Chickenpox facts for kids
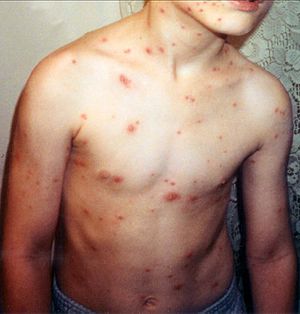
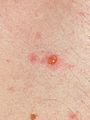
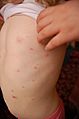
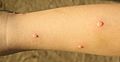
Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the chest, back, and face then spreads to the rest of the body.
Other symptoms may include fever, tiredness, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to seven days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, and bacterial skin infections. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin 10 to 21 days after exposure to the virus.
Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters.
People usually only get chickenpox once. Although reinfections by the virus occur, these reinfections usually do not cause any symptoms.
Getting chickenpox during a pregnancy is dangerous, because it can hurt both the mother and the child.
Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. In 2013 there were 140 million cases of chickenpox and herpes zoster worldwide. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%.
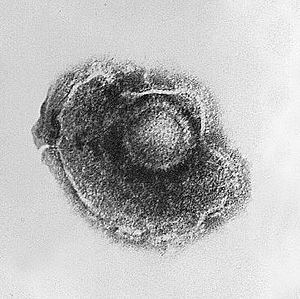
Chickenpox is caused by a virus of the herpes family. People who had chickenpox in the past can also get a related disease called shingles later. Shingles is caused by the same virus but usually is in only one part of the body.
There is a vaccine against chickenpox. Usually the vaccine is given to children, if they did not have the disease before the start of puberty, that is aged 9–13 years old. Sometimes to help your child not to scratch when they have chicken pox, you can get a special cream for it such as e45.
The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of "chicken" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.
Signs and symptoms
The early symptoms in adolescents and adults are nausea, loss of appetite, aching muscles, and headache. This is followed by the characteristic rash or oral sores, and a low-grade fever that signal the presence of the disease. The rash begins as small red dots on the face, scalp, torso, upper arms and legs; progressing over 10–12 hours to small bumps, blisters and followed by the formation of scabs.
The condition usually resolves by itself within a couple of weeks. The rash may, however, last for up to one month. Chickenpox is contagious starting from one to two days before the appearance of the rash and lasts until the lesions have crusted.
Chickenpox is rarely fatal, although it is generally more severe in adult men than in women or children.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Varicela para niños
In Spanish: Varicela para niños