Clinical trial facts for kids

Clinical trials are experiments or observations done in clinical research. Such biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants are designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments vaccines, drugs, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison.
Clinical trials generate data on safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought.
These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial – their approval does not mean that the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted.
The most common clinical trials evaluate new products, or other interventions. Clinical trials may be required before a national regulatory authority approves marketing of the innovation.
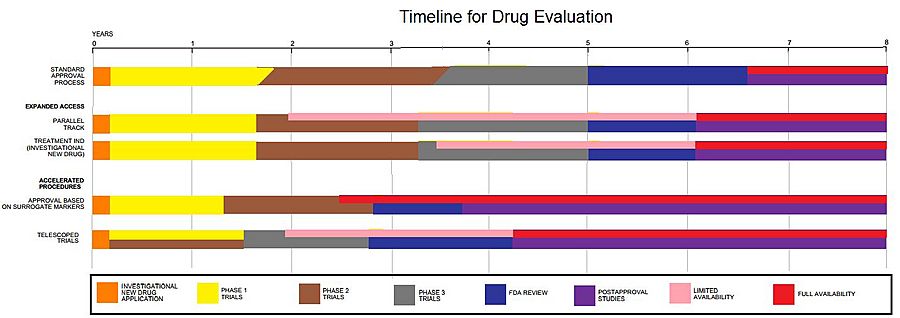
Duration
Clinical trials are only a small part of the research that goes into developing a new treatment. Potential drugs, for example, first have to be discovered, purified, characterized, and tested in labs before ever undergoing clinical trials.
In all, about 1,000 potential drugs are tested before just one reaches the point of being tested in a clinical trial. For example, a new cancer drug has, on average, six years of research behind it before it even makes it to clinical trials.
Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers and/or patients into small pilot studies, and subsequently conduct progressively larger scale comparative studies. Clinical trials can vary in size and cost, and they can involve a single research center or multiple centers, in one country or in multiple countries. Clinical study design aims to ensure the scientific validity and reproducibility of the results.
Trials can be quite costly, depending on a number of factors. The sponsor may be a governmental organization or a pharmaceutical, biotechnology or medical device company. Only 10 percent of all drugs started in human clinical trials become an approved drug.
Trials of drugs
Some clinical trials involve healthy subjects with no pre-existing medical conditions. Other clinical trials pertain to patients with specific health conditions who are willing to try an experimental treatment.
When participants are healthy volunteers who receive financial incentives, the goals are different than when the participants are sick. During dosing periods, study subjects typically remain under supervision for one to 40 nights.
Investigators
Many clinical trials do not involve any money. However, when the sponsor is a private company or a national health agency, investigators are almost always paid to participate.
Subjects
Participants in phase 1 drug trials do not gain any direct benefit from taking part. They are generally paid an inconvenience allowance because they give up their time (sometimes away from their homes); the amounts paid are regulated and are not related to the level of risk involved.
In most other trials, subjects are not paid to ensure their motivation for participating is the hope of getting better or contributing to medical knowledge, without their judgment being skewed by financial considerations. However, they are often given small payments for study-related expenses such as travel or as compensation for their time in providing follow-up information about their health after they are discharged from medical care.
All volunteers being considered for a trial are required to undertake a medical screening. Requirements differ according to the trial needs, but typically volunteers would be screened in a medical laboratory for:
- Measurement of the electrical activity of the heart (ECG)
- Measurement of blood pressure, heart rate and body temperature
- Blood sampling
- Urine sampling
- Weight and height measurement
Volunteers have the right to know and understand the details of what will happen during a clinical trial, a process called informed consent.
Examples of study designs:
- See if a certain drug is useful in treating a given disease.
- See if the disease or treatment improves with a different dose of medication.
- See if a drug that is already on the market can also help treat another disease (it was not designed for, at the start).
- See if a drug or treatment is better able to treat a patient's condition than the "standard" treatment already used.
- Compare two drugs or treatments to see which one is better able to treat a given condition.
History
Clinical trials were first introduced in Avicenna's The Canon of Medicine in 1025 AD, where he laid down rules for the experimental use and testing of drugs. He wrote a precise guide for practical experimentation in the process of discovering and proving the effectiveness of medical drugs and substances. He laid out the following rules and principles for testing the effectiveness of new drugs and medications, which still form the basis of modern clinical trials:
- The drug must be free from any extraneous accidental quality.
- It must be used on a simple, not a composite, disease.
- The drug must be tested with two contrary types of diseases, because sometimes a drug cures one disease by its essential qualities and another by its accidental ones.
- The quality of the drug must correspond to the strength of the disease. For example, there are some drugs whose heat is less than the coldness of certain diseases, so that they would have no effect on them.
- The time of action must be observed, so that essence and accident are not confused.
- The effect of the drug must be seen to occur constantly or in many cases, for if this did not happen, it was an accidental effect.
- The experimentation must be done with the human body, for testing a drug on a lion or a horse might not prove anything about its effect on man.
One of the most famous clinical trials was James Lind's demonstration in 1747 that citrus fruits cure scurvy. He compared the effects of various different acidic substances, ranging from vinegar to cider, on groups of afflicted sailors, and found that the group who were given oranges and lemons had largely recovered from scurvy after 6 days.
Images for kids
-
Edward Jenner vaccinating James Phipps, a boy of eight, on 14 May 1796. Jenner failed to use a control group.
See also
 In Spanish: Ensayo clínico para niños
In Spanish: Ensayo clínico para niños