Chicxulub crater facts for kids
| Chicxulub impact structure | |
|
|
| Impact crater/structure | |
|---|---|
| Confidence | Confirmed |
| Diameter | 180 km (110 mi) |
| Depth | 20 km (12 mi) |
| Impactor diameter | 10 km (6.2 mi) |
| Age | 66.043 ± 0.043 Ma Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary |
| Exposed | No |
| Drilled | Yes |
| Bolide type | CM or CR type carbonaceous chondrite |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 21°24′0″N 89°31′0″W / 21.40000°N 89.51667°W |
| Country | Mexico |
| State | Yucatán |
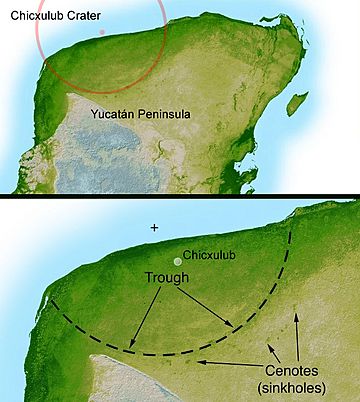
The Chicxulub crater is a very big crater. Some scientists believe that the Chicxulub crater was made by the meteor that caused the extinction of the dinosaurs, and many other animals. It is partly in the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico and partly underwater.
The Chicxulub crater is more than 180 km (110 mi) in diameter, making it the third largest confirmed impact crater. Petroleum prospectors found it in the late 1970s.
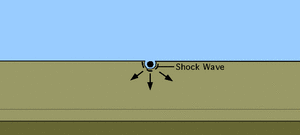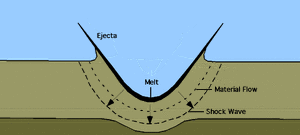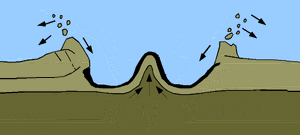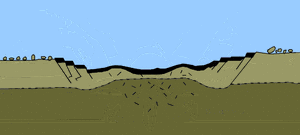
The bolide which formed the crater was at least 10 km (6 mi) in diameter. Evidence for the impact origin of the crater includes shocked quartz, a gravity anomaly, and tektites in surrounding areas. The age of the rocks and isotope analysis show that this impact structure dates from the end of the Cretaceous period, roughly 66 million years ago. The impact associated with the crater is implicated in causing the extinction of the dinosaurs.
A 2007 study suggests that the bolide may have been a piece of a much larger asteroid that broke up in a collision and also produced 298 Baptistina, 160 million years ago.
In March 2010, following analysis of the available evidence covering 20 years' worth of data in the fields of palaeontology, geochemistry, climate modelling, geophysics and sedimentology, 41 international experts from 33 institutions reviewed available evidence. They said the impact at Chicxulub triggered the mass extinctions during the K-T boundary, including that of dinosaurs.
Scientists can now describe in detail how the asteroid that wiped out the dinosaurs produced its huge crater. The reconstruction of the event 66 million years ago was made possible by drilling into the remnant bowl and analysing its rocks.
Evidence of impact
Scientists have found evidence of fallout from the asteroid impact. Excavations in North Dakota reveal fossils of fish and trees that were sprayed with rocky, glassy fragments that fell from the sky. The deposits also show evidence of being swamped with water. This was caused by the colossal sea surge caused by the impact.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Artistic impression of the asteroid slamming into tropical, shallow seas of the sulfur-rich Yucatán Peninsula in what is today Southeast Mexico. The aftermath of this immense asteroid collision, which occurred approximately 66 million years ago, is believed to have caused the mass extinction of dinosaurs and many other species on Earth. The impact spewed hundreds of billions of tons of sulfur into the atmosphere, producing a worldwide blackout and freezing temperatures which persisted for at least a decade.
See also
 In Spanish: Cráter de Chicxulub para niños
In Spanish: Cráter de Chicxulub para niños