Boronia virgata facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Boronia virgata |
|
|---|---|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
 |
|
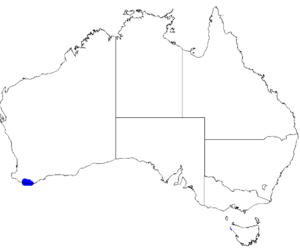
| Occurrence data from Australasian Virtual Herbarium |
Boronia virgata is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to the south coast of Western Australia. It is a virgate shrub with pinnate leaves with between three and five leaflets, and flowers with red sepals and deep pink, egg-shaped petals.
Description
Boronia virgata is a virgate shrub that typically grows to a height of 1 m (3 ft 3 in) with its branchlets covered with lines of tiny, fine hairs. The leaves are 10–15 mm (0.39–0.59 in) long and have between three and five, rarely seven leaflets that are oblong to elliptical and 3–10 mm (0.12–0.39 in) long. The flowers are borne singly or in groups of three in leaf axils on a thin, glabrous pedicel 6–14 mm (0.24–0.55 in) long. The sepals are very narrow triangular, 2–3 mm (0.079–0.118 in) long red and glabrous. The petals are egg-shaped, deep pink, about 8 mm (0.31 in) long with a minute hairs on the upper surface and the edges of their backs. The stamens are about 3 mm (0.12 in) long with anthers about 1 mm (0.039 in) long. Flowering occurs between August and February.
Taxonomy and naming
Boronia virgata was first formally described in 1971 by Paul Wilson and the description was published in Nuytsia from specimens he collected near the road between Denmark and Walpole in 1970. The specific epithet (virgata) is from the Latin word virgatus meaning "virgate", or "having long, slender but usually stiff twigs".
Distribution and habitat
This boronia grows in open forest in soil that is swampy, or waterlogged in winter, and has been found in near-coastal areas between Walpole and Nornalup.
Conservation status
This species of boronia is classified as "Priority Four" by the Government of Western Australia Department of Parks and Wildlife, meaning that is rare or near threatened.


