Battle of Nasiriyah (1915) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Battle of Nasiriyah (1915) |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Mesopotamian Campaign of World War I | |||||||
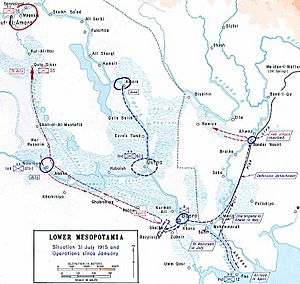 This map shows the British advance into Southern Mesopotamia, 1915 |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Charles Vere Ferrers Townshend Sir John Nixon G. F. Gorringe |
? | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 5,000 | around 5,000 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
104 killed 429 wounded |
2000 killed or wounded 1,000 taken prisoner 17 field guns captured |
||||||
The Battle of Nasiriyah was a battle in World War I that took place in the Mesopotamian city of Nasiriyah between British and Ottoman forces in July 1915. It was a pivotal battle in the Mesopotamian campaign of World War I and saw 5,000 British and Indian troops face off against a Turkish garrison of a similar number. British and Indian forces under the command of Lieutenant General Sir George Frederick Gorringe attacked Nasiriyah with the intention of protecting the British stronghold of Basra and destroying a major Turkish supply center in the region. British forces defeated the Turkish forces in Nasiriyah and it became the latest addition to a long string of successes against Ottoman forces in the campaign, coming right after the capture of Amara and the Battle of Qurna.
Background
With the beginning of the First World War in Europe, British commanders worried about losing access to precious oil reserves in the Persian Gulf region. The oil was vital to providing fuel for the Empire's ships and as such the British could not afford to lose access to the region under any circumstances. The threat in the region came from the Ottoman Empire whom had entered the war on the side of the Central Powers and were geographically the closest of Britain's enemies to Abadan where much of the Gulf's oil infrastructure was located. Another factor in the British desire to dominate the Mesopotamia region was to maintain its prestige in the eyes of its Indian subjects, fearing a revolt. The Ottoman military had very few assets positioned in Mesopotomia since it was considered backwater and there was only one division in the area with no supporting aircraft and little artillery when the British attacked. Despite the lack of Ottoman priority in Mesopotamia, British forces landed in Fao, at the mouths of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in November 1914 setting in motion the Mesopotamian Campaign of World War I.
By the end of November 1914, the city of Basra had been captured with Qurna, Shaiba, and Amara all falling into British hands by June 1915. The British successes were in large part due to the lack of effective Turkish opposition in the region with Sir Percy Cox remarking, "After earnest consideration of the arguments for and against I find it difficult to see how we can well avoid taking over Baghdad."
Nasiriyah in southern Mesopotamia was a critical supply juncture for Ottoman forces in the area and posed a threat to Basra and the western flank of Sir Charles Townshend's forces. As such Townshend ordered Major General G.F. Gorringe to lead a force to capture it.
Battle
Beginning on 27 June, Gorringe led a reinforced brigade of 5,000 British and Indian troops up the Euphrates River to reach the Ottoman stronghold. The district was covered in wetlands, the product of seasonal flooding, so the troops maneuvered north in small boats through the series of marshes and canals to reach the city. Temperatures soared to above a hundred degrees Fahrenheit and mosquitoes proved burdensome but the men arrived in the vicinity of Nasiriyah in early July. In a day and a half long operation, British engineers destroyed a dam across the Hakika Channel which had been set up by the Turks to impede British movement up the Euphrates. The engineers worked under heavy fire and suffered heavy casualties but ultimately the British and Indian troops pushed forward. Mines did not prove to be an issue because a Turkish prisoner divulged their location beforehand.
The main Turkish defenses were a series of entrenchments located on both sides of the Euphrates with their flanks defended by marshes. Gorringe called for reinforcements and an additional brigade arrived on 13 July. British forces attempted to assault the Turkish defenses through the marshes but were beaten back. The next couple weeks were marked by a stagnation in the fighting and illness and heat stroke running rampant in both armies. On 24 July, using intelligence gained from a British observation aircraft, Gorringe launched an attack on the Turks. A barge was towed to the middle of the river and engineers worked tirelessly under Turkish bullets to construct a bridge to no avail. However the barge managed to shore up the river enough to allow British and Indian troops to wade across where they overran the Turkish positions with gunboat support, routing the defenders entirely.
Nasiriyah fell on 25 July and the remaining Turkish troops retreated to Kut. 533 British and Indian troops had been killed or wounded in the battle with 2,000 killed and wounded on the Turkish side. 1,000 Turk soldiers were taken prisoner and large stockpiles of Ottoman military equipment were captured as well.

