Boronia ovata facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Boronia ovata |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
 |
|
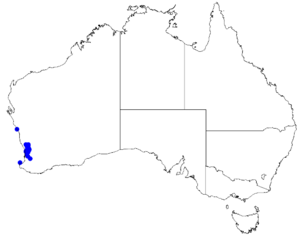
| Occurrence data from Australasian Virtual Herbarium |
Boronia ovata is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is an open shrub with simple, egg-shaped leaves and pink to mauve four-petalled flowers. It is found in the Darling Range near Perth.
Description
Boronia ovata is an open shrub that grows to a height of about 40 cm (16 in) and has broadly egg-shaped leaves that about 10 mm (0.39 in) long. The flowers are arranged in small groups on the ends of the branches, each flower on the end of a thin pedicel 5–15 mm (0.20–0.59 in) long. The four sepals are red, broadly egg-shaped with a pointed tip and about 2.5 mm (0.1 in) long. The four petals are pink to mauve, elliptic and about 8 mm (0.3 in) long. The eight stamens are glabrous with an anther about 1 mm (0.04 in) long with a small white tip. The stigma is minute. Flowering occurs from September to November.
Taxonomy and naming
Boronia ovata was first formally described in 1841 by John Lindley and the description was published in Edwards's Botanical Register. The specific epithet (ovata) is a Latin word meaning "egg-shaped".
Distribution and habitat
This boronia grows in eucalypt woodland in the Darling Range between New Norica and Boddington in the Avon Wheatbelt, Jarrah Forest and Swan Coastal Plain biogeographic regions.
Conservation
Boronia ovata is classified as "not threatened" by the Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife.

