Charles Dickens facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Charles Dickens
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Born | Charles John Huffam Dickens February 7, 1812 Landport, Portsmouth, England |
| Died | June 9, 1870 (aged 58) Gad's Hill Place, Higham, Kent, England |
| Resting place | Poet's Corner, Westminster Abbey |
| Occupation | Novelist |
| Notable works | Sketches by Boz, The Old Curiosity Shop, Oliver Twist, Nicholas Nickleby, Barnaby Rudge, A Christmas Carol, Martin Chuzzlewit, A Tale of Two Cities, David Copperfield, Great Expectations, Bleak House, Little Dorrit, Hard Times, Our Mutual Friend, The Pickwick Papers |
| Signature | |
 |
|
Charles John Huffam Dickens (February 7, 1812 – June 9, 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters. Many believe he is the greatest novelist of the Victorian era. His works were quite popular during his lifetime, and by the 20th century, critics and scholars had recognized him as a literary genius. His novels and short stories are still read by many today. A Christmas Carol, Oliver Twist, Great Expectations, and A Tale of Two Cities are his most famous works.
Even though he did not have a formal education, he wrote many different kinds of works. He wrote 15 novels, five novellas, and hundreds of short stories and non-fiction articles. He lectured and performed many readings. He was an active letter writer and edited a weekly journal for 20 years. He also battled for children's rights, education, and other social changes.
Dickens has been praised by fellow writers—from Leo Tolstoy to George Orwell, G. K. Chesterton and Tom Wolfe—for his realism, comedy, prose style, unique characterizations, and social criticism. The term Dickensian is used to describe something that is like that of Dickens and his writings, such as poor social conditions or comically repulsive characters.
Contents
Early life
Charles Dickens was born in Portsmouth, England. His parents were John Dickens (1785-1851), a naval pay clerk, and Elizabeth Barrow (1789-1863).
When Charles was ten years old, his family moved to Camden, London. He worked in a blacking (shoe polish) factory there while his father was in prison for debt. Charles's hard times in the factory gave him ideas for many of his novels. When Charles's grandmother died, Charles' father paid off his debts and was released from prison. Charles then finished his schooling and got a job as an office boy for an attorney. He found that job boring, so he taught himself shorthand and became a journalist that reported on the government. Dickens was a Unitarian.
Journalism and early novels
In 1832, at age 20, Dickens knew that he wanted to be famous, but did not know exactly what he wanted to do. In 1833, he submitted his first story, "A Dinner at Poplar Walk," to the London periodical Monthly Magazine. He worked as a political journalist, reporting on Parliamentary debates, and he traveled across Britain to write for the Morning Chronicle.
In January 1835, the Morning Chronicle began an evening edition called the Evening Chronicle. They hired the Chronicle's music critic, George Hogarth, to edit this edition. Hogarth invited Dickens to contribute Street Sketches. Dickens began visiting Hogarth at his home regularly and enjoyed the company of Hogarth's three daughters— Georgina, Mary, and nineteen-year-old Catherine, whom he would later marry.
Sketches by Boz got the attention of the publishers Chapman and Hall, who asked Dickens to write stories to go with engraved illustrations (pictures) in a monthly letterpress. In 1836, the story turned into The Pickwick Papers. The first few episodes were not successful, but the story became popular after Sam Weller was introduced. Within a few years, Dickens had become famous in more than just England, known for his humor, satire, and clever comments on character and society.
In November 1836, Charles accepted the position of editor of Bentley's Miscellany, a position he held for three years. In 1836, as he finished the last installments of The Pickwick Papers, he began writing the beginning installments of Oliver Twist—writing as many as 90 pages a month—while continuing work on Bentley's. During this time, he also wrote four plays and oversaw their production. Oliver Twist, published in 1838, became one of Dickens's better-known stories and was the first Victorian novel with a child protagonist. His books, most published in monthly or weekly installments (parts), began the serial publication of narrative fiction, which became the main way novels were published in England during this time. The audience greatly looked forward to each next installment.
His success as a novelist continued. The young Queen Victoria read both Oliver Twist and Pickwick, staying up until midnight to discuss them. Nicholas Nickleby (1838–39), The Old Curiosity Shop (1840–41), and, finally, his first historical novel, Barnaby Rudge: A Tale of the Riots of 'Eighty, as part of the Master Humphrey's Clock series (1840–41), were all published in monthly installments before being made into books.
First visit to the United States
In 1842, Charles and his wife Catherine made their first trip to the United States and Canada. At this time, Georgina Hogarth, sister of Catherine, joined the Dickens household, She lived at Devonshire Terrace, Marylebone, to care for the young family that her sister and brother-in-law had left behind. Georgina remained with them as a housekeeper, organizer, advisor, and friend until Dickens died in 1870.
Charles described his visit in a travelogue called American Notes for General Circulation, or Notes. In Notes, Dickens attacked slavery, which he had done in The Pickwick Papers as well. He recalled that, although he made quite a bit of money, he did not particularly enjoy his trip to America. During his trip, Dickens traveled to many of the northeastern states and Canada, where he lectured and appeared in stage comedies.
Return to England
Soon after his return to England, Dickens began working on the first of his Christmas stories, A Christmas Carol, written in 1843. He wrote two more Christmas-themed books, The Chimes in 1844 and The Cricket on the Hearth in 1845, but A Christmas Carol was his most famous. It helped encourage excitement for the joys of Christmas in both Britain and America.
Dickens lived in Italy for a short time (1844) and traveled to Switzerland. It was there that he began his more serious and carefully planned works: Dombey and Son and David Copperfield.
In June 1862, Charles was offered £10,000 (over $13,000) for a reading tour of Australia. Although he was excited, he decided against the tour. Two of his sons, however, Alfred D'Orsay Tennyson Dickens and Edward Bulwer Lytton Dickens, migrated to Australia. Edward became a member of the Parliament of New South Wales between 1889 and 1894.
Second visit to the United States
Charles wanted to return to the United States sooner than he was able. The outbreak of the Civil War in America in 1861 postponed his plans. Dickens arrived in America on November 9, 1867, and spent the rest of the month attending fancy dinner parties with famous people such as Ralph Waldo Emerson, Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, and his American publisher, James Thomas Fields.
In early December, Dickens began his reading tour. He performed 76 readings, making £19,000 (over $26,000), from December 1867 to April 1868. Charles traveled between Boston and New York, where he gave 22 readings at Steinway Hall. Although he had started to suffer from what he called the "true American catarrh," he kept to a busy schedule, even managing to squeeze in some sleighing in Central Park.
During his travels, Dickens said that he saw a change in the people and the circumstances of America. During his final American appearance at a banquet the American Press held in his honor at Delmonico's on April 18, he publicly stated that he was sorry for speaking negatively about America. On April 23, he boarded the Cunard liner Russia to return to Britain.
Last years
On May 2, Dickens made his last public appearance at a Royal Academy Banquet in the presence of the Prince and Princess of Wales. He paid a special tribute on the death of his friend, the illustrator Daniel Maclise.
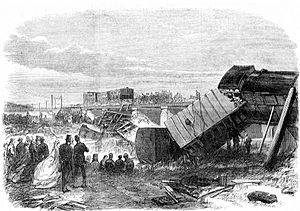
On June 9, 1865, while returning from Paris, Charles was involved in the Staplehurst rail crash. The train's first seven carriages fell off a cast iron bridge that was being repaired. The only first-class carriage to remain on the track was the one in which Dickens was traveling. Before rescuers arrived, Dickens tended to and comforted the wounded and the dying with a flask of brandy and a hat refreshed with water. He was able to save some lives. Dickens later used this experience as material for his short ghost story, "The Signal-Man," in which the main character has a premonition of his death in a rail crash.
Characters
Charles Dickens is thought of by many as the greatest creator of character in English fiction after Shakespeare. Dickensian characters are among the most memorable in English literature, especially because of their playful names.
Characters such as Ebenezer Scrooge, Tiny Tim, Jacob Marley, Bob Cratchit, Oliver Twist, The Artful Dodger, Fagin, Bill Sikes, Pip, Miss Havisham, Sydney Carton, Charles Darnay, David Copperfield, Mr. Micawber, Abel Magwitch, Daniel Quilp, Samuel Pickwick, Wackford Squeers, and Uriah Heep are so well-known that they are thought to be part of British culture.
Marriage
On April 2, 1836, after a one-year engagement, Charles married Catherine Thomson Hogarth (1816–1879), the daughter of George Hogarth, editor of the Evening Chronicle.
They were married in St. Luke's Church in Chelsea, London. After a brief honeymoon in Chalk, Kent, the couple returned to lodgings at Furnival's Inn. The first of their ten children, Charley, was born in January 1837, and a few months later the family set up their home in Bloomsbury at 48 Doughty Street, London.
In 1858, they divorced. When Catherine left, she took one child with her and left the other children to be raised by her sister Georgina. Catherine never saw Charles again.
Death
On June 8, 1870, Dickens suffered a stroke at his home after a full day's work. He never regained consciousness, and the next day, five years to the day after the Staplehurst rail crash, he died at Gads Hill Place. Dickens wished to be buried at Rochester Cathedral "in an inexpensive and strictly private manner," but because of his fame, he was laid to rest in the Poets' Corner of Westminster Abbey.
In his will, drafted more than a year before his death, Dickens left the care of his £80,000 (over $110,000) estate to his longtime colleague John Forster and his "best and truest friend" Georgina Hogarth who, along with Dickens's two sons, also received a tax-free sum of £8,000. This equals about £800,000 (over $1 million) in present terms. Although Dickens and his wife had been separated for several years at the time of his death, he provided her with an annual (yearly) income of £600 (about $830, or over $80,000 today) and made her similar allowances in his will.
Legacy
The legacy of Charles Dickens continues to live in both England and America:
- The Charles Dickens Museum in London, the Charles Dickens Birthplace Museum in Portsmouth, and Victoria and Albert Museum are museums that chronicle his life.
- Statues of Dickens include Dickens and Little Nell, which stands in Clark Park in the Spruce Hill neighborhood of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; Charles Dickens statue in Centennial Park, Sydney, Australia; and a life-sized statue of Dickens near his birthplace.
- Dickens was honored on the Series E £10 note issued by the Bank of England that circulated between 1992 and 2003. His portrait appeared on the reverse of the note along with a scene from The Pickwick Papers.
- The Charles Dickens School is a high school in Broadstairs, Kent.
- Dickens World, a theme park, stands in part on the site of the former naval dockyard where Dickens's father once worked in the Navy Pay Office.
- In 2002, Dickens was number 41 in the BBC's poll of the 100 Greatest Britons.
- In the UK survey The Big Read, carried out by the BBC in 2003, five of Dickens's books were named in the Top 100.
- Dickens and his publications have appeared on several postage stamps.
- To celebrate the 200th anniversary of the birth of Charles Dickens in 2012, the Museum of London held the UK's first major exhibition on the author in 40 years.
- In November 2018, it was reported that a previously lost portrait of a 31-year-old Dickens, by Margaret Gillies, had been found in Pietermaritzburg, South Africa.
Charles Dickens quotes
- “Have a heart that never hardens, and a temper that never tires, and a touch that never hurts.”
- “A day wasted on others is not wasted on one’s self.”
- “There is nothing in the world so irresistibly contagious as laughter and good humor.”
- “No one is useless in this world who lightens the burdens of another.”
- “The most important thing in life is to stop saying, ‘I wish’ and start saying, ‘I will.’ Consider nothing impossible, then treat possibilities as probabilities.”
- “The pain of parting is nothing to the joy of meeting again.”
- “Procrastination is the thief of time, collar him.”
Interesting facts about Charles Dickens
- Charles Dickens' pseudonym, "Boz," was a name that he called his brother when he was young.
- Little Red Riding Hood was Dickens's first muse.
- Charles' wife wrote a book under the pseudonym "Lady Maria Clutterbuck" entitled What Shall we Have for Dinner?
- Charles loved to invent nicknames for his children and himself, including "Flaster Floby" or the "Snodgering Blee"
(Charley), "Mild Glo’ster" (Mamie), "Lucifer Box" (Katey), "Young Skull" (Walter), "The Ocean Spectre" (Sydney), and "Skittles" (Alfred).
- It is speculated that Charles may have had epilepsy.
- Dickens used "cliffhangers" at the end of chapters when he wrote his novels. They were originally written in installments, and to keep readers buying the next chapters, he would conclude each chapter at an unresolved point in the story.
- Dickens' novel A Tale of Two Cities is one of the first times that potato chips are mentioned in literature.
- Charles Dickens began a rehabilitation home for homeless women.
- Charles owned pet ravens.
- When his pet cat Bob died, Dickens had its paw stuffed and attached to a letter opener.
Books
Dickens published well over a dozen major novels and novellas; a large number of short stories, including several Christmas-themed stories; a handful of plays; and several non-fiction books. Dickens's novels were initially organized in weekly and monthly magazines, then reprinted in standard book formats.
- The Pickwick Papers (The Posthumous Papers of the Pickwick Club; monthly serial, April 1836 to November 1837)
- Oliver Twist (The Adventures of Oliver Twist; monthly serial in Bentley's Miscellany, February 1837 to April 1839)
- Nicholas Nickleby (The Life and Adventures of Nicholas Nickleby; monthly serial, April 1838 to October 1839)
- The Old Curiosity Shop (weekly serial in Master Humphrey's Clock, April 1840 to November 1841)
- Barnaby Rudge (Barnaby Rudge: A Tale of the Riots of Eighty; weekly serial in Master Humphrey's Clock, February to November 1841)
- A Christmas Carol (A Christmas Carol in Prose: Being a Ghost-story of Christmas, 1843)
- Martin Chuzzlewit (The Life and Adventures of Martin Chuzzlewit; monthly serial, January 1843 to July 1844)
- The Chimes (The Chimes: A Goblin Story of Some Bells That Rang an Old Year Out and a New Year In, 1844)
- The Cricket on the Hearth (The Cricket on the Hearth: A Fairy Tale of Home, 1845)
- Dombey and Son (Dealings with the Firm of Dombey and Son: Wholesale, Retail and for Exportation; monthly serial, October 1846 to April 1848)
- The Haunted Man (The Haunted Man and the Ghost's Bargain: A Fancy for Christmas-time, 1848)
- David Copperfield (The Personal History, Adventures, Experience, and Observation of David Copperfield the Younger of Blunderstone Rookery; monthly serial, May 1849 to November 1850)
- Bleak House (monthly serial, March 1852 to September 1853)
- Hard Times (Hard Times: For These Times; weekly serial in Household Words, April 1, 1854 to August 12, 1854)
- Little Dorrit (monthly serial, December 1855 to June 1857)
- A Tale of Two Cities (weekly serial in All the Year Round, April 30, 1859, to November 26, 1859)
- Great Expectations (weekly serial in All the Year Round, December 1, 1860 to August 3, 1861)
- Our Mutual Friend (monthly serial, May 1864 to November 1865)
- The Signal-Man (1866), first published as part of the Mugby Junction collection in the 1866 Christmas edition of All the Year Round.
- Edwin Drood (The Mystery of Edwin Drood; monthly serial, April 1870 to September 1870), left unfinished due to Dickens's death
Images for kids
-
2 Ordnance Terrace, Chatham, Dickens's home 1817 – May 1821
-
The wise-cracking, warm-hearted servant Sam Weller from The Pickwick Papers—a publishing phenomenon that sparked numerous spin-offs and Pickwick merchandise—made the 24-year-old Dickens famous.
-
Young Charles Dickens by Daniel Maclise, 1839
-
Dickens's portrait by Margaret Gillies, 1843. Painted during the period when he was writing A Christmas Carol, it was in the Royal Academy of Arts' 1844 summer exhibition. After viewing it there, Elizabeth Barrett Browning said that it showed Dickens with "the dust and mud of humanity about him, notwithstanding those eagle eyes."
-
Poster promoting a reading by Dickens in Nottingham dated February 4, 1869, two months before he suffered a mild stroke
-
The Old Curiosity Shop in Holborn, London, which inspired The Old Curiosity Shop. Many of Dickens's works do not just use London as a backdrop; they are also about the city and its character.
-
The Artful Dodger from Oliver Twist. His dialect is rooted in Cockney English.
-
Bleak House (pictured in the 1920s) in Broadstairs, Kent, where Dickens wrote some of his novels
-
Dickens chalet in Rochester, Kent where he was writing the last chapters of Edwin Drood the day before he died
-
Dickens's portrait (top left), in between Shakespeare and Tennyson, on a stained glass window at the Ottawa Public Library, Ottawa, Canada
-
"Charles Dickens as he appears when reading." Wood engraving from Harper's Weekly, December 7, 1867. Author David Lodge called Dickens the "first writer to be an object of unrelenting public interest and adulation."
-
Dickens and Little Nell statue in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
-
A Christmas Carol significantly influenced the modern celebration of Christmas in many countries.
See also
 In Spanish: Charles Dickens para niños
In Spanish: Charles Dickens para niños