Bone marrow facts for kids
Bone marrow is a type of tissue that can be found in hollow bones of many animals including humans. In adults, the bone marrow in large bones makes new blood cells. Bone marrow makes up about 4% of an adult human's weight (about 2.6 kilograms).
Contents
Marrow types
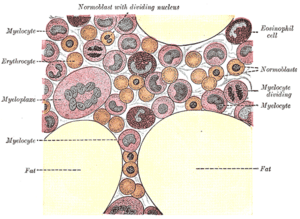
There are two types of bone marrow. Red marrow is made mostly of myeloid tissue (which makes new blood cells). Red blood cells, platelets, and most white blood cells are created by red marrow. Yellow marrow is made mainly of fat cells. Both types of bone marrow contain many blood vessels and capillaries.
When a person is born, all of their bone marrow is red. As the person ages, more and more of the bone marrow changes to the yellow type. By adulthood, about half of a person's bone marrow is red.
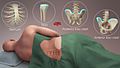
Red marrow is found mainly in the flat bones - like the hip bone, breast bone, skull, ribs, vertebra (the bones that make up the spinal column), and shoulder blades - and in the cancellous ("spongy") material at the ends of the long bones like the femur (thigh bone) and humerus (upper forearm bone). Yellow marrow is found inside the hollow middle section, or medullary cavity of the long bones.
In cases of severe blood loss, the body can change yellow marrow back to red marrow so that more blood cells are made to replace the lost blood.
Structure
At the cellular level, the main functional component of bone marrow includes the progenitor cells which are destined to mature into blood and lymphoid cells. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day. Marrow contains hematopoietic stem cells which give rise to the three classes of blood cells that are found in circulation: white blood cells (leukocytes), red blood cells (erythrocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes).
The stroma of the bone marrow includes all tissue not directly involved in the marrow's primary function of hematopoiesis. Cell types that constitute the bone marrow stroma include:
- fibroblasts (reticular connective tissue)
- macrophages, which contribute especially to red blood cell production, as they deliver iron for hemoglobin production.
- adipocytes (fat cells)
- osteoblasts (synthesize bone)
- osteoclasts (resorb bone)
- endothelial cells, which form the sinusoids. These derive from endothelial stem cells, which are also present in the bone marrow.
Function
Bone marrow is a priming site for T-cell responses to blood-borne antigens.
It is also a nest for migratory memory T cells and a sanctuary for plasma cells.
The red bone marrow is a key element of the lymphatic system, being one of the primary lymphoid organs that generate lymphocytes from immature hematopoietic progenitor cells. The bone marrow and thymus constitute the primary lymphoid tissues involved in the production and early selection of lymphocytes. Furthermore, bone marrow performs a valve-like function to prevent the backflow of lymphatic fluid in the lymphatic system.
Images for kids
-
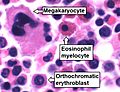
Bone marrow aspirate showing normal "trilineage hematopoiesis": myelomonocytic cells (an eosinophil myelocyte marked), erythroid cells (an orthochromatic erythroblast marked), and megakaryocytic cells.
-
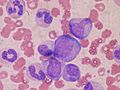
A Wright's-stained bone marrow aspirate smear from a patient with leukemia.
-
Bone marrow may have first evolved in Eusthenopteron, a species of prehistoric fish with close links to early tetrapods.
See also
 In Spanish: Médula ósea para niños
In Spanish: Médula ósea para niños