Bristol Lake facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Bristol Lake |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Location | Mojave Desert San Bernardino County, California |
| Coordinates | 34°27′44″N 115°40′26″W / 34.4622°N 115.6738°W |
| Lake type | Endorheic basin |
| Primary outflows | Terminal (evaporation) |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Max. length | 23 km (14 mi) |
| Max. width | 20 km (12 mi) |
| Shore length1 | 70 km (43 mi) |
| Surface elevation | 183 m (600 ft) |
| Settlements | Amboy, California Saltus, California |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
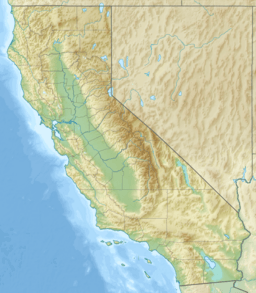
Bristol Lake is a dry lake in the Mojave Desert of San Bernardino County, California, 42 km (26 mi) northeast of Twentynine Palms.
Bristol Lake is located southeast of Amboy, California and U.S. Route 66, and is also south of Cadiz, California. Amboy Crater and the Bullion Mountains are to the west, and Old Woman Mountains to the east.
The lake is approximately 23 km (14 mi) long and 20 km (12 mi) at its widest point.
Geological setting
Bristol Lake is located in San Bernardino County's Mojave Desert. It is a Playa Lake in the Basin and Range Province and is the northernmost member of a northwest-southeast trending playa lake system that includes Cadiz Lake and Danby Lake.
Mineralogy
Bristol Lake's mineralogy is described as having a bullseye pattern of minerals with lithofacies consisting of halite at the center surrounded by mud, gypsum, and finally a sand flat playa margin. These minerals also have vertical lithofacies which resemble the horizontal facies stratification with gypsum occurring deeper in the playa followed by mud-halite and halite on top.
The mud lithofacies consists of thick detrital mud, and the halite lithofacies is defined by giant hopper shaped crystals. Gypsum occurs in large lenticular crystals throughout the playa but is mostly concentrated around the mud lithofacies. Gypsum crystal sizes increase toward the center of the playa.
Industry
A salt evaporator operation is situated on the dry lake bed just east of Amboy Road.