population, and by 1904 Indians outnumbered whites in Natal. In 1894, Gandhi helped to establish the Natal Indian Congress to fight discrimination against Indians.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Colonia de Natal para niños
In Spanish: Colonia de Natal para niños