Chromatin facts for kids
Chromatin is the complex combination of DNA and proteins that makes up chromosomes. It is found inside the nuclei of eukaryotic cells.
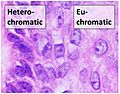
Chromatin is divided into heterochromatin (condensed) and euchromatin (extended) forms. Heterochromatin is composed mostly of satellite DNA tandem repeats. The active components of chromatin are DNA and histone proteins, although other proteins also occur. The functions of chromatin are:
- to package DNA into a smaller volume to fit in the cell
- to strengthen the DNA to allow mitosis and meiosis
- to control DNA replication and gene expression. How this works is not yet clear.
Chromatin definitions
- Simple and concise definition: Chromatin is a macromolecular complex of a DNA macromolecule and protein macromolecules (and RNA). The proteins package and arrange the DNA and control its functions in the cell nucleus.
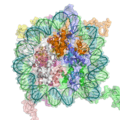
- The DNA + histone = chromatin definition: The DNA double helix in the cell nucleus is packaged by special proteins termed histones. The formed protein/DNA complex is called chromatin. The basic structural unit of chromatin is the nucleosome.
Images for kids
-
A cartoon representation of the nucleosome structure. From PDB 1KX5.
See also
 In Spanish: Cromatina para niños
In Spanish: Cromatina para niños

All content from Kiddle encyclopedia articles (including the article images and facts) can be freely used under Attribution-ShareAlike license, unless stated otherwise. Cite this article:
Chromatin Facts for Kids. Kiddle Encyclopedia.