Battle of Olustee facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Battle of Olustee |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the American Civil War | |||||||
 Battle of Olustee, by Kurz and Allison, 1894 |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Truman Seymour | Joseph Finegan | ||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
| District of Florida | District of East Florida | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 5,500 | 5,000 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 1,861 (203 killed 1,152 wounded 506 captured/missing) |
946 (93 killed 847 wounded 6 captured/missing) |
||||||
The Battle of Olustee or Battle of Ocean Pond was fought in Baker County, Florida on February 20, 1864, during the American Civil War. It was the largest battle fought in Florida during the war.
Union General Truman Seymour had landed troops at Jacksonville, aiming chiefly to disrupt Confederate food supply. Meeting little resistance, he proceeded towards the state capital of Tallahassee, against orders, assuming that he would face only the small Florida militia. Confederates in Charleston sent reinforcements under General Alfred H. Colquitt and the two armies collided near Ocean Pond in Olustee.
The Union forces were repulsed and retreated to Jacksonville. Some were garrisoned there to occupy territory. Other troops were transferred to other, more active, areas where they were needed.
Background
In February 1864, Major General Quincy A. Gillmore, commander of the Union's Department of the South at Hilton Head, South Carolina, ordered an expedition into Florida to secure Union enclaves, sever Confederate supply routes (especially for beef and salt), and recruit black soldiers. Brigadier General Truman Seymour, in command of the expedition, landed troops at Jacksonville, in an area already seized by the Union in March 1862. Seymour's forces made several raids into the northeast and north-central Florida. During these raids, he met little resistance, seized several Confederate camps, captured small bands of troops and artillery pieces, liberated slaves, etc. But, Seymour was under orders from Gillmore not to advance deep into the state.
Seymour's preparations at Hilton Head had concerned the Confederate command in the key port city of Charleston, South Carolina. General P. G. T. Beauregard, correctly guessing Seymour's objective was Florida, believed these Union actions posed enough of a threat for him to detach reinforcements under Georgian Alfred H. Colquitt to bolster Florida's defenses and stop Seymour. Colquitt arrived in time to reinforce Florida troops under the command of Brigadier General Joseph Finegan. As Colquitt's troops began arriving, Seymour, without Gillmore's knowledge, began a new drive across north Florida with the capture of Tallahassee as a possible objective.
Opposing forces
Union
-
Brig. Gen.
Truman Seymour, USA -
Col.
James Montgomery, USA -
Col.
Guy Vernor Henry, USA
Confederate
-
Col.
George Paul Harrison, Jr., CSA
Battle
Following the Florida, Atlantic and Gulf Central Railroad, Seymour led his 5,500 men in the direction of Lake City. At approximately 2:30 in the afternoon of February 20, the Union force approached General Finegan's 5,000 Confederates entrenched near Olustee Station. Finegan sent out an infantry brigade to meet Seymour's advance units and lure them into the Confederate entrenchments, but this plan went awry. The opposing forces met at Ocean Pond and the battle began. Seymour made the mistake of assuming he was once again facing Florida militia units he had previously routed with ease and committed his troops piecemeal into the battle. Finegan and Seymour both reinforced their engaged units during the afternoon and the battle took place in open pine woods. The Union forces attacked but were savagely repulsed by withering barrages of rifle and cannon fire.
The battle raged throughout the afternoon until, as Finegan committed the last of his reserves, the Union line broke and began to retreat. Finegan did not exploit the retreat, allowing most of the fleeing Union forces to reach Jacksonville. The Confederates did make a final attempt to engage the rear element of Seymour's forces just before nightfall, but they were repulsed by elements of the 54th Massachusetts Volunteer Infantry Regiment and the 35th United States Colored Troops, both composed of Black soldiers. Rather than pursue Seymour's retreat.
Aftermath

Union casualties were 203 killed, 1,152 wounded, and 506 missing, a total of 1,861 men—about 34 percent. Confederate losses were lower: 93 killed, 847 wounded, and 6 missing, a total of 946 casualties in all—but still about 19 percent. Union forces also lost six artillery pieces and 39 horses that were captured. The ratio of Union casualties to the number of troops involved made this the second bloodiest battle of the War for the Union, with 265 casualties per 1,000 troops. Soldiers on both sides were veterans of the great battles in the eastern and western theaters of war, but many of them remarked in letters and diaries that they had never undergone such terrible fighting. The Confederate dead were buried at Oaklawn Cemetery in nearby Lake City.
The Union losses caused Northern authorities to question the necessity of further Union involvement in the militarily insignificant state of Florida.
On the morning of February 22, as the Union forces were still retreating to Jacksonville, the 54th Massachusetts was ordered to countermarch back to Ten-Mile Station. The locomotive of a train carrying wounded Union soldiers had broken down and the wounded were in danger of capture. When the 54th Massachusetts arrived, the men attached ropes to the engine and cars and manually pulled the train approximately three miles to Camp Finegan, where horses were secured to help pull the train. After that, the train was pulled by both men and horses to Jacksonville for a total distance of 10 miles (16 km). It took 42 hours to pull the train that distance.
In the South, the battle was seen as a spirit-raising rout. One Georgia newspaper referred to Union forces as walking "forty miles over the most barren land of the South, frightening the salamanders and the gophers, and getting a terrible thrashing".
Today, the battlefield is commemorated by the Olustee Battlefield Historic State Park, a part of the Florida State Park system. This park is located within the Osceola National Forest, on U.S. 90. The battlefield is partially protected as state park, and part of the national forest. Part of it is privately held land on the south side of U.S. 90.
Nearby Lake City (in Columbia County) has hosted the yearly Olustee Battle Festival since 1976.
On Presidents' Day weekend each February (see Citations), an annual historical reenactment is conducted on the site of the battle. Thousands of reenactors from across the U.S., and even from overseas, have participated over the years.
Some reenactors begin arriving as early as Thursday to set up. Friday is "School Day", as hundreds of students are brought to watch demonstrations and listen to historians discuss various aspects of the war and life in the United States during the 1860s. The event is open to the public on Friday, Saturday and Sunday. There are numerous sutler tents for Civil War merchandise. The battles take place on Saturday and Sunday. A selection of modern-day food is available from Friday through Sunday inside the park.
The reenactment of the Battle of Olustee is co-sponsored by four organizations: the Olustee Battlefield Historic State Park Citizens Support Organization; the Florida Department of Environmental Protection – Recreation and Parks; the USDA Forest Service – Osceola National Forest; and The Blue-Grey Army, Inc.
Battle lithograph
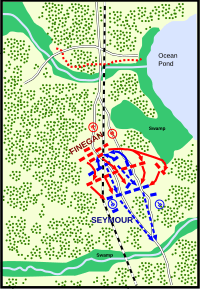
The lithograph at the top of the page was printed by the firm of Kurz and Allison in 1894. It depicts soldiers of the 8th U.S. Colored Troops advancing against Confederate entrenchments. While frequently used in media about the Battle of Olustee, the image is inaccurate and reveals the artist's ignorance about the events. During the battle, Confederates operated well in advance of their prepared positions. Neither side fought from behind fortifications, as the fighting took place in a pine forest (see map – top of the map is approximately due West), and there were few large cleared area. The dotted red line on the map indicates the location of the Confederate trenches.
See also
 In Spanish: Batalla de Olustee para niños
In Spanish: Batalla de Olustee para niños